Related Research Articles
Nephrology is a specialty for both adult internal medicine and pediatric medicine that concerns the study of the kidneys, specifically normal kidney function and kidney disease, the preservation of kidney health, and the treatment of kidney disease, from diet and medication to renal replacement therapy. The word "renal" is an adjective meaning "relating to the kidneys", and its roots are French or late Latin. Whereas according to some opinions, "renal" and "nephro" should be replaced with "kidney" in scientific writings such as "kidney medicine" or "kidney replacement therapy", other experts have advocated preserving the use of renal and nephro as appropriate including in "nephrology" and "renal replacement therapy", respectively.

Kidney disease, or renal disease, technically referred to as nephropathy, is damage to or disease of a kidney. Nephritis is an inflammatory kidney disease and has several types according to the location of the inflammation. Inflammation can be diagnosed by blood tests. Nephrosis is non-inflammatory kidney disease. Nephritis and nephrosis can give rise to nephritic syndrome and nephrotic syndrome respectively. Kidney disease usually causes a loss of kidney function to some degree and can result in kidney failure, the complete loss of kidney function. Kidney failure is known as the end-stage of kidney disease, where dialysis or a kidney transplant is the only treatment option.

Podocytes are cells in Bowman's capsule in the kidneys that wrap around capillaries of the glomerulus. Podocytes make up the epithelial lining of Bowman's capsule, the third layer through which filtration of blood takes place. Bowman's capsule filters the blood, retaining large molecules such as proteins while smaller molecules such as water, salts, and sugars are filtered as the first step in the formation of urine. Although various viscera have epithelial layers, the name visceral epithelial cells usually refers specifically to podocytes, which are specialized epithelial cells that reside in the visceral layer of the capsule.

Membranous glomerulonephritis (MGN) is a slowly progressive disease of the kidney affecting mostly people between ages of 30 and 50 years, usually white people.
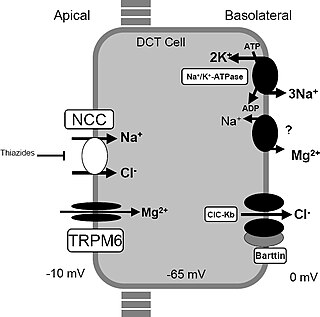
Gitelman syndrome (GS) is an autosomal recessive kidney tubule disorder characterized by low blood levels of potassium and magnesium, decreased excretion of calcium in the urine, and elevated blood pH. It is the most frequent hereditary salt-losing tubulopathy. Gitelman syndrome is caused by disease-causing variants on both alleles of the SLC12A3 gene. The SLC12A3 gene encodes the thiazide-sensitive sodium-chloride cotransporter, which can be found in the distal convoluted tubule of the kidney.

Galloway–Mowat syndrome is a very rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder, consisting of a variety of features including hiatal hernia, microcephaly and nephrotic syndrome.
Podocin is a protein component of the filtration slits of podocytes. Glomerular capillary endothelial cells, the glomerular basement membrane and the filtration slits function as the filtration barrier of the kidney glomerulus. Mutations in the podocin gene NPHS2 can cause nephrotic syndrome, such as focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) or minimal change disease (MCD). Symptoms may develop in the first few months of life or later in childhood.

Nephronophthisis is a genetic disorder of the kidneys which affects children. It is classified as a medullary cystic kidney disease. The disorder is inherited in an autosomal recessive fashion and, although rare, is the most common genetic cause of childhood kidney failure. It is a form of ciliopathy. Its incidence has been estimated to be 0.9 cases per million people in the United States, and 1 in 50,000 births in Canada.
Primary hyperoxaluria is a rare condition, resulting in increased excretion of oxalate, with oxalate stones being common.
AA amyloidosis is a form of amyloidosis, a disease characterized by the abnormal deposition of fibers of insoluble protein in the extracellular space of various tissues and organs. In AA amyloidosis, the deposited protein is serum amyloid A protein (SAA), an acute-phase protein which is normally soluble and whose plasma concentration is highest during inflammation.

A ciliopathy is any genetic disorder that affects the cellular cilia or the cilia anchoring structures, the basal bodies, or ciliary function. Primary cilia are important in guiding the process of development, so abnormal ciliary function while an embryo is developing can lead to a set of malformations that can occur regardless of the particular genetic problem. The similarity of the clinical features of these developmental disorders means that they form a recognizable cluster of syndromes, loosely attributed to abnormal ciliary function and hence called ciliopathies. Regardless of the actual genetic cause, it is clustering of a set of characteristic physiological features which define whether a syndrome is a ciliopathy.

Polycystic kidney disease is a genetic disorder in which the renal tubules become structurally abnormal, resulting in the development and growth of multiple cysts within the kidney. These cysts may begin to develop in utero, in infancy, in childhood, or in adulthood. Cysts are non-functioning tubules filled with fluid pumped into them, which range in size from microscopic to enormous, crushing adjacent normal tubules and eventually rendering them non-functional as well.
Glomerulonephrosis is a non-inflammatory disease of the kidney (nephrosis) presenting primarily in the glomerulus as nephrotic syndrome. The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney and it contains the glomerulus, which acts as a filter for blood to retain proteins and blood lipids. Damage to these filtration units results in important blood contents being released as waste in urine. This disease can be characterized by symptoms such as fatigue, swelling, and foamy urine, and can lead to chronic kidney disease and ultimately end-stage renal disease, as well as cardiovascular diseases. Glomerulonephrosis can present as either primary glomerulonephrosis or secondary glomerulonephrosis.

