
Ballston is a town in Saratoga County, New York, United States. The population was 11,831 at the 2020 census. The name is derived from an early settler, Eliphalet Ball, a Presbyterian minister who relocated there from Westchester County, New York in 1770. The town is in the southern part of the county, and is north of Schenectady.

Mechanicville is a city in Saratoga County, New York, United States. The population was 5,163 at the 2020 census, a small decrease from 5,196 in 2010. It is the smallest city by area in the state. The name is derived from the occupations of early residents.

The Boston and Maine Railroad was a U.S. Class I railroad in northern New England. It was chartered in 1835, and became part of what was the Pan Am Railways network in 1983.

The Mohawk Valley region of the U.S. state of New York is the area surrounding the Mohawk River, sandwiched between the Adirondack Mountains and Catskill Mountains, northwest of the Capital District. As of the 2010 United States Census, the region's counties have a combined population of 622,133 people. In addition to the Mohawk River valley, the region contains portions of other major watersheds such as the Susquehanna River.

The Adirondack is a daily intercity passenger train operated by Amtrak between New York City and Montreal. The scenic route follows the Empire Corridor through the Hudson Valley with major stops in Yonkers, Poughkeepsie, Albany–Rensselaer, and Schenectady. North of Saratoga Springs the route runs between the Adirondack Mountains and Lake Champlain until crossing the Canada–U.S. border at Rouses Point. Trains take approximately 11 hours to travel the 381-mile (613 km) route.

The Hoosac Tunnel is a 4.75-mile (7.64 km) active railroad tunnel in western Massachusetts that passes through the Hoosac Range, an extension of Vermont's Green Mountains. It runs in a straight line from its east portal, along the Deerfield River in the town of Florida, to its west portal, in the city of North Adams.

The Delaware and Hudson Railway (D&H) is a railroad that operates in the Northeastern United States. In 1991, after more than 150 years as an independent railroad, the D&H was purchased by the Canadian Pacific Railway (CP). CP, which would itself become part of Canadian Pacific Kansas City in 2023, operated D&H under its subsidiary Soo Line Corporation, which also operates Soo Line Railroad.

Pan Am Railways, Inc. (PAR) is a subsidiary of CSX Corporation that operates Class II regional railroads covering northern New England from Mattawamkeag, Maine, to Rotterdam Junction, New York. Pan Am Railways is primarily made up of former Class II regional railroads such as Boston and Maine Corporation, Maine Central Railroad Company, Portland Terminal Company, and Springfield Terminal Railway Company. It was formerly known as Guilford Transportation Industries and was also known as Guilford Rail System. Guilford bought the name, colors, and logo of Pan American World Airways in 1998.
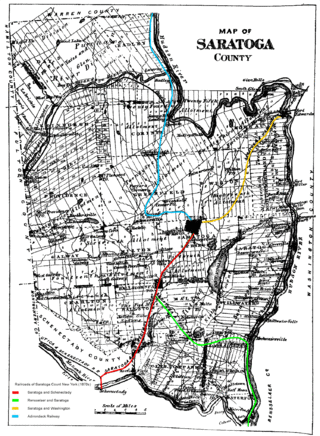
The Saratoga and Schenectady Railroad was incorporated on February 16, 1831. The founders were Henry Walton, John Clarke, William A. Langworthy, John H. Steele, Miles Beach, Gideon W. Davison, and Rockwell Putnam. The line was opened from Schenectady to Ballston Spa on July 12, 1832, and extended to Saratoga Springs in 1833 for a total of 20.8 miles (33.5 km). The Rensselaer and Saratoga Railroad leased the line on January 1, 1851, and the lease was reassigned to the Delaware and Hudson Canal Company on May 1, 1871.

The Rensselaer and Saratoga Railroad was a railway company that operated in the states of New York and Vermont in the 19th century. At its peak it controlled a 150-mile (240 km) network. The Delaware and Hudson Railway leased the company in 1871 and formally merged it in 1945.

