
A metallocene is a compound typically consisting of two cyclopentadienyl anions (C
5H−
5, abbreviated Cp) bound to a metal center (M) in the oxidation state II, with the resulting general formula (C5H5)2M. Closely related to the metallocenes are the metallocene derivatives, e.g. titanocene dichloride or vanadocene dichloride. Certain metallocenes and their derivatives exhibit catalytic properties, although metallocenes are rarely used industrially. Cationic group 4 metallocene derivatives related to [Cp2ZrCH3]+ catalyze olefin polymerization.
Ferrocene is an organometallic compound with the formula Fe(C5H5)2. The molecule is a complex consisting of two cyclopentadienyl rings sandwiching a central iron atom. It is an orange solid with a camphor-like odor that sublimes above room temperature, and is soluble in most organic solvents. It is remarkable for its stability: it is unaffected by air, water, strong bases, and can be heated to 400 °C without decomposition. In oxidizing conditions it can reversibly react with strong acids to form the ferrocenium cation Fe(C5H5)+2. Ferrocene and the ferrocenium cation are sometimes abbreviated as Fc and Fc+ respectively.
Cyclopentadiene is an organic compound with the formula C5H6. It is often abbreviated CpH because the cyclopentadienyl anion is abbreviated Cp−.
An ylide or ylid is a neutral dipolar molecule containing a formally negatively charged atom (usually a carbanion) directly attached to a heteroatom with a formal positive charge (usually nitrogen, phosphorus or sulfur), and in which both atoms have full octets of electrons. The result can be viewed as a structure in which two adjacent atoms are connected by both a covalent and an ionic bond; normally written X+–Y−. Ylides are thus 1,2-dipolar compounds, and a subclass of zwitterions. They appear in organic chemistry as reagents or reactive intermediates.
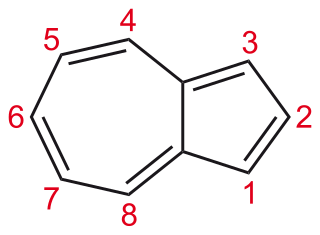
Azulene is an aromatic organic compound and an isomer of naphthalene. Naphthalene is colourless, whereas azulene is dark blue. The compound is named after its colour, as "azul" is Spanish for blue. Two terpenoids, vetivazulene (4,8-dimethyl-2-isopropylazulene) and guaiazulene (1,4-dimethyl-7-isopropylazulene), that feature the azulene skeleton are found in nature as constituents of pigments in mushrooms, guaiac wood oil, and some marine invertebrates.

A cyclopentadienyl complex is a coordination complex of a metal and cyclopentadienyl groups. Cyclopentadienyl ligands almost invariably bind to metals as a pentahapto (η5-) bonding mode. The metal–cyclopentadienyl interaction is typically drawn as a single line from the metal center to the center of the Cp ring.

Nickelocene is the organonickel compound with the formula Ni(η5-C5H5)2. Also known as bis(cyclopentadienyl)nickel or NiCp2, this bright green paramagnetic solid is of enduring academic interest, although it does not yet have any known practical applications.

Titanocene dichloride is the organotitanium compound with the formula (η5-C5H5)2TiCl2, commonly abbreviated as Cp2TiCl2. This metallocene is a common reagent in organometallic and organic synthesis. It exists as a bright red solid that slowly hydrolyzes in air. It shows antitumour activity and was the first non-platinum complex to undergo clinical trials as a chemotherapy drug.

The trispyrazolylborate ligand, abbreviated Tp−, is an anionic tridentate and tripodal ligand. Trispyrazolylborate refers specifically to the anion [HB(C3N2H3)3]−. However, the term can also be used to refer to derivatives having substituents on the pyrazolyl rings. This class of compounds belongs to the family of ligands called scorpionate ligands.

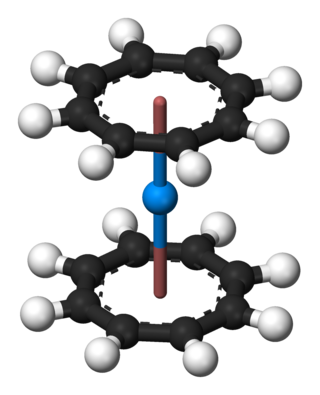
In organometallic chemistry, a sandwich compound is a chemical compound featuring a metal bound by haptic, covalent bonds to two arene (ring) ligands. The arenes have the formula CnHn, substituted derivatives and heterocyclic derivatives. Because the metal is usually situated between the two rings, it is said to be "sandwiched". A special class of sandwich complexes are the metallocenes.

