
Twin Peaks is an American mystery horror drama television series created by Mark Frost and David Lynch that premiered on April 8, 1990, on ABC. It was one of the top-rated series of 1990, but declining ratings led to its cancellation after its second season in 1991. It nonetheless gained a cult following and has been referenced in a wide variety of media. In subsequent years, Twin Peaks has often been listed among the greatest television series of all time.
The amplitude of a periodic variable is a measure of its change over a single period. There are various definitions of amplitude, which are all functions of the magnitude of the difference between the variable's extreme values. In older texts the phase is sometimes called the amplitude.

Alternating current (AC) is an electric current which periodically reverses direction, in contrast to direct current (DC) which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in which electric power is delivered to businesses and residences, and it is the form of electrical energy that consumers typically use when they plug kitchen appliances, televisions, fans and electric lamps into a wall socket. A common source of DC power is a battery cell in a flashlight. The abbreviations AC and DC are often used to mean simply alternating and direct, as when they modify current or voltage.

The Peak District is an upland area in England at the southern end of the Pennines. It is mostly in northern Derbyshire, but also includes parts of Cheshire, Greater Manchester, Staffordshire, West Yorkshire and South Yorkshire. An area of great diversity, it is split into the Dark Peak, where most of the moorland is found and the geology is gritstone, and the limestone area of the White Peak.
In statistics and its applications, the root mean square is defined as the square root of the mean square .
The RMS is also known as the quadratic mean and is a particular case of the generalized mean with exponent 2.
RMS can also be defined for a continuously varying function in terms of an integral of the squares of the instantaneous values during a cycle.

Derbyshire is a county in the East Midlands of England. A substantial portion of the Peak District National Park lies within Derbyshire, containing the southern extremity of the Pennine range of hills which extend into the north of the county. The county contains part of the National Forest, and borders on Greater Manchester to the northwest, West Yorkshire to the north, South Yorkshire to the northeast, Nottinghamshire to the east, Leicestershire to the southeast, Staffordshire to the west and southwest and Cheshire also to the west.
Kinder Scout, at 636 metres (2,087 ft), is the highest point in the county, whilst Trent Meadows, where the River Trent leaves Derbyshire, is its lowest point at 27 metres (89 ft). The River Derwent is the county's longest river at 66 miles (106 km), and runs roughly north to south through the county. In 2003 the Ordnance Survey placed Church Flatts Farm at Coton in the Elms as the furthest point from the sea in Great Britain.
In topography, prominence measures the height of a mountain or hill's summit relative to the lowest contour line encircling it but containing no higher summit within it. It is a measure of the independence of a summit. A peak's key col is a unique point on this contour line and the parent peak is some higher mountain, selected according to various objective criteria.

A summit is a point on a surface that is higher in elevation than all points immediately adjacent to it. The topographic terms acme, apex, peak, and zenith are synonymous.

The Sangre de Cristo Mountains are the southernmost subrange of the Rocky Mountains. They are located in southern Colorado and northern New Mexico in the United States. The mountains run from Poncha Pass in South-Central Colorado, trending southeast and south, ending at Glorieta Pass, southeast of Santa Fe, New Mexico.
The mountains contain a number of fourteen thousand foot peaks in the Colorado portion, as well as all the peaks in New Mexico which are over thirteen thousand feet.

Peak oil is the theorized point in time when the maximum rate of extraction of petroleum is reached, after which it is expected to enter terminal decline. Peak oil theory is based on the observed rise, peak, fall, and depletion of aggregate production rate in oil fields over time. It is often confused with oil depletion; however, whereas depletion refers to a period of falling reserves and supply, peak oil refers to the point of maximum production. The concept of peak oil is often credited to geologist M. King Hubbert whose 1956 paper first presented a formal theory.
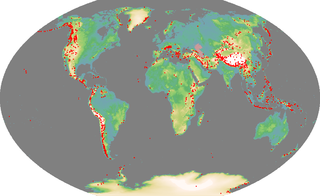
An ultra-prominent peak, or Ultra for short, is a mountain summit with a topographic prominence of 1,500 metres (4,900 ft) or more; it is also called a P1500. There are approximately 1,524 such peaks on Earth. Some peaks, such as the Matterhorn and Eiger, are not Ultras because they are connected to higher mountains by high cols and therefore do not achieve enough topographic prominence.
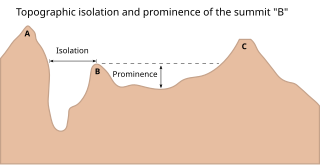
The topographic isolation of a summit is the minimum great-circle distance to a point of equal elevation, representing a radius of dominance in which the peak is the highest point. It can be calculated for small hills and islands as well as for major mountain peaks, and can even be calculated for submarine summits.

The Gates of Firestorm Peak is an adventure module for the second edition of the Advanced Dungeons & Dragons fantasy role-playing game. The adventure was published in 1996, and was written by Bruce Cordell, with cover art by Jeff Easley and interior art by Arnie Swekel.

Pikes Peak is the highest summit of the southern Front Range of the Rocky Mountains, in North America. The ultra-prominent 14,115-foot (4,302.31 m) fourteener is located in Pike National Forest, 12 miles (19 km) west of downtown Colorado Springs, Colorado. The mountain is named in honor of American explorer Zebulon Pike, who was unable to reach the summit. The summit is higher than any point in the United States east of its longitude.

The third season of Twin Peaks, also known as Twin Peaks: The Return, consists of 18 episodes and premiered on Showtime on May 21, 2017. Developed and written by David Lynch and Mark Frost over several years, the season is a continuation of the 1990–91 ABC series. An ensemble of returning and new cast members appear, led by original star Kyle MacLachlan.












