Related Research Articles

Electrical telegraphy is a point-to-point text messaging system, primarily used from the 1840s until the late 20th century. It was the first electrical telecommunications system and the most widely used of a number of early messaging systems called telegraphs, that were devised to send text messages more quickly than physically carrying them. Electrical telegraphy can be considered the first example of electrical engineering.

An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the magnitude of a signal. It is a two-port electronic circuit that uses electric power from a power supply to increase the amplitude of a signal applied to its input terminals, producing a proportionally greater amplitude signal at its output. The amount of amplification provided by an amplifier is measured by its gain: the ratio of output voltage, current, or power to input. An amplifier is defined as a circuit that has a power gain greater than one.

Frequency, most often measured in hertz, is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as temporal frequency for clarity and to distinguish it from spatial frequency. Ordinary frequency is related to angular frequency by a factor of 2π. The period is the interval of time between events, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency: T = 1/f.

Morse code is a telecommunications method which encodes text characters as standardized sequences of two different signal durations, called dots and dashes, or dits and dahs. Morse code is named after Samuel Morse, one of the early developers of the system adopted for electrical telegraphy.

Signals intelligence (SIGINT) is the act and field of intelligence-gathering by interception of signals, whether communications between people or from electronic signals not directly used in communication. As classified and sensitive information is usually encrypted, signals intelligence may necessarily involve cryptanalysis. Traffic analysis—the study of who is signaling to whom and in what quantity—is also used to integrate information, and it may complement cryptanalysis.

Wireless telegraphy or radiotelegraphy is transmission of text messages by radio waves, analogous to electrical telegraphy using cables. Before about 1910, the term wireless telegraphy was also used for other experimental technologies for transmitting telegraph signals without wires. In radiotelegraphy, information is transmitted by pulses of radio waves of two different lengths called "dots" and "dashes", which spell out text messages, usually in Morse code. In a manual system, the sending operator taps on a switch called a telegraph key which turns the transmitter on and off, producing the pulses of radio waves. At the receiver the pulses are audible in the receiver's speaker as beeps, which are translated back to text by an operator who knows Morse code.

In electrical engineering, ground or earth may be a reference point in an electrical circuit from which voltages are measured, a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth.

In signal processing, the Nyquist rate, named after Harry Nyquist, is a value equal to twice the highest frequency (bandwidth) of a given function or signal. It has units of samples per unit time, conventionally expressed as samples per second, or hertz (Hz). When the signal is sampled at a higher sample rate, the resulting discrete-time sequence is said to be free of the distortion known as aliasing. Conversely, for a given sample rate the corresponding Nyquist frequency is one-half the sample rate. Note that the Nyquist rate is a property of a continuous-time signal, whereas Nyquist frequency is a property of a discrete-time system.

In telecommunications, a repeater is an electronic device that receives a signal and retransmits it. Repeaters are used to extend transmissions so that the signal can cover longer distances or be received on the other side of an obstruction. Some types of repeaters broadcast an identical signal, but alter its method of transmission, for example, on another frequency or baud rate.

In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna with the purpose of signal transmission up to a radio receiver. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the antenna. When excited by this alternating current, the antenna radiates radio waves.

A radiotelephone, abbreviated RT, is a radio communication system for conducting a conversation; radiotelephony means telephony by radio. It is in contrast to radiotelegraphy, which is radio transmission of telegrams (messages), or television, transmission of moving pictures and sound. The term is related to radio broadcasting, which transmit audio one way to listeners. Radiotelephony refers specifically to two-way radio systems for bidirectional person-to-person voice communication between separated users, such as CB radio or marine radio. In spite of the name, radiotelephony systems are not necessarily connected to or have anything to do with the telephone network, and in some radio services, including GMRS, interconnection is prohibited.
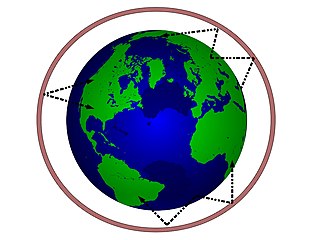
In radio communication, skywave or skip refers to the propagation of radio waves reflected or refracted back toward Earth from the ionosphere, an electrically charged layer of the upper atmosphere. Since it is not limited by the curvature of the Earth, skywave propagation can be used to communicate beyond the horizon, at intercontinental distances. It is mostly used in the shortwave frequency bands.
CHU is the call sign of a shortwave time signal radio station operated by the Institute for National Measurement Standards of the National Research Council. CHU's signal is used for continuous dissemination of official Canadian government time signals, derived from atomic clocks.
A continuous wave or continuous waveform (CW) is an electromagnetic wave of constant amplitude and frequency, typically a sine wave, that for mathematical analysis is considered to be of infinite duration. It may refer to e.g. a laser or particle accelerator having a continuous output, as opposed to a pulsed output.

In radio communications, a radio receiver, also known as a receiver, a wireless, or simply a radio, is an electronic device that receives radio waves and converts the information carried by them to a usable form. It is used with an antenna. The antenna intercepts radio waves and converts them to tiny alternating currents which are applied to the receiver, and the receiver extracts the desired information. The receiver uses electronic filters to separate the desired radio frequency signal from all the other signals picked up by the antenna, an electronic amplifier to increase the power of the signal for further processing, and finally recovers the desired information through demodulation.

The United States Army Signal Corps (USASC) is a branch of the United States Army that creates and manages communications and information systems for the command and control of combined arms forces. It was established in 1860, the brainchild of Major Albert J. Myer, and had an important role in the American Civil War. Over its history, it had the initial responsibility for portfolios and new technologies that were eventually transferred to other U.S. government entities. Such responsibilities included military intelligence, weather forecasting, and aviation.
In a digitally modulated signal or a line code, symbol rate, modulation rate or baud rate is the number of symbol changes, waveform changes, or signaling events across the transmission medium per unit of time. The symbol rate is measured in baud (Bd) or symbols per second. In the case of a line code, the symbol rate is the pulse rate in pulses per second. Each symbol can represent or convey one or several bits of data. The symbol rate is related to the gross bit rate, expressed in bits per second.
Pulse-code modulation (PCM) is a method used to digitally represent analog signals. It is the standard form of digital audio in computers, compact discs, digital telephony and other digital audio applications. In a PCM stream, the amplitude of the analog signal is sampled at uniform intervals, and each sample is quantized to the nearest value within a range of digital steps.

Telecommunication, often used in its plural form or abbreviated as telecom, is the transmission of information with an immediacy comparable to face-to-face communication. As such, slow communications technologies like postal mail and pneumatic tubes are excluded from the definition. Many transmission media have been used for telecommunications throughout history, from smoke signals, beacons, semaphore telegraphs, signal flags, and optical heliographs to wires and empty space made to carry electromagnetic signals. These paths of transmission may be divided into communication channels for multiplexing, allowing for a single medium to transmit several concurrent communication sessions. Several methods of long-distance communication before the modern era used sounds like coded drumbeats, the blowing of horns, and whistles. Long-distance technologies invented during the 20th and 21st centuries generally use electric power, and include the telegraph, telephone, television, and radio.
References
- ↑ Rudolf F. Graf (1999). Modern Dictionary of Electronics. Newnes. ISBN 0-7506-9866-7.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22. (in support of MIL-STD-188).
This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22. (in support of MIL-STD-188).