
A blizzard is a severe snowstorm characterized by strong sustained winds of at least 35 mph (56 km/h) and lasting for a prolonged period of time—typically three hours or more. A ground blizzard is a weather condition where snow is not falling but loose snow on the ground is lifted and blown by strong winds. Blizzards can have an immense size and usually stretch to hundreds or thousands of kilometres.

Lake Ontario is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is surrounded on the north, west, and southwest by the Canadian province of Ontario, and on the south and east by the American state of New York, whose water boundaries meet in the middle of the lake. Ontario, Canada's most populous province, was named for the lake. Many of Ontario's most populous cities, including Toronto, Canada's most populous city, and Hamilton, are on the lake's northern or western shores. In the Huron language, the name Ontarí'io means "Lake of Shining Waters". Its primary inlet is the Niagara River from Lake Erie. The last in the Great Lakes chain, Lake Ontario serves as the outlet to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. It is the only Great Lake not to border the state of Michigan.

Lake-effect snow is produced during cooler atmospheric conditions when a cold air mass moves across long expanses of warmer lake water, warming the lower layer of air which picks up water vapor from the lake, rises up through the colder air above, freezes and is deposited on the leeward (downwind) shores.

The Niagara Escarpment is a long escarpment, or cuesta, in the United States and Canada that runs predominantly east/west from New York, through Ontario, Michigan, Wisconsin, and Illinois. The escarpment is most famous as the cliff over which the Niagara River plunges at Niagara Falls, for which it is named.

Continental climates often have a significant annual variation in temperature. They tend to occur in the middle latitudes, where prevailing winds blow overland, and temperatures are not moderated by bodies of water such as oceans or seas. Continental climates occur mostly in the Northern Hemisphere, which has the kind of large landmasses on temperate latitudes required for this type of climate to develop. Most of northern and northeastern China, eastern and southeastern Europe, central and southeastern Canada, and the central and upper eastern United States have this type of climate.

The blizzard of 1977 hit Western New York as well as Southern Ontario from January 28 to February 1. Daily peak wind gusts ranging from 46 to 69 mph were recorded by the National Weather Service in Buffalo, with snowfall as high as 100 in (254 cm) recorded in areas, and the high winds blew this into drifts of 30 to 40 ft. There were 23 total storm-related deaths in western New York, with five more in northern New York.

Thundersnow, also known as a winter thunderstorm or a thundersnowstorm, is an unusual kind of thunderstorm with snow falling as the primary precipitation instead of rain. It typically falls in regions of strong upward motion within the cold sector of an extratropical cyclone. Thermodynamically, it is not different from any other type of thunderstorm, but the top of the cumulonimbus cloud is usually quite low. In addition to snow, graupel or hail may fall.
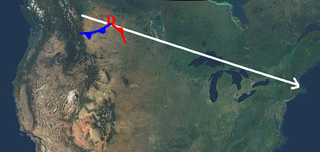
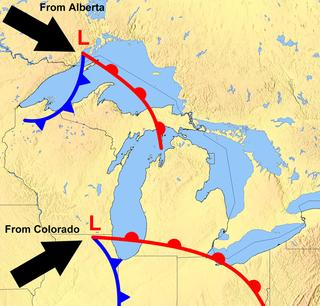
An Alberta-clipper is a fast moving low pressure area weather system which generally affects the central provinces of Canada, as well as parts of the Upper Midwest, Great Lakes, and Northeastern United States regions, precipitating a sudden temperature drop and sharp winds. Alberta clippers take their name from Alberta, the province from which they appear to descend, and from clipper ships of the 19th century, one of the fastest ships of that time.