The Fitchburg Railroad is a former railroad company, which built a railroad line across northern Massachusetts, United States, leading to and through the Hoosac Tunnel. The Fitchburg was leased to the Boston and Maine Railroad in 1900. The main line from Boston to Fitchburg is now operated as the MBTA Fitchburg Line; Pan Am Railways runs freight service on some other portions.
The West Shore Railroad was a railroad that ran from Weehawken, New Jersey, on the west bank of the Hudson River opposite New York City, north to Albany, New York, and then west to Buffalo. It was organized in 1864 as the Saratoga and Hudson River Railroad, a competitor to the New York Central and Hudson River Railroad, but was soon taken over by that company. The Saratoga and Hudson River Railroad was renamed several times over the years; it became part of the CSX Transportation system in 1999.

The Capital District Transportation Authority (CDTA) is a New York State public-benefit corporation overseeing a number of multi-modal parts of public transportation in the Capital District of New York State. CDTA runs local and express buses, including four lines of an express bus service called BusPlus, and day-to-day management of three Amtrak stations in the Capital region–the Albany-Rensselaer, Schenectady and Saratoga Springs Amtrak stations. In 2023, the system had a ridership of 15,779,000, or about 57,500 per weekday as of the third quarter of 2024.

Area codes 518 and 838 are telephone area codes in the North American Numbering Plan for eastern Upstate New York in the United States. 518 is one of the 86 original North American area codes created in 1947. Area code 838 was added to the 518 numbering plan area in 2017. The two area codes serve 24 counties and 1,200 ZIP Code areas in a numbering plan area (NPA) that extends from the eastern Mohawk Valley to the Vermont border, and from the Canada–US border to south of Albany. The bulk of the population is in the Capital District, the vicinity of the cities Albany, Schenectady, and Troy. Other cities in the NPA are Glens Falls, Plattsburgh, and Saratoga Springs. It includes the Upper Hudson Valley counties, Greene and Columbia counties, and some northern parts of Dutchess County.

New York State Route 146 (NY 146) is a state highway in the Capital District of New York in the United States. It extends for 43 miles (69 km) from Gallupville at NY 443 to near Mechanicville at U.S. Route 4 (US 4) and NY 32. NY 146 is a major thoroughfare in the city of Schenectady, just outside Albany. Most of the route follows an east–west alignment; however, the middle third of the route between Guilderland and Clifton Park runs in a more north–south manner in order to serve Schenectady. At one time, NY 146 had three spur routes; only one—NY 146A—still exists.

New York State Route 50 (NY 50) is a 31.67-mile (50.97 km) state highway in the Capital District of New York in the United States. The southern terminus of the route is at an intersection with NY 5 in Scotia. Its northern terminus is at a junction with NY 32 in the Saratoga County hamlet of Gansevoort.

New York State Route 67 (NY 67) is an 86.55-mile-long (139.29 km) east–west state highway in eastern New York in the United States. The western terminus of the route is at an intersection with NY 5 in the town of St. Johnsville. Its eastern terminus is at the Vermont state line in Hoosick, where it continues eastward as Vermont Route 67 (VT 67).

Pan Am Southern, LLC is a freight railroad jointly owned by Norfolk Southern Railway (NS) and CSX Corporation. PAS is independently operated by the Berkshire and Eastern Railroad, a subsidiary of Genesee & Wyoming. PAS owns trackage known as the Patriot Corridor between Albany, New York, and the Boston, Massachusetts, area, utilizing rail lines formerly owned by the Fitchburg Railroad and later on the Boston and Maine Railroad. It was previously operated by PAR subsidiary Springfield Terminal Railway.

The Boston, Hoosac Tunnel and Western Railway was a railway company that operated in the states of New York and Vermont in the 1880s. At its peak it controlled a 61-mile (98 km) network centered on Mechanicville, New York. Plans to extend the line west to Buffalo, New York, on Lake Ontario, were never realized, and the Fitchburg Railroad, a predecessor of the Boston and Maine Railroad, acquired control of the company in 1887 and merged it in 1892.
The Canadian Subdivision is a railway line in the state of New York. It runs north–south along the west side of Lake Champlain from the vicinity of Schenectady, New York, to Rouses Point, New York, on the border with Quebec. While the oldest part of the line was built in 1832–1833, the majority was constructed between 1869 and 1876. Once part of the Delaware and Hudson Railway main line, today Canadian Pacific Kansas City owns the line. Amtrak's Adirondack operates over the full length, providing daily service between New York City and Montreal.
















