
Ethernet is a family of wired computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN) and wide area networks (WAN). It was commercially introduced in 1980 and first standardized in 1983 as IEEE 802.3. Ethernet has since been refined to support higher bit rates, a greater number of nodes, and longer link distances, but retains much backward compatibility. Over time, Ethernet has largely replaced competing wired LAN technologies such as Token Ring, FDDI and ARCNET.

IEEE 802.11 is part of the IEEE 802 set of local area network (LAN) technical standards, and specifies the set of media access control (MAC) and physical layer (PHY) protocols for implementing wireless local area network (WLAN) computer communication. The standard and amendments provide the basis for wireless network products using the Wi-Fi brand and are the world's most widely used wireless computer networking standards. IEEE 802.11 is used in most home and office networks to allow laptops, printers, smartphones, and other devices to communicate with each other and access the Internet without connecting wires. IEEE 802.11 is also a basis for vehicle-based communication networks with IEEE 802.11p.
Network throughput refers to the rate of message delivery over a communication channel, such as Ethernet or packet radio, in a communication network. The data that these messages contain may be delivered over physical or logical links, or through network nodes. Throughput is usually measured in bits per second, and sometimes in data packets per second or data packets per time slot.
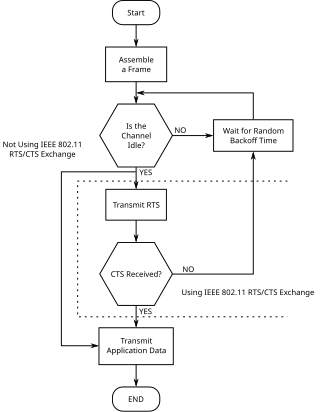
Carrier-sense multiple access with collision avoidance (CSMA/CA) in computer networking, is a network multiple access method in which carrier sensing is used, but nodes attempt to avoid collisions by beginning transmission only after the channel is sensed to be "idle". When they do transmit, nodes transmit their packet data in its entirety.
Carrier-sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD) is a medium access control (MAC) method used most notably in early Ethernet technology for local area networking. It uses carrier-sensing to defer transmissions until no other stations are transmitting. This is used in combination with collision detection in which a transmitting station detects collisions by sensing transmissions from other stations while it is transmitting a frame. When this collision condition is detected, the station stops transmitting that frame, transmits a jam signal, and then waits for a random time interval before trying to resend the frame.
ALOHAnet, also known as the ALOHA System, or simply ALOHA, was a pioneering computer networking system developed at the University of Hawaii. ALOHAnet became operational in June 1971, providing the first public demonstration of a wireless packet data network. ALOHA originally stood for Additive Links On-line Hawaii Area.
The data link layer, or layer 2, is the second layer of the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking. This layer is the protocol layer that transfers data between nodes on a network segment across the physical layer. The data link layer provides the functional and procedural means to transfer data between network entities and may also provide the means to detect and possibly correct errors that can occur in the physical layer.

In IEEE 802 LAN/MAN standards, the medium access control sublayer is the layer that controls the hardware responsible for interaction with the wired, optical or wireless transmission medium. The MAC sublayer and the logical link control (LLC) sublayer together make up the data link layer. The LLC provides flow control and multiplexing for the logical link, while the MAC provides flow control and multiplexing for the transmission medium.
IEEE 802.11e-2005 or 802.11e is an approved amendment to the IEEE 802.11 standard that defines a set of quality of service (QoS) enhancements for wireless LAN applications through modifications to the media access control (MAC) layer. The standard is considered of critical importance for delay-sensitive applications, such as Voice over Wireless LAN and streaming multimedia. The amendment has been incorporated into the published IEEE 802.11-2007 standard.
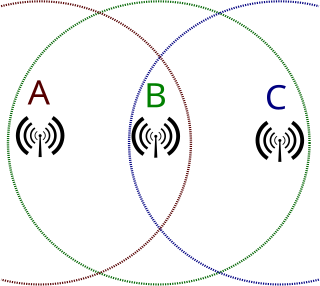
In wireless networking, the hidden node problem or hidden terminal problem occurs when a node can communicate with a wireless access point (AP), but cannot directly communicate with other nodes that are communicating with that AP. This leads to difficulties in medium access control sublayer since multiple nodes can send data packets to the AP simultaneously, which creates interference at the AP resulting in no packet getting through.