Fulvalene (bicyclopentadienylidene) is the member of the fulvalene family with the molecular formula C10H8. It is of theoretical interest as one of the simplest non-benzenoid conjugated hydrocarbons. Fulvalene is an unstable isomer of the more common benzenoid aromatic compounds naphthalene and azulene. Fulvalene consists of two 5-membered rings, each with two double bonds, joined by yet a fifth double bond. It has D2h symmetry.

Organotitanium chemistry is the science of organotitanium compounds describing their physical properties, synthesis, and reactions. Organotitanium compounds in organometallic chemistry contain carbon-titanium chemical bonds. They are reagents in organic chemistry and are involved in major industrial processes.
Organouranium chemistry is the science exploring the properties, structure, and reactivity of organouranium compounds, which are organometallic compounds containing a carbon to uranium chemical bond. The field is of some importance to the nuclear industry and of theoretical interest in organometallic chemistry.
In organometallic chemistry, a transition metal indenyl complex is a coordination compound that contains one or more indenyl ligands. The indenyl ligand is formally the anion derived from deprotonation of indene. The η5-indenyl ligand is related to the η5cyclopentadienyl anion (Cp), thus indenyl analogues of many cyclopentadienyl complexes are known. Indenyl ligands lack the 5-fold symmetry of Cp, so they exhibit more complicated geometries. Furthermore, some indenyl complexes also exist with only η3-bonding mode. The η5- and η3-bonding modes sometimes interconvert.

Sodium cyclopentadienide is an organosodium compound with the formula C5H5Na. The compound is often abbreviated as NaCp, where Cp− is the cyclopentadienide anion. Sodium cyclopentadienide is a colorless solid, although samples often are pink owing to traces of oxidized impurities.
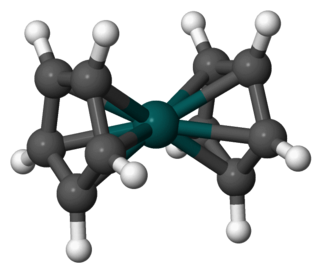
Rhodocene is a chemical compound with the formula [Rh(C5H5)2]. Each molecule contains an atom of rhodium bound between two planar aromatic systems of five carbon atoms known as cyclopentadienyl rings in a sandwich arrangement. It is an organometallic compound as it has (haptic) covalent rhodium–carbon bonds. The [Rh(C5H5)2] radical is found above 150 °C (302 °F) or when trapped by cooling to liquid nitrogen temperatures (−196 °C [−321 °F]). At room temperature, pairs of these radicals join via their cyclopentadienyl rings to form a dimer, a yellow solid.
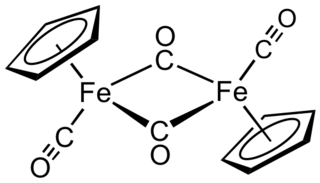
Cyclopentadienyliron dicarbonyl dimer is an organometallic compound with the formula [(η5-C5H5)Fe(CO)2]2, often abbreviated to Cp2Fe2(CO)4, [CpFe(CO)2]2 or even Fp2, with the colloquial name "fip dimer". It is a dark reddish-purple crystalline solid, which is readily soluble in moderately polar organic solvents such as chloroform and pyridine, but less soluble in carbon tetrachloride and carbon disulfide. Cp2Fe2(CO)4 is insoluble in but stable toward water. Cp2Fe2(CO)4 is reasonably stable to storage under air and serves as a convenient starting material for accessing other Fp (CpFe(CO)2) derivatives (described below).

In chemistry, the cyclooctatetraenide anion or cyclooctatetraenide, more precisely cyclooctatetraenediide, is an aromatic species with a formula of [C8H8]2− and abbreviated as COT2−. It is the dianion of cyclooctatetraene. Salts of the cyclooctatetraenide anion can be stable, e.g., Dipotassium cyclooctatetraenide or disodium cyclooctatetraenide. More complex coordination compounds are known as cyclooctatetraenide complexes, such as the actinocenes.
Germyl, trihydridogermanate(1-), trihydrogermanide, trihydridogermyl or according to IUPAC Red Book: germanide is an anion containing germanium bounded with three hydrogens, with formula GeH−3. Germyl is the IUPAC term for the –GeH3 group. For less electropositive elements the bond can be considered covalent rather than ionic as "germanide" indicates. Germanide is the base for germane when it loses a proton.
Organothorium chemistry describes the synthesis and properties of organothorium compounds, chemical compounds containing a carbon to thorium chemical bond.
















