Related Research Articles
Jean Bart may refer to one of the following ships of the French Navy or privateers named in honour of Jean Bart, a French naval commander and privateer.

HMS Ambuscade was a 32-gun fifth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy, built in the Grove Street shipyard of Adams & Barnard at Depford in 1773. The French captured her in 1798 but the British recaptured her in 1803. She was broken up in 1810.
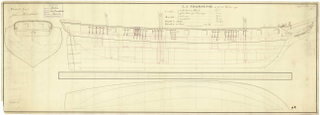
HMS Trompeuse was the French privateer Mercure, captured in 1799. She foundered in the English Channel in 1800.
During the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars Égyptienne, or Egypt, which commemorated Napoleon's Egyptian Campaign, was a popular name for French vessels, including naval vessels and privateers. Between 1799 and 1804, warships of the Royal Navy captured one French frigate and five different French privateers all with the name Égyptienne, and at least one privateer with the name Égypte.
Several French ships have borne the name Courageux, Courageaux, or Courageuse:

HMS Seagull, was a Royal Navy Diligence-class brig-sloop, launched in 1795. During the French Revolutionary Wars she shared in the capture of a number of small French and Dutch privateers. Then early in the Napoleonic Wars she participated in a notable single-ship action before she disappeared without a trace in 1805.

During the late 18th and early 19th centuries, many French privateers and letters of marque bore the name Duguay-Trouin, named for René Duguay-Trouin: René Trouin, Sieur du Gué, French privateer, admiral and Commander in the Order of Saint Louis. Between 1760 and 1810, warships of the Royal Navy captured seven different French privateers all with the name Duguay-Trouin.
HMS Speedwell was a mercantile vessel that the Admiralty purchased in 1780. During the American Revolutionary War she served at Gibraltar during the Great Siege. In 1796 she was converted to a brig. Although she did capture two French privateers and participate in an incident in which the Royal Navy violated Swedish neutrality, her service in the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars was apparently relatively uneventful. A storm in February 1807 destroyed her with the loss of her entire crew.

HMS Swallow was an 18-gun Albatross-class brig-sloop of the British Royal Navy, launched in 1795 and sold in 1802. During her naval career she captured a number of French privateers while on the Jamaica station. After her sale she became an armed whaler sailing under a letter of marque. As a privateer she captured two French whaling vessels but then is no longer listed after 1810.
Numerous vessels have been named Vautour :
His Majesty's hired armed cutter Nox served the British Royal Navy under contract from 17 April 1798 to 31 October 1801. She was of 10973⁄94 tons (bm), and carried twelve 12-pounder carronades.
Numerous French privateers have borne the name Vengeur ("Avenger"):
HM hired armed cutter Flora served the British Royal Navy under contract from 16 August 1794 until a French privateer captured her on 1 December 1798.

HMS Eugenie was the French privateer Nouvelle Eugénie, launched at Nantes in 1796 that the British Royal Navy captured in 1797 and took into service. As a brig-sloop she served in the Channel, primarily escorting convoys, and was sold in 1803.
Adolphe was launched in 1807 and captured on 4 December 1807 after having taken several British prizes.
Adolphe was a lugger launched at Dieppe in 1803. She made several cruises as a French privateer and captured numerous prizes until January 1807 when the British captured her.
HMS Growler was a Courser-class gun-brig built for the British Royal Navy at Northfleet and launched in 1797 as GB No. 26; she was renamed Growler on 7 August the same year.
Saint Ann was launched at Liverpool in 1797. She made one voyage as a slave ship in the triangular trade in enslaved people. She foundered or was shipwrecked or destroyed in 1798 after she had delivered her slaves but before she could return to Liverpool.
Mentor was launched in 1792 at Wemyss. With the out break of war with France in early 1793, the Royal Navy needed smaller vessels to protect convoys from privateers. The Navy employed Mentor as a hired armed vessel, releasing her from her contract at the end of 1801 after the signing of the Treaty of Amiens. She then returned to mercantile service, sailing first to Hamburg and then Oporto. She became a coaster on England's east coast, or a Baltic trader. She was last listed in 1832.
References
- Demerliac, Alain (1999). La Marine de la Révolution: Nomenclature des Navires Français de 1792 A 1799 (in French). Éditions Ancre. ISBN 2-906381-24-1.
- Demerliac, Alain (2003). La Marine du Consulat et du Premier Empire: Nomenclature des Navires Français de 1800 A 1815 (in French). Éditions Ancre. ISBN 2-903179-30-1.