

Frederick William Collard (baptised 1772, died 1860) was a British piano manufacturer.


Frederick William Collard (baptised 1772, died 1860) was a British piano manufacturer.

Collard, son of William and Thamosin Collard, was baptised at Wiveliscombe, Somerset, on 21 June 1772, and coming to London at the age of fourteen, obtained a situation in the house of Longman, Lukey, & Broderip, music publishers and pianoforte makers at 26 Cheapside.
In 1799 Longman & Co. fell into commercial difficulties, and a new company, consisting of John Longman, Muzio Clementi, Frederick Augustus Hyde, F. W. Collard, Josiah Banger, and David Davis, took over the business, but on 28 June 1800 Longman and Hyde retired, and the firm henceforth was known as Muzio Clementi & Co. After some time William Frederick Collard was admitted a partner, and on 24 June 1817 Banger went out. On 24 June 1831 the partnership between F. W. Collard, W. F. Collard, and Clementi expired, and the two brothers continued the business until 24 June 1842, when W. F. Collard retired, and F. W. Collard, then sole proprietor, took into partnership his two nephews, Frederick William Collard, jun., and Charles Lukey Collard.
After 1832 the pianos which had long borne the name of Clementi began to be called Collard & Collard, and many patents were in course of time taken out for improvements both in the action and the frame of the instruments. The firm soon gave up the business of music publishing, and confined themselves to pianoforte making, except that they had also the contract for supplying bugles, fifes, and drums to the regiments of the East India Company until 1858, when the government of India was transferred to the queen. About this time a novelty was brought out, which was suggested by an article in Chambers's Journal, a piano of the cottage class styled pianoforte for the people, which was sold in considerable numbers. To the Great Exhibition of 1851 Collard sent a grand, for which the musical jury awarded the council medal, but this award was not confirmed, owing to some feeling of jealousy.
The firm suffered twice from large fires; on 20 March 1807 the manufactory in Tottenham Court Road was burnt to the ground, and on 10 Dec. 1851 a new manufactory in Oval Road, Camden Town, was entirely destroyed.
F. W. Collard died at 26 Cheapside on 31 Jan. 1860, aged 88, having always lived in the same house since his arrival in London in 1786. He was buried in a family vault on the western side of Highgate Cemetery.
William Frederick Collard, the brother and partner of the above, was baptised at Wiveliscombe on 25 Aug. 1776, and, in addition to an inventive genius respecting improvements in pianos, also developed a taste for lyric poetry.
William retired from business in 1842, died at Folkestone on 11 Oct. 1866 and was buried a week later in the Collard family vault in Highgate Cemetery.

Muzio Filippo Vincenzo Francesco Saverio Clementi was an Italian-British composer, virtuoso pianist, pedagogue, conductor, music publisher, editor, and piano manufacturer, who was mostly active in England.

Johann Carl Gottfried Loewe, usually called Carl Loewe, was a German composer, tenor singer and conductor. In his lifetime, his songs ("Balladen") were well enough known for some to call him the "Schubert of North Germany", and Hugo Wolf came to admire his work. He is less known today, but his ballads and songs, which number over 400, are occasionally performed.

John Field was an Irish pianist, composer and teacher widely credited as the creator of the nocturne. While other composers were writing in a similar style at this time, Field was the first to use the term 'Nocturne' specifically to apply to a character piece featuring a cantabile melody over an arpeggiated accompaniment.
This article is about music-related events in 1826.
This is a list of music-related events in 1802.

Johann Nepomuk Hummel was an Austrian composer and virtuoso pianist. His music reflects the transition from the Classical to the Romantic musical era. He was a pupil of Mozart, Salieri and Haydn. Hummel significantly influenced later piano music of the 19th century, particularly in the works of Chopin, Liszt and Mendelssohn.
A sonatina is a small sonata. As a musical term, sonatina has no single strict definition; it is rather a title applied by the composer to a piece that is in basic sonata form, but is shorter and lighter in character, or technically more elementary, than a typical sonata. The term has been in use at least since the late baroque; there is a one-page, one-movement harpsichord piece by Handel called "Sonatina". It is most often applied to solo keyboard works, but a number of composers have written sonatinas for violin and piano, for example the Sonatina in G major for Violin and Piano by Antonín Dvořák, and occasionally for other instruments, for example the Clarinet Sonatina by Malcolm Arnold.

A piano sonata is a sonata written for a solo piano. Piano sonatas are usually written in three or four movements, although some piano sonatas have been written with a single movement, others with two movements, some contain five or even more movements. The first movement is generally composed in sonata form.

