This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page . (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
| Gobby | |
|---|---|
 | |
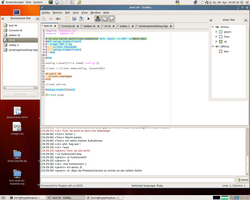 Gobby 0.4.0 | |
| Original author | Armin Burgmeier |
| Developer | 0x539 dev group |
| Stable release | 0.6.0 / January 21, 2021 |
| Repository | |
| Written in | C++, C. [1] |
| Operating system | Unix, Windows |
| Type | Text editor |
| License | GNU GPLv2+ [2] |
| Website | gobby |
Gobby is a free software collaborative real-time editor available on Windows and Unix-like platforms. [3] (It runs on Mac OS X using Apple's X11.app.) It was initially released in June 2005 by the 0x539 dev group [4] (the hexadecimal value 0x539 is equal to 1337 in decimal). Gobby uses GTK+ for its GUI widgets.