
Aromatic compounds, also known as "mono- and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons", are organic compounds containing one or more aromatic rings. The parent member of aromatic compounds is benzene. The word "aromatic" originates from the past grouping of molecules based on smell, before their general chemical properties are understood. The current definition of aromatic compounds does not have any relation with their smell.

A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is known as covalent bonding. For many molecules, the sharing of electrons allows each atom to attain the equivalent of a full valence shell, corresponding to a stable electronic configuration. In organic chemistry, covalent bonding is much more common than ionic bonding.

In theoretical chemistry, a conjugated system is a system of connected p-orbitals with delocalized electrons in a molecule, which in general lowers the overall energy of the molecule and increases stability. It is conventionally represented as having alternating single and multiple bonds. Lone pairs, radicals or carbenium ions may be part of the system, which may be cyclic, acyclic, linear or mixed. The term "conjugated" was coined in 1899 by the German chemist Johannes Thiele.

In chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property of cyclic (ring-shaped), typically planar (flat) molecular structures with pi bonds in resonance that gives increased stability compared to saturated compounds having single bonds, and other geometric or connective non-cyclic arrangements with the same set of atoms. Aromatic rings are very stable and do not break apart easily. Organic compounds that are not aromatic are classified as aliphatic compounds—they might be cyclic, but only aromatic rings have enhanced stability. The term aromaticity with this meaning is historically related to the concept of having an aroma, but is a distinct property from that meaning.
In chemistry, resonance, also called mesomerism, is a way of describing bonding in certain molecules or polyatomic ions by the combination of several contributing structures into a resonance hybrid in valence bond theory. It has particular value for analyzing delocalized electrons where the bonding cannot be expressed by one single Lewis structure.
In electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions, existing substituent groups on the aromatic ring influence the overall reaction rate or have a directing effect on positional isomer of the products that are formed. An electron donating group (EDG) or electron releasing group is an atom or functional group that donates some of its electron density into a conjugated π system via resonance (mesomerism) or inductive effects —called +M or +I effects, respectively—thus making the π system more nucleophilic. As a result of these electronic effects, an aromatic ring to which such a group is attached is more likely to participate in electrophilic substitution reaction. EDGs are therefore often known as activating groups, though steric effects can interfere with the reaction.
3-Methylenecyclopropene, also called methylenecyclopropene or triafulvene, is a hydrocarbon with chemical formula C4H4. It is a colourless gas that polymerizes readily as a liquid or in solution but is stable as a gas. This highly strained and reactive molecule was synthesized and characterized for the first time in 1984, and has been the subject of considerable experimental and theoretical interest. It is an example of a cross-conjugated alkene, being composed of cyclopropene with an exocyclic double bond attached.
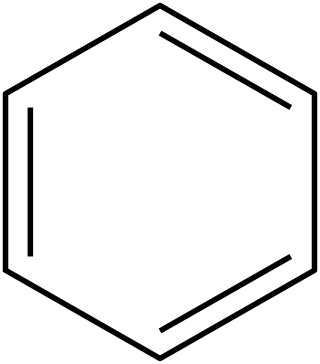
In organic chemistry, Hückel's rule predicts that a planar ring molecule will have aromatic properties if it has 4n + 2 π electrons, where n is a non-negative integer. The quantum mechanical basis for its formulation was first worked out by physical chemist Erich Hückel in 1931. The succinct expression as the 4n + 2 rule has been attributed to W. v. E. Doering (1951), although several authors were using this form at around the same time.
Antiaromaticity is a chemical property of a cyclic molecule with a π electron system that has higher energy, i.e., it is less stable due to the presence of 4n delocalised electrons in it, as opposed to aromaticity. Unlike aromatic compounds, which follow Hückel's rule and are highly stable, antiaromatic compounds are highly unstable and highly reactive. To avoid the instability of antiaromaticity, molecules may change shape, becoming non-planar and therefore breaking some of the π interactions. In contrast to the diamagnetic ring current present in aromatic compounds, antiaromatic compounds have a paramagnetic ring current, which can be observed by NMR spectroscopy.
The 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition is a chemical reaction between a 1,3-dipole and a dipolarophile to form a five-membered ring. The earliest 1,3-dipolar cycloadditions were described in the late 19th century to the early 20th century, following the discovery of 1,3-dipoles. Mechanistic investigation and synthetic application were established in the 1960s, primarily through the work of Rolf Huisgen. Hence, the reaction is sometimes referred to as the Huisgen cycloaddition. 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition is an important route to the regio- and stereoselective synthesis of five-membered heterocycles and their ring-opened acyclic derivatives. The dipolarophile is typically an alkene or alkyne, but can be other pi systems. When the dipolarophile is an alkyne, aromatic rings are generally produced.
In chemistry, a non-covalent interaction differs from a covalent bond in that it does not involve the sharing of electrons, but rather involves more dispersed variations of electromagnetic interactions between molecules or within a molecule. The chemical energy released in the formation of non-covalent interactions is typically on the order of 1–5 kcal/mol. Non-covalent interactions can be classified into different categories, such as electrostatic, π-effects, van der Waals forces, and hydrophobic effects.