Ignaz (Ignace) Joseph Pleyel was an Austrian composer, music publisher and piano builder of the Classical period. He grew up in Austria, and was educated there; in his mid-twenties he moved to France, and was based in France for the rest of his life.

Friedrich Wilhelm Michael Kalkbrenner, also known as Frédéric Kalkbrenner, was a pianist, composer, piano teacher and piano manufacturer. German by birth, Kalkbrenner studied at the Conservatoire de Paris, starting at a young age and eventually settled in Paris, where he lived until his death in 1849. Kalkbrenner composed more than 200 piano works, as well as many piano concertos and operas.
F-sharp minor is a minor scale based on F♯, consisting of the pitches F♯, G♯, A, B, C♯, D, and E. Its key signature has three sharps. Its relative major is A major and its parallel major is F-sharp major.
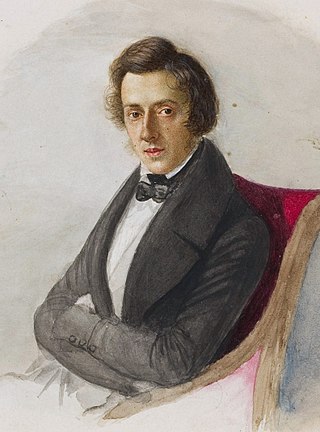
The Études by Frédéric Chopin are three sets of études for the piano published during the 1830s. There are twenty-seven compositions overall, comprising two separate collections of twelve, numbered Op. 10 and Op. 25, and a set of three without opus number.

Étude Op. 10, No. 1 in C major is a study for solo piano composed by Frédéric Chopin in 1829. It was first published in 1833 in France, Germany, and England as the first piece of his Études Op. 10. This study in reach and arpeggios focuses on stretching the fingers of the right hand. The American music critic James Huneker (1857–1921) compared the "hypnotic charm" that these "dizzy acclivities and descents exercise for eye as well as ear" to the frightening staircases in Giovanni Battista Piranesi's prints of the Carceri d'invenzione. Virtuoso pianist Vladimir Horowitz, who refused to perform this étude in public, said, "For me, the most difficult one of all is the C Major, the first one, Op. 10, No. 1."

Étude Op. 10, No. 2, in A minor, is a technical study composed by Frédéric Chopin for the piano. It was preceded by a relative major key. Composed in November 1829, it was first published in 1833 in France, Germany, and England. This étude is an exercise in developing the independence of the weaker fingers of the right hand by playing rapid chromatic scale figures with the third, fourth, and fifth fingers of the right hand. Meanwhile, the first two fingers of the right and the left hand play an accompaniment of short intervals and single notes. Chopin indicated the fingering himself note by note for almost 800 notes.

Étude Op. 10, No. 3, in E major, is a study for solo piano composed by Frédéric Chopin in 1832. It was first published in 1833 in France, Germany, and England as the third piece of his Études Op. 10. This is a slow cantabile study for polyphonic and expressive legato playing. In fact, Chopin himself believed the melody of the piece to be the most beautiful one he ever composed. It became famous through numerous popular arrangements. Although this étude is sometimes identified by the names "Tristesse" (Sadness) or "Farewell (L'Adieu)", neither is a name given by Chopin, but rather his critics.

Finchcocks is an early Georgian manor house in Goudhurst, Kent. For 45 years it housed a large, visitor-friendly museum of historical keyboard instruments, displaying a collection of harpsichords, clavichords, fortepianos, square pianos, organs and other musical instruments. The museum was run by the owners of the house, Richard and Katrina Burnett until 2017. It is now owned by Neil and Harriet Nichols who use it as a family home and a venue for residential piano courses and classical concerts.

Peter Roy Katin was a British classical pianist and teacher.

Robert Wornum (1780–1852) was a piano maker working in London during the first half of the 19th century. He is best known for introducing small cottage and oblique uprights and an action considered to be the predecessor of the modern upright action which was used in Europe through the early 20th century. His piano manufacturing business eventually became Robert Wornum & Sons and continued half a century after his death.
Johann Peter Fritz was a piano maker based in Vienna. He was one of Vienna's most distinguished piano makers. His pianos were valued for good quality and melodiousness. It is known, that Giuseppe Verdi was very fond of Johann Fritz's pianos and used the Viennese 6-pedal Fritz piano from the time of Rigoletto in 1851 to Aida in 1871. This exact piano can be seen in the composer's Villa Verdi in Province of Piacenza in Italy.