
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosome abnormality. Although polygenic disorders are the most common, the term is mostly used when discussing disorders with a single genetic cause, either in a gene or chromosome. The mutation responsible can occur spontaneously before embryonic development, or it can be inherited from two parents who are carriers of a faulty gene or from a parent with the disorder. When the genetic disorder is inherited from one or both parents, it is also classified as a hereditary disease. Some disorders are caused by a mutation on the X chromosome and have X-linked inheritance. Very few disorders are inherited on the Y chromosome or mitochondrial DNA.
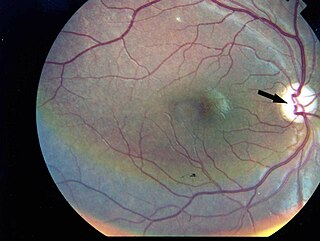
Wolfram syndrome, also called DIDMOAD, is a rare autosomal-recessive genetic disorder that causes childhood-onset diabetes mellitus, optic atrophy, and deafness as well as various other possible disorders including neurodegeneration. Symptoms can start to appear as early as childhood to adult years. There is a 25% recurrence risk in children.

Behr syndrome is characterized by the association of early-onset optic atrophy with spinocerebellar degeneration resulting in ataxia, pyramidal signs, peripheral neuropathy and developmental delay.

Cohen syndrome is a very rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder with varied expression, characterised by obesity, intellectual disability, distinct craniofacial abnormalities and potential ocular dysfunction.

Costeff syndrome, or 3-methylglutaconic aciduria type III, is a genetic disorder caused by mutations in the OPA3 gene. It is typically associated with the onset of visual deterioration in early childhood followed by the development of movement problems and motor disability in later childhood, occasionally along with mild cases of cognitive deficiency. The disorder is named after Hanan Costeff, the doctor who first described the syndrome in 1989.
Vici syndrome, also called immunodeficiency with cleft lip/palate, cataract, hypopigmentation and absent corpus callosum, is a rare autosomal recessive congenital disorder characterized by albinism, agenesis of the corpus callosum, cataracts, cardiomyopathy, severe psychomotor retardation, seizures, immunodeficiency and recurrent severe infections. To date, about 50 cases have been reported.
Progressive Myoclonic Epilepsies (PME) are a rare group of inherited neurodegenerative diseases characterized by myoclonus, resistance to treatment, and neurological deterioration. The cause of PME depends largely on the type of PME. Most PMEs are caused by autosomal dominant or recessive and mitochondrial mutations. The location of the mutation also affects the inheritance and treatment of PME. Diagnosing PME is difficult due to their genetic heterogeneity and the lack of a genetic mutation identified in some patients. The prognosis depends largely on the worsening symptoms and failure to respond to treatment. There is no current cure for PME and treatment focuses on managing myoclonus and seizures through antiepileptic medication (AED).

Woodhouse–Sakati syndrome, is a rare autosomal recessive multisystem disorder which causes malformations throughout the body, and deficiencies affecting the endocrine system.

Antley–Bixler syndrome is a rare, severe autosomal recessive congenital disorder characterized by malformations and deformities affecting the majority of the skeleton and other areas of the body.
3-M syndrome or 3M3 is a rare hereditary disorder characterized by severe growth retardation, facial dysmorphia, and skeletal abnormalities. The name 3-M is derived from the initials of the three researchers who first identified it: Miller, McKusick, and Malvaux and report their findings in the medical literature in 1972. Mutations in any one of the following three genes: CUL7, OBSL1, and CCDC8 are responsible for the occurrence of this disorder. It is inherited through an autosomal recessive pattern and considered very rare, so far less than 100 cases worldwide have been identified. Diagnosis is based on the presence of clinical features. Genetic testing can confirm the diagnosis and identify the specific gene involved. Treatment is aimed at addressing the growth and skeletal problems and may include surgical bone lengthening, adaptive aids, and physical therapy. An endocrinologist may assist with growth hormone replacement and appropriate evaluations during puberty.