Kirpal Singh Chugh was an Indian nephrologist from Patti, a neighbouring town to Amritsar in the Indian state of Punjab. He was reportedly the first qualified Indian nephrologist and is considered by many to have been the father of Nephrology in India for his pioneering efforts in starting the first medical department in the discipline in 1956 and establishing the first medical course in nephrology (DM) at the Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh.
Sree Bhushan Raju M.D., D.M., Diplomate of National Board, is a nephrologist from Telangana, India. He is currently Senior professor and Unit head, Dept of Nephrology, Nizam's Institute of Medical Sciences Panjagutta, Hyderabad. Which is one of the largest Nephrology teaching Department in India having ten DM seats. He is one of the principal investigators of CKD task force by Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) to evaluate the prevalence of CKD in adult urban population in India. He is currently an associate editor of Indian Journal of Nephrology, Indian Journal of Organ Transplantation and Frontiers in Medicine. He is a popular advocator of Public Health and early detection of non-communicable disease. He frequency writes editorials in various Regional and National News papers about quality of care, public health, health care systems

Thomas Martin Barratt was a British paediatrician and professor of paediatric nephrology. Barratt was most notable for developing a specialist service for children with kidney diseases in Britain, bringing peritoneal dialysis, haemodialysis, and later renal transplantation to ever younger children. Barratt was an early advocate for multidisciplinary care and developed a model that was later taken up by many other specialist centres across the world. His research led to a new treatments for many types of childhood kidney diseases., and for research into childhood Nephrotic syndrome and Hemolytic-uremic syndrome.

Tetratricopeptide repeat domain 21B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TTC21B gene.
Adeera Levin MD, FRCPC is a Professor of Medicine, and is head of the Division of Nephrology at University of British Columbia.

Katalin Susztak (Suszták) is a Hungarian American scientist and nephrologist at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. She is a professor of medicine and genetics, and currently the codirector of the Complications Unit at the Institute for Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism. Her laboratory made major contributions to the current understanding of kidney disease development. She is also the founder of the Transformative Research In DiabEtic NephropaThy (TRIDENT), a collaborative network of physicians and basic scientists, to find cures for diabetic kidney disease.

Richard Henry Reeve White was a paediatric nephrologist, emeritus Professor of Paediatric Nephrology from the University of Birmingham morphologist and archivist for British Association for Paediatric Nephrology.
References
- ↑ "BCH Division of Nephrology". BCH Division of Nephrology Hildebrandt. Retrieved 29 March 2020.
- ↑ "HHMI". HHMI - Hildebrandt. HHMI. Retrieved 29 March 2020.
- ↑ "UoM" (PDF). UoM Hildebrandt. University of Michigan. Retrieved 29 March 2020.
- ↑ Hildebrandt, F; Benzing, T; Katsanis, N (21 April 2011). "Ciliopathies". The New England Journal of Medicine. 364 (16): 1533–43. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1010172. PMC 3640822 . PMID 21506742.
- ↑ Vivante, A; Hildebrandt, F (March 2016). "Exploring the genetic basis of early-onset chronic kidney disease". Nature Reviews. Nephrology. 12 (3): 133–46. doi:10.1038/nrneph.2015.205. PMC 5202482 . PMID 26750453.
- ↑ "National Academy of Medicine". National Academy of Medicine - Hildebrandt. Retrieved 29 March 2020.
- ↑ "Leopoldina". Leopoldina - Hildebrandt. Retrieved 29 March 2020.
- ↑ "Association of American Physicians". Association of American Physicians. AAP. Retrieved 29 March 2020.
- ↑ "ASN - Homer Smith Award". Homer Smoth W. Award. American Society of Nephrology. Retrieved 29 March 2020.
- ↑ "ISN Awards". A.N. Richards Award. International Society of Nephrology. Retrieved 29 March 2020.
- ↑ "Past Award Recipients". E. Mead Johnson Award. Society for Pediatric Research. Retrieved 29 March 2020.
- 1 2 Search Results for author Hildebrandt F on PubMed .
- ↑ Sadowski, Carolin E.; Lovric, Svjetlana; Ashraf, Shazia; Pabst, Werner L.; Gee, Heon Yung; Kohl, Stefan; Engelmann, Susanne; Vega-Warner, Virginia; Fang, Humphrey; Halbritter, Jan; Somers, Michael J.; Tan, Weizhen; Shril, Shirlee; Fessi, Inès; Lifton, Richard P.; Bockenhauer, Detlef; El-Desoky, Sherif; Kari, Jameela A.; Zenker, Martin; Kemper, Markus J.; Mueller, Dominik; Fathy, Hanan M.; Soliman, Neveen A.; Hildebrandt, Friedhelm (June 2015). "A Single-Gene Cause in 29.5% of Cases of Steroid-Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome". Journal of the American Society of Nephrology. 26 (6): 1279–1289. doi:10.1681/ASN.2014050489. PMC 4446877 . PMID 25349199.
- ↑ Braun, Daniela A.; Schueler, Markus; Halbritter, Jan; Gee, Heon Yung; Porath, Jonathan D.; Lawson, Jennifer A.; Airik, Rannar; Shril, Shirlee; Allen, Susan J.; Stein, Deborah; Al Kindy, Adila; Beck, Bodo B.; Cengiz, Nurcan; Moorani, Khemchand N.; Ozaltin, Fatih; Hashmi, Seema; Sayer, John A.; Bockenhauer, Detlef; Soliman, Neveen A.; Otto, Edgar A.; Lifton, Richard P.; Hildebrandt, Friedhelm (February 2016). "Whole exome sequencing identifies causative mutations in the majority of consanguineous or familial cases with childhood-onset increased renal echogenicity". Kidney International. 89 (2): 468–475. doi:10.1038/ki.2015.317. PMC 4840095 . PMID 26489029.