A panhandle hook is a relatively infrequent winter storm system whose cyclogenesis occurs in the South to southwestern United States from the late fall through winter and into the early spring months. They trek to the northeast on a path towards the Great Lakes region, as the southwesterly jet streams are most prevalent, usually affecting the Midwestern United States and Eastern Canada. Panhandle hooks account for some of the most memorable and deadly blizzards and snowstorms in North America. The name is derived from the region of surface cyclogenesis in the Texas panhandle and Oklahoma panhandle regions. In some winters, there are no panhandle hook storms; in others, there are several.
The Great Lakes Storm of 1913, historically referred to as the "Big Blow," the "Freshwater Fury," or the "White Hurricane," was a blizzard with hurricane-force winds that devastated the Great Lakes Basin in the Midwestern United States and the province of Ontario in Canada from November 7 through November 10, 1913. The storm was most powerful on November 9, battering and overturning ships on four of the five Great Lakes, particularly Lake Huron. Deceptive lulls in the storm and the slow pace of weather reports contributed to the storm's destructiveness.
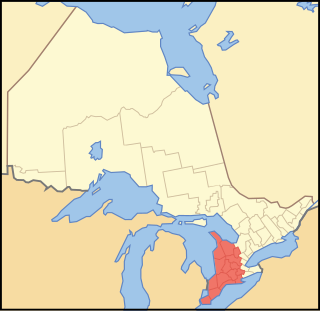
Southwestern Ontario is a secondary region of Southern Ontario in the Canadian province of Ontario. It occupies most of the Ontario Peninsula bounded by Lake Huron, including Georgian Bay, to the north and northwest; the St. Clair River, Lake St. Clair, and Detroit River, to the west; and Lake Erie to the south. To the east, on land, Southwestern Ontario is bounded by Central Ontario and the Golden Horseshoe. The region had a population of 2,583,544 in 2016.

A snowsquall is a sudden moderately heavy snow fall with blowing snow and strong, gusty surface winds. It is often referred to as a whiteout and is similar to a blizzard but is localized in time or in location and snow accumulations may or may not be significant.

Ontario is located in East/Central Canada. It is Canada's second largest province in total land area. Its physical features vary greatly from the Mixedwood Plains in the southeast to the boreal forests and tundra in the north. Ontario borders Manitoba to the west, Hudson Bay and James Bay to the north, Quebec to the east, and the Great Lakes and the United States to the south. The province is named for Great Lake Ontario, an adaptation of the Iroquois word Onitariio, meaning "beautiful lake", or Kanadario, variously translated as "beautiful water". There are approximately 250,000 lakes and over 100,000 kilometres (62,000 mi) of rivers in the province.

Fruit Belt is a term in the United States for an area where the microclimate provides good conditions for fruit growing.

Global storm activity of 2008 profiles the major worldwide storms, including blizzards, ice storms, and other winter events, from January 1, 2008 to December 31, 2008. A winter storm is an event in which the dominant varieties of precipitation are forms that only occur at cold temperatures, such as snow or sleet, or a rainstorm where ground temperatures are cold enough to allow ice to form. It may be marked by strong wind, thunder and lightning, heavy precipitation, such as ice, or wind transporting some substance through the atmosphere. Major dust storms, Hurricanes, cyclones, tornados, gales, flooding and rainstorms are also caused by such phenomena to a lesser or greater existent.
Global storm activity of 2007 profiles the major worldwide storms, including blizzards, ice storms, and other winter events, from January 1, 2007, to December 31, 2007. Winter storms are events in which the dominant varieties of precipitation are forms that only occur at cold temperatures, such as snow or sleet, or a rainstorm where ground temperatures are cold enough to allow ice to form. It may be marked by strong wind, thunder and lightning, heavy precipitation, such as ice, or wind transporting some substance through the atmosphere. Other major non winter events such as large dust storms, Hurricanes, cyclones, tornados, gales, flooding and rainstorms are also caused by such phenomena to a lesser or greater existent.
Global storm activity of 2006 profiles the major worldwide storms, including blizzards, ice storms, and other winter events, from January 1, 2006 to December 31, 2006. Winter storms are events in which the dominant varieties of precipitation are forms that only occur at cold temperatures, such as snow or sleet, or a rainstorm where ground temperatures are cold enough to allow ice to form. It may be marked by strong wind, thunder and lightning, heavy precipitation, such as ice, or wind transporting some substance through the atmosphere. Other major non winter events such as large dust storms, Hurricanes, cyclones, tornados, gales, flooding and rainstorms are also caused by such phenomena to a lesser or greater existent.

From November 13–21, 2014, a potent winter storm and particularly severe lake-effect snowstorm affected the United States, originating from the Pacific Northwest on November 13, which brought copious amounts of lake-effect snow to the Central US and New England from November 15 until November 21, when the system departed the East Coast of the United States. The snowstorm elicited an enormous response from emergency crews and the National Guard, requiring more manpower than any other snowstorm in the history of New York state as it buried cars and stranded thousands of people in their homes in Western New York. Eight months after the storm, the snow's remnants still remained in Buffalo, New York.

From February 14–15, 2015, a potent blizzard occurred in the Northeast United States. The storm dropped up to 25 inches (64 cm) of snow in the regions already hit hard with snow from the past 2 weeks. The storm system also brought some of the most coldest temperatures to the Northeast in its wake.






