Gillespie syndrome, also called aniridia, cerebellar ataxia and mental deficiency, is a rare genetic disorder. The disorder is characterized by partial aniridia, ataxia, and, in most cases, intellectual disability. It is heterogeneous, inherited in either an autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive manner. Gillespie syndrome was first described by American ophthalmologist Fredrick Gillespie in 1965.

Lethal congenital contracture syndrome 1 (LCCS1), also called Multiple contracture syndrome, Finnish type, is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder characterized by total immobility of a fetus, detectable at around the 13th week of pregnancy. LCCS1 invariably leads to prenatal death before the 32nd gestational week. LCCS1 is one of 40 Finnish heritage diseases. It was first described in 1985 and since then, approximately 70 cases have been diagnosed.

Acrofrontofacionasal dysostosis is an extremely rare disorder, characterized by intellectual disability, short stature, hypertelorism, broad notched nasal tip, cleft lip/palate, postaxial camptobrachypolysyndactyly, fibular hypoplasia, and anomalies of foot structure.

De Barsy syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder. Symptoms include cutis laxa as well as other eye, musculoskeletal, and neurological abnormalities. It is usually progressive, manifesting side effects that can include clouded corneas, cataracts, short stature, dystonia, or progeria.

Kohlschütter–Tönz syndrome (KTS), also called amelo-cerebro-hypohidrotic syndrome, is a rare inherited syndrome characterized by epilepsy, psychomotor delay or regression, intellectual disability, and yellow teeth caused by amelogenesis imperfecta. It is a type A ectodermal dysplasia.

Cerebral autosomal recessive arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CARASIL) is disease of the arteries in the brain, which causes tissue loss in the subcortical region of the brain and the destruction of myelin in the CNS. CARASIL is characterized by symptoms such as gait disturbances, hair loss, low back pain, dementia, and stroke. CARASIL is a rare disease, having only been diagnosed in about 50 patients, of which ten have been genetically confirmed. Most cases have been reported in Japan, but Chinese and caucasian individuals have also been diagnosed with the disease. CARASIL is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern. There is currently no cure for CARASIL. Other names for CARASIL include familial young-adult-onset arteriosclerotic leukoencephalopathy with alopecia and lumbago without arterial hypertension, Nemoto disease and Maeda syndrome.
Kenny-Caffey syndrome type 2 (KCS2) is an extremely rare autosomal dominant genetic condition characterized by dwarfism, hypermetropia, microphthalmia, and skeletal abnormalities. This subtype of Kenny-Caffey syndrome is caused by a heterozygous mutation in the FAM111A gene (615292) on chromosome 11q12.
Nestor-Guillermo progeria syndrome is an extremely rare novel genetic disorder that is part of a group of syndromes called progeria. This disorder is characterized by the same symptoms of other progeria syndromes, which are premature aging with accompanying aged physical appearance, osteolysis, osteoporosis, scoliosis and lipoatrophy, however, what makes this disorder unique from other progeroid syndromes is the absence of any atherosclerotic, cardiovascular, and metabolic symptoms/complications, this makes the life-span of a person with NGPS somewhat longer than the average life-span of someone with progeria itself, although in place of the complications mentioned above, there's also additional symptoms, such as joint stiffness, growth retardation, facial dysmorphisms, wide cranial sutures, micrognathia, atrophic skin and a high risk of developing severe skeletal abnormalities

Wolfram-like syndrome is a rare autosomal dominant genetic disorder that shares some of the features shown by those affected with the autosomal recessive Wolfram syndrome. It is a type of WFS1-related disorder.

Salt and pepper developmental regression syndrome, also known as Amish infantile epileptic syndrome or GM3 deficiency syndrome, is a rare autosomal recessive progressive neurological disorder characterized by developmental delay, severe intellectual disability, seizures, and skin pigmentation irregularities. The clinical symptoms of this condition start manifesting soon after birth, during the newborn/neo-natal stage of life.






