
Alexanderplatz is a large public square and transport hub in the central Mitte district of Berlin. The square is named after the Russian Tsar Alexander I, which also denotes the larger neighbourhood stretching from Mollstraße in the north-east to Spandauer Straße and the Rotes Rathaus in the south-west.

Schloßplatz is a square located on Museum Island (Museumsinsel) in Berlin, Germany. It measures about 225 m by 175 m, with its long side oriented on an axis approximately southwest/northeast. At its west corner is the Schlossbrücke, from which Unter den Linden leads west to the Brandenburg Gate. From the same corner, Karl-Liebknecht-Straße runs northeast alongside the square and on to Alexanderplatz. Until the early 20th century, only the square south of the palace was so named, the square north of it being the Lustgarten.
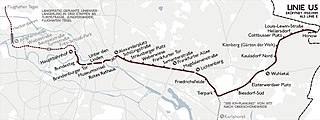
U5 is a line on the Berlin U-Bahn. It runs from Hauptbahnhof in Mitte eastwards through Alexanderplatz, Friedrichshain, Lichtenberg and Friedrichsfelde, surfaces in Biesdorf-Süd to pass Kaulsdorf and Hellersdorf above ground and finally reaches city limits at Hönow.

Friedrichshain is a quarter (Ortsteil) of the borough of Friedrichshain-Kreuzberg in Berlin, Germany. From its creation in 1920 until 2001, it was a freestanding city borough. Formerly part of East Berlin, it is adjacent to Mitte, Prenzlauer Berg, Kreuzberg and Lichtenberg.

Karl-Marx-Allee is a monumental socialist boulevard built by the GDR between 1952 and 1960 in Berlin Friedrichshain and Mitte. Today the boulevard is named after Karl Marx. It should not be confused with the Karl-Marx-Straße in the Neukölln district of Berlin.

Alfred Frederik Elias Grenander was a Swedish architect, who became one of the most prominent engineers during the first building period of the Berlin U-Bahn network in the early twentieth century.

The Innenstadt is the central city district of Frankfurt am Main, Germany. It is part of the Ortsbezirk Innenstadt I. Its western part forms part of Frankfurt's central business district, the Bankenviertel. Germany's most expensive shopping streets and real estate are found within the city district.

Weberwiese is a Berlin U-Bahn station located on the line, which currently runs from Berlin Central Station to Hönow. The station is located under Karl-Marx-Allee directly east of Straße der Pariser Kommune. Although the next station on the line is called Frankfurter Tor, the historical city gate Frankfurter Tor actually stood at the location of the Weberwiese station. Several of the stations on this line have been recently redeveloped and are now colour-coded. In 2003, Weberwiese station was renovated and now has a very different appearance, with yellow tiles in contrast to its former white ones.

The Bundesstraße 5 is a German federal highway running in a northwesterly to southeasterly direction from the Danish border near Niebüll to Frankfurt (Oder). It provides a direct route for motorists traveling between Berlin and Hamburg. In Berlin B5 forms among others the following squares and streets Heerstraße, Theodor-Heuss-Platz, Kaiserdamm, Straße des 17. Juni, Großer Stern, Unter den Linden, Karl-Liebknecht-Straße, Alexanderplatz, Karl-Marx-Allee, Frankfurter Tor, and Frankfurter Allee. The section north of Hamburg is partially paralleled by Bundesautobahn 23.

Karl-Liebknecht-Straße is a major street in the central Mitte district of the German capital Berlin. It is named after Karl Liebknecht (1871–1919), one of the founders of the Communist Party of Germany. The street connects the Unter den Linden boulevard with the Prenzlauer Allee arterial road leading to the northern city limits. Although part of the street dates back to medieval times, most of the buildings at its side were built in the 1960s, when East Berlin's centre was redesigned as the capital of East Germany.

Hermann Henselmann was a German architect most famous for his buildings constructed in East Germany during the 1950s and 1960s.

Warschauer Straße is a major thoroughfare in the Friedrichshain-Kreuzberg district of central Berlin, the capital of Germany. The street begins at Frankfurter Tor to the North and spans 1.6km South to the intersection of the Oberbaumbrücke, Mühlenstraße and Stralauer Allee. The street acts as a section of Bundesstraße 96a and the Berlin Inner Ring Road. The street is named after Warsaw, the capital of Poland.

The Bundesstraße 1 is a German federal highway running in an east-west direction from the Dutch border near Aachen to the Polish border at Küstrin-Kietz on the Oder River.

Frankfurter Tor is a station on U-Bahn line in Berlin, Germany. It is situated under Frankfurter Tor, a large square.

Mitte is a central locality of Berlin in the eponymous district of Mitte. Until 2001, it was itself an autonomous district.
Eschenheimer Turm was a city gate, part of the late-medieval fortifications of Frankfurt am Main, and is a landmark of the city. The tower, which was erected at the beginning of the fifteenth century, is at once the oldest and most unaltered building in the largely reconstructed Frankfurter Neustadt, now better known as the Frankfurt-Innenstadt.

The Frankfurter Allee is one of the oldest roads of Berlin, the capital city of Germany. It extends the Karl-Marx-Allee from Frankfurter Tor in the direction of the city of Frankfurt (Oder). It is part of Bundesstraße 1 and has a length of 3.6 kilometres (2.2 mi).

The Berlin Customs Wall was a ring wall around the historic city of Berlin, between 1737 and 1860; the wall itself had no defence function but was used to facilitate the levying of taxes on the import and export of goods (tariffs) which was the primary income of many cities at the time.

The Berlin Stalin statue was a bronze portrayal of the Soviet leader Joseph Stalin. A Komsomol delegation had presented the sculpture to the East Berlin government on the occasion of the Third World Festival of Youth and Students in 1951. The monument was formally dedicated on 3 August 1951 after temporary placement at a location on a newly designed and impressive boulevard, Stalinallee, being constructed at the time in what was then the Berlin district of Friedrichshain. Stalin monuments were generally removed from public view by the leadership of the Soviet Union and other associated countries, including East Germany, during the period of De-Stalinization. In Berlin the statue and all street signs designating Stalinallee were hastily removed one night in a clandestine operation and the street was renamed Karl-Marx-Allee and Frankfurter Allee. The bronze sculpture was smashed and the pieces were recycled.

Edmund Collein was an East German architect and urban planner. He is also known for his photography while studying at the Bauhaus art school.

![]() , is located under the square. [1]
, is located under the square. [1] 

