Beacon frame is one of the management frames in IEEE 802.11 based WLANs. It contains all the information about the network. Beacon frames are transmitted periodically, they serve to announce the presence of a wireless LAN and to synchronise the members of the service set. Beacon frames are transmitted by the access point (AP) in an infrastructure basic service set (BSS). In IBSS network beacon generation is distributed among the stations. For the 2.4 GHz spectrum, when having more than 15 SSIDs on non-overlapping channels, beacon frames start to consume significant amount of air time and degrade performance even when most of the networks are idle.
A duplex communication system is a point-to-point system composed of two or more connected parties or devices that can communicate with one another in both directions. Duplex systems are employed in many communications networks, either to allow for simultaneous communication in both directions between two connected parties or to provide a reverse path for the monitoring and remote adjustment of equipment in the field. There are two types of duplex communication systems: full-duplex (FDX) and half-duplex (HDX).
IEEE 802.11n-2009 or 802.11n is a wireless-networking standard that uses multiple antennas to increase data rates. The Wi-Fi Alliance has also retroactively labelled the technology for the standard as Wi-Fi 4. It standardized support for multiple-input multiple-output, frame aggregation, and security improvements, among other features, and can be used in the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz frequency bands.

A computer network is a set of computers sharing resources located on or provided by network nodes. The computers use common communication protocols over digital interconnections to communicate with each other. These interconnections are made up of telecommunication network technologies, based on physically wired, optical, and wireless radio-frequency methods that may be arranged in a variety of network topologies.
Nitro from Conexant is a proprietary 802.11g performance enhancement technology introduced in 2003 as part of the PRISM chipset. The first implementation was designed to help compensate for the performance loss of higher-speed 802.11g devices when they share a wireless network with slower 802.11b devices.
Frame aggregation is a feature that allows communicating on shared link or channel, typically a TDM shared channel, with minimum time slot that for efficiency reasons benefit from filling the time slot with data, i.e. sending two or more data frames in a single transmission. The feature is an important part of the IEEE 802.11e, 802.11n and 802.11ac wireless LAN standards that increases throughput with frame aggregation. The MoCA protocol used for communication over coaxial networks also implements frame aggregation for the same reason. In protocol standards and implementations, the frame aggregation is usually combined with segmentation and reassembly of frames so that the time slots can be filled to 100%. E.g., an aggregation MAC PDU can be filled with 3.5 frames to ensure the time slot is utilized to 100% and in the next time slot the rest of the fragmented frame is sent together with any additional complete frames.
ITU-T Y.1564 is an Ethernet service activation test methodology, which is the new ITU-T standard for turning up, installing and troubleshooting Ethernet-based services. It is the only standard test methodology that allows for complete validation of Ethernet service-level agreements (SLAs) in a single test.
Traffic indication map (TIM) is a structure used in 802.11 wireless network management frames.
IEEE 802.11ah is a wireless networking protocol published in 2017 called Wi-Fi HaLow as an amendment of the IEEE 802.11-2007 wireless networking standard. It uses 900 MHz license-exempt bands to provide extended-range Wi-Fi networks, compared to conventional Wi-Fi networks operating in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. It also benefits from lower energy consumption, allowing the creation of large groups of stations or sensors that cooperate to share signals, supporting the concept of the Internet of things (IoT). The protocol's low power consumption competes with Bluetooth and has the added benefit of higher data rates and wider coverage range.
Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) is a set of standards under development by the Time-Sensitive Networking task group of the IEEE 802.1 working group. The TSN task group was formed in November 2012 by renaming the existing Audio Video Bridging Task Group and continuing its work. The name changed as a result of the extension of the working area of the standardization group. The standards define mechanisms for the time-sensitive transmission of data over deterministic Ethernet networks.