Cyclooctadecanonaene or [18]annulene is an organic compound with chemical formula C
18H
18. It belongs to the class of highly conjugated compounds known as annulenes and is aromatic. The usual isomer that [18]annulene refers to is the most stable one, containing six interior hydrogens and twelve exterior ones, with the nine formal double bonds in the cis,trans,trans,cis,trans,trans,cis,trans,trans configuration. It is reported to be a red-brown crystalline solid.

In chemistry, pi stacking refers to the presumptive attractive, noncovalent pi interactions between the pi bonds of aromatic rings. However this is a misleading description of the phenomena since direct stacking of aromatic rings is electrostatically repulsive. What is more commonly observed is either a staggered stacking or pi-teeing interaction both of which are electrostatic attractive For example, the most commonly observed interactions between aromatic rings of amino acid residues in proteins is a staggered stacked followed by a perpendicular orientation. Sandwiched orientations are relatively rare.
The Hückel method or Hückel molecular orbital theory, proposed by Erich Hückel in 1930, is a simple method for calculating molecular orbitals as linear combinations of atomic orbitals. The theory predicts the molecular orbitals for π-electrons in π-delocalized molecules, such as ethylene, benzene, butadiene, and pyridine. It provides the theoretical basis for Hückel's rule that cyclic, planar molecules or ions with π-electrons are aromatic. It was later extended to conjugated molecules such as pyridine, pyrrole and furan that contain atoms other than carbon and hydrogen (heteroatoms). A more dramatic extension of the method to include σ-electrons, known as the extended Hückel method (EHM), was developed by Roald Hoffmann. The extended Hückel method gives some degree of quantitative accuracy for organic molecules in general and was used to provide computational justification for the Woodward–Hoffmann rules. To distinguish the original approach from Hoffmann's extension, the Hückel method is also known as the simple Hückel method (SHM).
Homoaromaticity, in organic chemistry, refers to a special case of aromaticity in which conjugation is interrupted by a single sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Although this sp3 center disrupts the continuous overlap of p-orbitals, traditionally thought to be a requirement for aromaticity, considerable thermodynamic stability and many of the spectroscopic, magnetic, and chemical properties associated with aromatic compounds are still observed for such compounds. This formal discontinuity is apparently bridged by p-orbital overlap, maintaining a contiguous cycle of π electrons that is responsible for this preserved chemical stability.

