
The Trojan Range is a mountain range rising to 2,760 metres (9,055 ft), extending northward from Mount Francais along the east side of Iliad Glacier, Anvers Island, in the Palmer Archipelago of the British Antarctic Territory. It was surveyed by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) in 1955 and named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) for the Trojans, one of the opposing sides in the Trojan War in Homer's Iliad.

Sikorsky Glacier is a glacier on the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica draining northwestwards into Hughes Bay both north and south of Sladun Peninsula, branching to enter Cierva Cove and Duarte Cove respectively.
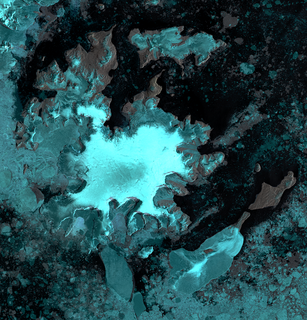
Ineson Glacier is a glacier flowing northwest into Gin Cove, James Ross Island, Antarctica. Following geological work by the British Antarctic Survey (BAS), 1981–83, it was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee after Jonathan R. Ineson, a BAS geologist in the area.

Astudillo Glacier is a small glacier flowing into Paradise Harbor between Leith Cove and Skontorp Cove on the Danco Coast of Graham Land. The glacier was surveyed by the Chilean Antarctic Expedition of 1950–51, which applied the name, probably after an expedition member.

Andrew Glacier is a glacier 3 nautical miles (6 km) long, flowing northeast into Ognen Cove in Charcot Bay immediately west of the Webster Peaks on Trinity Peninsula, northern Graham Land. It was charted in 1948 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) who named the feature for Dr. James Darby Andrew, medical officer at the FIDS Hope Bay station in 1946–47.
Bob Island is a rocky island 1 nautical mile (2 km) long and 145 metres (480 ft) high, lying 4 nautical miles (7 km) southeast of Cape Errera, on Wiencke Island in the Palmer Archipelago. An island in this vicinity was surveyed and photographed by the Belgian Antarctic Expedition (BelgAE) under Gerlache in 1898. It was originally called "Ile Famine", but in the reports resulting from the expedition it was renamed "Ile Bob". In a survey of the area in 1955, the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) made a landing on this island. Although it differs somewhat in size and position from the BelgAE reports, the FIDS found it closely resembles the BelgAE photograph and consider it to be the island originally named.
Damoy Point is a headland 900 metres (980 yd) west-northwest of Flag Point, the northern entrance point to the harbour of Port Lockroy, on the western side of Wiencke Island in the Palmer Archipelago of Antarctica. It was discovered and named by the French Antarctic Expedition, 1903–05, under Jean-Baptiste Charcot.
Janssen Peak is a conspicuous peak, 1,085 metres (3,560 ft) high, forming the southwestern end of the Sierra DuFief in the southwestern part of Wiencke Island, in the Palmer Archipelago, Antarctica. It was discovered by the Belgian Antarctic Expedition, 1897–99, under Gerlache, and charted by the French Antarctic Expedition, 1903–05, under Jean-Baptiste Charcot, who named it for Jules Janssen, a noted French astronomer.

Py Point is a point forming the south extremity of Doumer Island, in the Palmer Archipelago. Discovered by the French Antarctic Expedition, 1903–05, and named by Charcot for Monsieur Py, president of the French Chamber of Commerce in Buenos Aires at that time.
False Island is the largest of three islands lying at the east side of Hackapike Bay, off the northeast coast of Anvers Island, in the Palmer Archipelago. Two islands were charted in this approximate position by the French Antarctic Expedition, 1903–05, under Jean-Baptiste Charcot. False Island was named by Discovery Investigations personnel on the Discovery in 1927.
Fridtjof Sound is a sound, 6 nautical miles (11 km) long in a north–south direction and 2 nautical miles (4 km) wide, which separates Andersson Island and Jonassen Island from Tabarin Peninsula, at the northeast end of the Antarctic Peninsula. It was discovered by the Swedish Antarctic Expedition, 1901–04, under Otto Nordenskiöld, and named after the Fridtjof, a vessel dispatched from Sweden to search for the expedition when it was feared lost in 1903.
Gossler Islands are a group of north–south trending islands 3 nautical miles (6 km) in extent, lying 1.5 nautical miles (3 km) west of Cape Monaco, Anvers Island, in the Palmer Archipelago. They were discovered and named by a German expedition under Eduard Dallmann, 1873–74, in honour of the Gossler banking family of Hamburg. The expedition was funded by the Deutsche Polar-Schifffahrtsgesellschaft shipping company, that was co-owned by Ernst Gossler (1838–1893), a grandson of Senator Johann Heinrich Gossler and a great-grandson of Johann Hinrich Gossler.

Gourdon Glacier is a glacier 4 nautical miles (7 km) long on the east side of James Ross Island, flowing southeast into Markham Bay between Saint Rita Point and Rabot Point. It has a conspicuous rock wall at its head. The glacier was first surveyed by the Swedish Antarctic Expedition under Otto Nordenskiöld, 1901–04, who named it for Ernest Gourdon, geologist and glaciologist of the French Antarctic Expedition, 1903–05.
Mouillard Glacier is a glacier flowing into the southeast corner of Brialmont Cove, on the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. It was photographed by the Falkland Islands and Dependencies Aerial Survey Expedition in 1956–57, and mapped from these photos by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey. The glacier was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1960 for Louis P. Mouillard, a French pioneer of gliding flight.
Lobel Island is an island nearly 1 nautical mile (1.9 km) long, laying 2 nautical miles (4 km) southwest of Brown Island in the Wauwermans Islands of the Wilhelm Archipelago, Antarctica. It was charted by the Third French Antarctic Expedition under Jean-Baptiste Charcot, 1903–05, and named for Loicq de Lobel.
Rudolphy Point is the southwest point of Bryde Island, Danco Coast, Graham Land. Named "Punta Rudolphy" by the Chilean Antarctic Expedition, 1950–51, after Captain Raul Rudolphy of the Chilean Navy, commander of the expedition transport ship Angamos.

Lemaire Island is an island 4.5 nautical miles (8 km) long and 1.5 nautical miles (3 km) wide, lying 1 nautical mile (2 km) west of Duthiers Point off the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. It was discovered by the Belgian Antarctic Expedition, 1897–99, under Adrien de Gerlache, who named it for Charles Antoine Lemaire. The island is bordered by the Aguirre Passage which separates it from the Danco Coast.
Emma Island is an island 2.4 km (1.5 mi) long, with bare jagged peaks projecting through an icecap, lying 1.6 km (1 mi) east of Louise Island and 6.4 km (4 mi) west of Nansen Island in the southwestern half of the entrance to Wilhelmina Bay, off the west coast of Graham Land. It was discovered by the Belgian Antarctic Expedition, 1897–99, under Lieutenant Adrien de Gerlache, and named after his mother, Emma de Gerlache de Gomery.









