
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms. Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes physical and chemical properties, and evaluation of chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical study.

Stereochemistry, a subdiscipline of chemistry, involves the study of the relative spatial arrangement of atoms that form the structure of molecules and their manipulation. The study of stereochemistry focuses on the relationships between stereoisomers, which by definition have the same molecular formula and sequence of bonded atoms (constitution), but differ in the geometric positioning of the atoms in space. For this reason, it is also known as 3D chemistry—the prefix "stereo-" means "three-dimensionality".
Ferrocene is an organometallic compound with the formula Fe(C5H5)2. The molecule is a complex consisting of two cyclopentadienyl rings sandwiching a central iron atom. It is an orange solid with a camphor-like odor that sublimes above room temperature, and is soluble in most organic solvents. It is remarkable for its stability: it is unaffected by air, water, strong bases, and can be heated to 400 °C without decomposition. In oxidizing conditions it can reversibly react with strong acids to form the ferrocenium cation Fe(C5H5)+2. Ferrocene and the ferrocenium cation are sometimes abbreviated as Fc and Fc+ respectively.

In organic chemistry, an acetyl group is a functional group denoted by the chemical formula −COCH3 and the structure −C(=O)−CH3. It is sometimes represented by the symbol Ac. In IUPAC nomenclature, an acetyl group is called an ethanoylgroup.
William von Eggers Doering was the Mallinckrodt Professor of Chemistry at Harvard University. Before Harvard, he taught at Columbia (1942–1952) and Yale (1952–1968).

Annulenes are monocyclic hydrocarbons that contain the maximum number of non-cumulated or conjugated double bonds ('mancude'). They have the general formula CnHn (when n is an even number) or CnHn+1 (when n is an odd number). The IUPAC accepts the use of 'annulene nomenclature' in naming carbocyclic ring systems with 7 or more carbon atoms, using the name '[n]annulene' for the mancude hydrocarbon with n carbon atoms in its ring, though in certain contexts (e.g., discussions of aromaticity for different ring sizes), smaller rings (n = 3 to 6) can also be informally referred to as annulenes. Using this form of nomenclature 1,3,5,7-cyclooctatetraene is [8]annulene and benzene is [6]annulene (and occasionally referred to as just 'annulene').

Steric effects arise from the spatial arrangement of atoms. When atoms come close together there is generally a rise in the energy of the molecule. Steric effects are nonbonding interactions that influence the shape (conformation) and reactivity of ions and molecules. Steric effects complement electronic effects, which dictate the shape and reactivity of molecules. Steric repulsive forces between overlapping electron clouds result in structured groupings of molecules stabilized by the way that opposites attract and like charges repel.
Organic synthesis is a branch of chemical synthesis concerned with the construction of organic compounds. Organic compounds are molecules consisting of combinations of covalently-linked hydrogen, carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms. Within the general subject of organic synthesis, there are many different types of synthetic routes that can be completed including total synthesis, stereoselective synthesis, automated synthesis, and many more. Additionally, in understanding organic synthesis it is necessary to be familiar with the methodology, techniques, and applications of the subject.

In chemistry, a supramolecular assembly is a structure consisting of molecules held together by noncovalent bonds. While a supramolecular assembly can be simply composed of two molecules, or a defined number of stoichiometrically interacting molecules within a quaternary complex, it is more often used to denote larger complexes composed of indefinite numbers of molecules that form sphere-, rod-, or sheet-like species. Colloids, liquid crystals, biomolecular condensates, micelles, liposomes and biological membranes are examples of supramolecular assemblies, and their realm of study is known as supramolecular chemistry. The dimensions of supramolecular assemblies can range from nanometers to micrometers. Thus they allow access to nanoscale objects using a bottom-up approach in far fewer steps than a single molecule of similar dimensions.

Titanocene dichloride is the organotitanium compound with the formula (η5-C5H5)2TiCl2, commonly abbreviated as Cp2TiCl2. This metallocene is a common reagent in organometallic and organic synthesis. It exists as a bright red solid that slowly hydrolyzes in air. It shows antitumour activity and was the first non-platinum complex to undergo clinical trials as a chemotherapy drug.
Bullvalene is a hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C10H10. The molecule has a cage-like structure formed by the fusion of one cyclopropane and three cyclohepta-1,4-diene rings. Bullvalene is unusual as an organic molecule due to the C−C and C=C bonds forming and breaking rapidly on the NMR timescale; this property makes it a fluxional molecule.

Fulvalene (bicyclopentadienylidene) is the member of the fulvalene family with the molecular formula C10H8. It is of theoretical interest as one of the simplest non-benzenoid conjugated hydrocarbons. Fulvalene is an unstable isomer of the more common benzenoid aromatic compounds naphthalene and azulene. Fulvalene consists of two 5-membered rings, each with two double bonds, joined by yet a fifth double bond. It has D2h symmetry.

Tetrathiafulvalene (TTF) is an organosulfur compound with the formula 2. Studies on this heterocyclic compound contributed to the development of molecular electronics. TTF is related to the hydrocarbon fulvalene, (C5H4)2, by replacement of four CH groups with sulfur atoms. Over 10,000 scientific publications discuss TTF and its derivatives.

Organotitanium chemistry is the science of organotitanium compounds describing their physical properties, synthesis, and reactions. Organotitanium compounds in organometallic chemistry contain carbon-titanium chemical bonds. They are reagents in organic chemistry and are involved in major industrial processes.
Physical organic chemistry, a term coined by Louis Hammett in 1940, refers to a discipline of organic chemistry that focuses on the relationship between chemical structures and reactivity, in particular, applying experimental tools of physical chemistry to the study of organic molecules. Specific focal points of study include the rates of organic reactions, the relative chemical stabilities of the starting materials, reactive intermediates, transition states, and products of chemical reactions, and non-covalent aspects of solvation and molecular interactions that influence chemical reactivity. Such studies provide theoretical and practical frameworks to understand how changes in structure in solution or solid-state contexts impact reaction mechanism and rate for each organic reaction of interest.
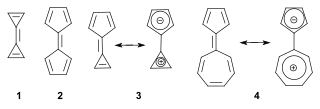
A fulvalene is a hydrocarbon obtained by formally cross-conjugating two rings through a common exocyclic double bond. The name is derived from the similarly structured fulvenes which lack one ring. Pentafulvalene (2) is also called simply fulvalene, the parent structure of this class. Triapentafulvalene (3) is also known as calicene from the words calix or chalice because of its wine-glass appearance.

Sesquifulvalene or pentaheptafulvalene is a hydrocarbon in the fulvalene class with chemical formula C12H10. It is composed of linked cyclopentadiene and cycloheptatriene rings.

Fulvenes are the class of hydrocarbon obtained by formally cross-conjugating one ring and methylidene through a common exocyclic double bond.

Biferrocene is the organometallic compound with the formula [(C5H5)Fe(C5H4)]2. It is the product of the formal dehydrocoupling of ferrocene, analogous the relationship between biphenyl and benzene. It is an orange, air-stable solid that is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents.

Bis(fulvalene)diiron is the organoiron complex with the formula (C5H4-C5H4)2Fe2. Structurally, the molecule consists of two ferrous centers sandwiched between fulvalene dianions. The compound is an orange solid with lower solubility in benzene than ferrocene. Its structure has been verified by X-ray crystallography. The compound has attracted some interest for its redox properties.















