
Candidiasis is a fungal infection due to any type of Candida. When it affects the mouth, in some countries it is commonly called thrush. Signs and symptoms include white patches on the tongue or other areas of the mouth and throat. Other symptoms may include soreness and problems swallowing. When it affects the vagina, it may be referred to as a yeast infection or thrush. Signs and symptoms include genital itching, burning, and sometimes a white "cottage cheese-like" discharge from the vagina. Yeast infections of the penis are less common and typically present with an itchy rash. Very rarely, yeast infections may become invasive, spreading to other parts of the body. This may result in fevers along with other symptoms depending on the parts involved.

Flax, also known as common flax or linseed, is a flowering plant, Linum usitatissimum, in the family Linaceae. It is cultivated as a food and fiber crop in regions of the world with temperate climate. Textiles made from flax are known in Western countries as linen, and are traditionally used for bed sheets, underclothes, and table linen. Its oil is known as linseed oil. In addition to referring to the plant itself, the word "flax" may refer to the unspun fibers of the flax plant. The plant species is known only as a cultivated plant, and appears to have been domesticated just once from the wild species Linum bienne, called pale flax. The plants called "flax" in New Zealand are, by contrast, members of the genus Phormium.

Athlete's foot, known medically as tinea pedis, is a common skin infection of the feet caused by fungus. Signs and symptoms often include itching, scaling, cracking and redness. In rare cases the skin may blister. Athlete's foot fungus may infect any part of the foot, but most often grows between the toes. The next most common area is the bottom of the foot. The same fungus may also affect the nails or the hands. It is a member of the group of diseases known as tinea.
Gordon Herriot Cunningham, CBE, FRS was the first New Zealand-based mycologist and plant pathologist. In 1936 he was appointed the first director of the DSIR Plant Diseases Division. Cunningham established the New Zealand Fungal Herbarium, and he published extensively on taxonomy of many fungal groups. He is regarded as the 'Father' of New Zealand mycology.
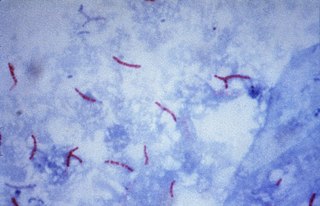
Ziehl-Neelsen staining is a type of acid-fast stain, first introduced by Paul Ehrlich. Ziehl–Neelsen staining is a bacteriological stain used to identify acid-fast organisms, mainly Mycobacteria. It is named for two German doctors who modified the stain: the bacteriologist Franz Ziehl (1859–1926) and the pathologist Friedrich Neelsen (1854–1898).

Manaaki Whenua – Landcare Research is a New Zealand Crown Research Institute whose focus of research is the environment, biodiversity, and sustainability.

Mycosis is a fungal infection of animals, including humans. Mycoses are common and a variety of environmental and physiological conditions can contribute to the development of fungal diseases. Inhalation of fungal spores or localized colonization of the skin may initiate persistent infections; therefore, mycoses often start in the lungs or on the skin.

A leaf spot is a limited, discoloured, diseased area of a leaf that is caused by fungal, bacterial or viral plant diseases, or by injuries from nematodes, insects, environmental factors, toxicity or herbicides. These discoloured spots or lesions often have a centre of necrosis or cell death. Symptoms can overlap across causal agents, however differing signs and symptoms of certain pathogens can lead to the diagnosis of the type of leaf spot disease. Prolonged wet and humid conditions promote leaf spot disease and most pathogens are spread by wind, splashing rain or irrigation that carry the disease to other leaves.

Dermatophytosis, also known as ringworm, is a fungal infection of the skin. Typically it results in a red, itchy, scaly, circular rash. Hair loss may occur in the area affected. Symptoms begin four to fourteen days after exposure. Multiple areas can be affected at a given time.

Onychomycosis, also known as tinea unguium, is a fungal infection of the nail. Symptoms may include white or yellow nail discoloration, thickening of the nail, and separation of the nail from the nail bed. Toenails or fingernails may be affected, but it is more common for toenails to be affected. Complications may include cellulitis of the lower leg. A number of different types of fungus can cause onychomycosis, including dermatophytes and Fusarium. Risk factors include athlete's foot, other nail diseases, exposure to someone with the condition, peripheral vascular disease, and poor immune function. The diagnosis is generally suspected based on the appearance and confirmed by laboratory testing.

Fungal pneumonia is an infection of the lungs by fungi. It can be caused by either endemic or opportunistic fungi or a combination of both. Case mortality in fungal pneumonias can be as high as 90% in immunocompromised patients, though immunocompetent patients generally respond well to anti-fungal therapy.

Oidium is a genus of Deuteromycetes, where traditionally most anamorphs of the order Erysiphales are included. Most of them are plant pathogens causing different forms of powdery mildew, for example:
A fungal keratitis is an inflammation of the cornea that results from infection by a fungal organism. Keratomycosis is the fungal infection of the cornea, the anterior part of the eye which covers the pupil. Those experiencing these symptoms are typically advised to immediately visit the appropriate eyecare professional.
Microdochium bolleyi is a fungal plant pathogen that causes root rot in flax and wheat.

Pyrenophora tritici-repentis (telomorph) and Drechslera tritici-repentis (anamorph) is a necrotrophic plant pathogen of fungal origin, phylum Ascomycota. The pathogen causes a disease originally named yellow spot but now commonly called tan spot, yellow leaf spot, yellow leaf blotch or helminthosporiosis. At least eight races of the pathogen are known to occur based on their virulence on a wheat differential set.
Phoma exigua var. linicola is a fungal plant pathogen that affects flax.
Phoma tracheiphila is a fungal plant pathogen. It causes a disease known as Mal secco on citrus trees. It occurs in dry, cool climates such as the Mediterranean, Black Sea and Asia Minor. It forms pycniospores that are carried short distances by rain, or by wind to new leaves, where germinated hyphae invade stomata or more likely fresh wounds.
Pathogenic fungi are fungi that cause disease in humans or other organisms. Approximately 300 fungi are known to be pathogenic to humans. The study of fungi pathogenic to humans is called "medical mycology". Although fungi are eukaryotic, many pathogenic fungi are microorganisms. The study of fungi and other organisms pathogenic to plants is called plant pathology.
In biology, a pathogen in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ.










