Jamie Werner Zawinski, commonly known as jwz, is an American computer programmer, blogger and impresario. He is best known for his role in the creation of Netscape Navigator, Netscape Mail, Lucid Emacs, Mozilla.org, and XScreenSaver. He is also the proprietor of DNA Lounge, a nightclub and live music venue in San Francisco.
In computing, a desktop environment (DE) is an implementation of the desktop metaphor made of a bundle of programs running on top of a computer operating system that share a common graphical user interface (GUI), sometimes described as a graphical shell. The desktop environment was seen mostly on personal computers until the rise of mobile computing. Desktop GUIs help the user to easily access and edit files, while they usually do not provide access to all of the features found in the underlying operating system. Instead, the traditional command-line interface (CLI) is still used when full control over the operating system is required.

Xfce or XFCE is a free and open-source desktop environment for Linux and other Unix-like operating systems.

GNOME Files, formerly and internally known as Nautilus, is the official file manager for the GNOME desktop. Nautilus was originally developed by Eazel with many luminaries from the tech world including Andy Hertzfeld (Apple), chief architect for Nautilus. The nautilus name was a play on words, evoking the shell of a nautilus to represent an operating system shell. Nautilus replaced Midnight Commander in GNOME 1.4 (2001) and has been the default file manager from version 2.0 onwards.

A screensaver is a computer program that blanks the display screen or fills it with moving images or patterns when the computer has been idle for a designated time. The original purpose of screensavers was to prevent phosphor burn-in on CRT or plasma computer monitors. Though most modern monitors are not susceptible to this issue, screensaver programs are still used for other purposes. Screensavers are often set up to offer a basic layer of security by requiring a password to re-access the device. Some screensaver programs also use otherwise-idle computer resources to do useful work, such as processing for volunteer computing projects.

GNOME Web, called Epiphany until 2012 and still known by that code name, is a free and open-source web browser based on the GTK port of Apple's WebKit rendering engine, called WebKitGTK. It is developed by the GNOME project for Unix-like systems. It is the default and official web browser of GNOME, and part of the GNOME Core Applications.

XScreenSaver is a free and open-source collection of 240+ screensavers for Unix, macOS, iOS and Android operating systems. It was created by Jamie Zawinski in 1992 and is still maintained by him, with new releases coming out several times a year.
Print Screen is a key present on most PC keyboards. It is typically situated in the same section as the break key and scroll lock key. The print screen may share the same key as system request.

Assistive Technology Service Provider Interface (AT-SPI) is a platform-neutral framework for providing bi-directional communication between assistive technologies (AT) and applications. It is the de facto standard for providing accessibility to free and open desktops, like Linux or OpenBSD, led by the GNOME Project.

openSUSE is a free and open source Linux distribution developed by the openSUSE project. It is offered in two main variations: Tumbleweed, an upstream rolling release distribution, and Leap, a stable release distribution which is sourced from SUSE Linux Enterprise.

NetworkManager is a daemon that sits on top of libudev and other Linux kernel interfaces and provides a high-level interface for the configuration of the network interfaces.

GNOME Panel is a highly configurable taskbar for GNOME. It formed a core part of the desktop in GNOME 1 and GNOME 2. It has been replaced in GNOME 3 by default with GNOME Shell, which only works with the Mutter window manager.

Empathy was an instant messaging (IM) and voice over IP (VoIP) client which supported text, voice, video, file transfers, and inter-application communication over various IM communication protocols.

GNOME, originally an acronym for GNU Network Object Model Environment, is a free and open-source desktop environment for Linux and other Unix-like operating systems.

GNOME Shell is the graphical shell of the GNOME desktop environment starting with version 3, which was released on April 6, 2011. It provides basic functions like launching applications, switching between windows and is also a widget engine. GNOME Shell replaced GNOME Panel and some ancillary components of GNOME 2.
Mutter is a window manager initially designed and implemented for the X Window System, but then evolved to be a Wayland compositor. It became the default window manager in GNOME 3, replacing Metacity which used GTK for rendering.
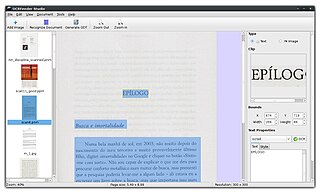
OCRFeeder is an optical character recognition suite for GNOME, which also supports virtually any command-line OCR engine, such as CuneiForm, GOCR, Ocrad and Tesseract. It converts paper documents to digital document files and can serve to make them accessible to visually impaired users.

Cinnamon is a free and open-source desktop environment for Linux and other Unix-like operating systems, which was originally based from GNOME 3 but follows traditional desktop metaphor conventions.
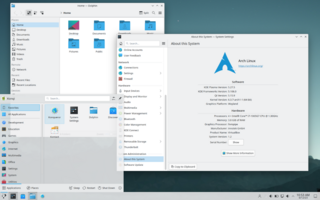
KDE Plasma 5 is the fifth generation of the graphical workspaces environment created by KDE primarily for Linux systems. KDE Plasma 5 is the successor of KDE Plasma 4 and was first released on 15 July 2014. The successor is KDE Plasma 6, with planned release date 28 February 2024.