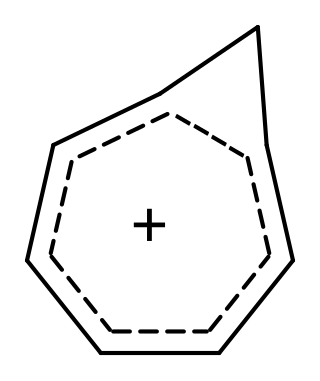
In organic chemistry, Möbius aromaticity is a special type of aromaticity believed to exist in a number of organic molecules. In terms of molecular orbital theory these compounds have in common a monocyclic array of molecular orbitals in which there is an odd number of out-of-phase overlaps, the opposite pattern compared to the aromatic character to Hückel systems. The nodal plane of the orbitals, viewed as a ribbon, is a Möbius strip, rather than a cylinder, hence the name. The pattern of orbital energies is given by a rotated Frost circle (with the edge of the polygon on the bottom instead of a vertex), so systems with 4n electrons are aromatic, while those with 4n + 2 electrons are anti-aromatic/non-aromatic. Due to incrementally twisted nature of the orbitals of a Möbius aromatic system, stable Möbius aromatic molecules need to contain at least 8 electrons, although 4 electron Möbius aromatic transition states are well known in the context of the Dewar-Zimmerman framework for pericyclic reactions. Möbius molecular systems were considered in 1964 by Edgar Heilbronner by application of the Hückel method, but the first such isolable compound was not synthesized until 2003 by the group of Rainer Herges. However, the fleeting trans-C9H9+ cation, one conformation of which is shown on the right, was proposed to be a Möbius aromatic reactive intermediate in 1998 based on computational and experimental evidence.

Cyclopropenone is an organic compound with molecular formula C3H2O consisting of a cyclopropene carbon framework with a ketone functional group. It is a colorless, volatile liquid that boils near room temperature. Neat cyclopropenone polymerizes upon standing at room temperature. The chemical properties of the compound are dominated by the strong polarization of the carbonyl group, which gives a partial positive charge with aromatic stabilization on the ring and a partial negative charge on oxygen. It is an aromatic compound.

Bicalicene is polycyclic hydrocarbon with chemical formula C16H8, composed of two cyclopentadiene and two cyclopropene rings linked into a larger eight-membered ring. There are two isomers: cis-bicalicene and trans-bicalicene. It is a dimer of calicene.
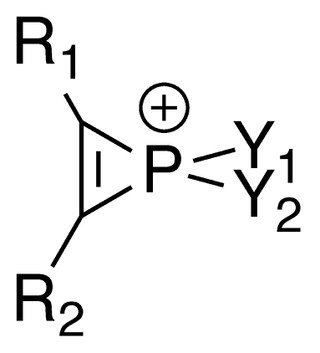
Phosphirenium ions are a series of organophosphorus compounds containing unsaturated three-membered ring phosphorus (V) heterocycles and σ*-aromaticity is believed to be present in such molecules. Many of the salts containing phosphirenium ions have been isolated and characterized by NMR spectroscopy and X-ray crystallography.

The triboracyclopropenyl fragment is a cyclic structural motif in boron chemistry, named for its geometric similarity to cyclopropene. In contrast to nonplanar borane clusters that exhibit higher coordination numbers at boron (e.g., through 3-center 2-electron bonds to bridging hydrides or cations), triboracyclopropenyl-type structures are rings of three boron atoms where substituents at each boron are also coplanar to the ring. Triboracyclopropenyl-containing compounds are extreme cases of inorganic aromaticity. They are the lightest and smallest cyclic structures known to display the bonding and magnetic properties that originate from fully delocalized electrons in orbitals of σ and π symmetry. Although three-membered rings of boron are frequently so highly strained as to be experimentally inaccessible, academic interest in their distinctive aromaticity and possible role as intermediates of borane pyrolysis motivated extensive computational studies by theoretical chemists. Beginning in the late 1980s with mass spectrometry work by Anderson et al. on all-boron clusters, experimental studies of triboracyclopropenyls were for decades exclusively limited to gas-phase investigations of the simplest rings (ions of B3). However, more recent work has stabilized the triboracyclopropenyl moiety via coordination to donor ligands or transition metals, dramatically expanding the scope of its chemistry.













