
Greenland is located between the Arctic Ocean and the North Atlantic Ocean, northeast of Canada and northwest of Iceland. The territory comprises the island of Greenland—the largest island in the world—and more than a hundred other smaller islands. Greenland has a 1.2-kilometer-long (0.75 mi) border with Canada on Hans Island. A sparse population is confined to small settlements along certain sectors of the coast. Greenland possesses the world's second-largest ice sheet.

Ellesmere Island is Canada's northernmost and third largest island, and the tenth largest in the world. It comprises an area of 196,236 km2 (75,767 sq mi), slightly smaller than Great Britain, and the total length of the island is 830 km (520 mi).

Baffin Island, in the Canadian territory of Nunavut, is the largest island in Canada, the second-largest island in the Americas, and the fifth-largest island in the world. Its area is 507,451 km2 (195,928 sq mi) with a population density of 0.03/km2; the population was 13,039 according to the 2021 Canadian census; and it is located at 68°N70°W. It also contains the city of Iqaluit, which is the capital of Nunavut.
The Paleo-Eskimo meaning "old Eskimos", also known as, pre-Thule or pre-Inuit, were the peoples who inhabited the Arctic region from Chukotka in present-day Russia across North America to Greenland before the arrival of the modern Inuit (Eskimo) and related cultures. The first known Paleo-Eskimo cultures developed by 3900 to 3600 BCE, but were gradually displaced in most of the region, with the last one, the Dorset culture, disappearing around 1500 CE.

Baffin Bay, located between Baffin Island and the west coast of Greenland, is defined by the International Hydrographic Organization as a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is sometimes considered a sea of the North Atlantic Ocean. It is connected to the Atlantic via Davis Strait and the Labrador Sea. The narrower Nares Strait connects Baffin Bay with the Arctic Ocean. The bay is not navigable most of the year because of the ice cover and high density of floating ice and icebergs in the open areas. However, a polynya of about 80,000 km2 (31,000 sq mi), known as the North Water, opens in summer on the north near Smith Sound. Most of the aquatic life of the bay is concentrated near that region.

Nares Strait is a waterway between Ellesmere Island and Greenland that connects the northern part of Baffin Bay in the Atlantic Ocean with the Lincoln Sea in the Arctic Ocean. From south to north, the strait includes Smith Sound, Kane Basin, Kennedy Channel, Hall Basin and Robeson Channel. Nares Strait has a nearly permanent current from the north, powered by the Beaufort Gyre, making it harder to traverse for ships coming from the south.

Uummannaq Fjord is a large fjord system in the northern part of western Greenland, the largest after Kangertittivaq fjord in eastern Greenland. It has a roughly south-east to west-north-west orientation, emptying into the Baffin Bay in the northwest.
Cape York is a cape on the northwestern coast of Greenland, in northern Baffin Bay.
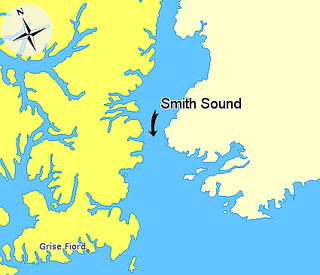
Smith Sound is an Arctic sea passage between Greenland and Nunavut's northernmost island, Ellesmere Island. It links Baffin Bay with Kane Basin and forms part of the Nares Strait. On the Canadian side it extends from Cape Sabine in the north to Cape Isabella in the south.
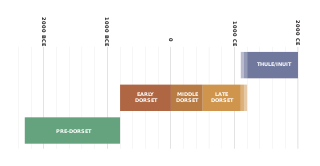
The history of Nunavut covers the period from the arrival of the Paleo-Eskimo thousands of years ago to present day. Prior to the colonization of the continent by Europeans, the lands encompassing present-day Nunavut were inhabited by several historical cultural groups, including the Pre-Dorset, the Dorsets, the Thule and their descendants, the Inuit.

The Arctic Cordillera is a terrestrial ecozone in northern Canada characterized by a vast, deeply dissected chain of mountain ranges extending along the northeastern flank of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago from Ellesmere Island to the northeasternmost part of the Labrador Peninsula in northern Labrador and northern Quebec, Canada. It spans most of the eastern coast of Nunavut with high glaciated peaks rising through ice fields and some of Canada's largest ice caps, including the Penny Ice Cap on Baffin Island. It is bounded to the east by Baffin Bay, Davis Strait and the Labrador Sea while its northern portion is bounded by the Arctic Ocean.

Etah is an abandoned settlement in the Avannaata municipality in northern Greenland. It was a starting point of discovery expeditions to the North Pole and the landing site of the last migration of the Inuit from the Canadian Arctic.

The MacGregor Arctic Expedition was a privately funded expedition which set out to reoccupy Fort Conger, Ellesmere Island, Canada, a site within flying distance of the North Pole. The expedition, which took place from July 1, 1937, to October 3, 1938, had four main objectives: To collect weather data; to make a magnetic survey; to photograph the aurora borealis and study its effects upon radio transmission; and to explore the area northwest of Ellesmere Island, in order to clear up the questions about Crocker Land, which Robert Peary placed on the map more than 30 years earlier.

The Baffin Mountains are a mountain range running along the northeastern coast of Baffin Island and Bylot Island, Nunavut, Canada. The ice-capped mountains are part of the Arctic Cordillera and have some of the highest peaks of eastern North America, reaching a height of 1,525–2,146 metres (5,003–7,041 ft) above sea level. While they are separated by bodies of water to make Baffin Island, they are closely related to the other mountain ranges that make the much larger Arctic Cordillera mountain range.

Independence Fjord or Independence Sound is a large fjord or sound in the eastern part of northern Greenland. It is about 200 km (120 mi) long and up to 30 km (19 mi) wide. Its mouth, opening to the Wandel Sea of the Arctic Ocean is located at 82°15′N21°54′W.

Nuussuaq Peninsula is a large peninsula in western Greenland.

Petermann Glacier is a large glacier located in North-West Greenland to the east of Nares Strait. It connects the Greenland ice sheet to the Arctic Ocean at 81°10' north latitude, near Hans Island.
David Haig-Thomas was a British ornithologist, wildlife photographer, explorer and rower who competed for Great Britain in the 1932 Summer Olympics. He was an army commando during the Second World War, and was killed in action during the Normandy Landings. Haig-Thomas Island in the Canadian Arctic is named after him.
Upernavik Archipelago is a vast coastal archipelago in the Avannaata municipality in northwestern Greenland, off the shores of northeastern Baffin Bay. The archipelago extends from the northwestern coast of Sigguup Nunaa peninsula in the south at approximately 71°50′N56°00′W to the southern end of Melville Bay in the north at approximately 74°50′N57°30′W.
















