
Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), also known as estrogen receptor agonists/antagonists (ERAAs), are a class of drugs that act on estrogen receptors (ERs). Compared to pure ER agonists–antagonists, SERMs are more tissue-specific, allowing them to selectively inhibit or stimulate estrogen-like action in various tissues.
Exelixis, Inc. is a genomics-based drug discovery company located in Alameda, California, and the producer of Cometriq, a treatment approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for medullary thyroid cancer with clinical activity in several other types of metastatic cancer.

Toremifene, sold under the brand name Fareston among others, is a medication which is used in the treatment of advanced breast cancer in postmenopausal women. It is taken by mouth.
A nonsteroidal compound is a drug that is not a steroid nor a steroid derivative. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are distinguished from corticosteroids as a class of anti-inflammatory agents.

Selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) are a class of drugs that selectively activate the androgen receptor in specific tissues, promoting muscle and bone growth while having less effect on male reproductive tissues like the prostate gland.

Afimoxifene, also known as 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4-OHT) and by its tentative brand name TamoGel, is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) of the triphenylethylene group and an active metabolite of tamoxifen. The drug is under development under the tentative brand name TamoGel as a topical gel for the treatment of hyperplasia of the breast. It has completed a phase II clinical trial for cyclical mastalgia, but further studies are required before afimoxifene can be approved for this indication and marketed.

Enobosarm, also formerly known as ostarine and by the developmental code names GTx-024, MK-2866, and S-22, is a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) which is under development for the treatment of androgen receptor-positive breast cancer in women and for improvement of body composition in people taking GLP-1 receptor agonists like semaglutide. It was also under development for a variety of other indications, including treatment of cachexia, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, muscle atrophy or sarcopenia, and stress urinary incontinence, but development for all other uses has been discontinued. Enobosarm was evaluated for the treatment of muscle wasting related to cancer in late-stage clinical trials, and the drug improved lean body mass in these trials, but it was not effective in improving muscle strength. As a result, enobosarm was not approved and development for this use was terminated. Enobosarm is taken by mouth.
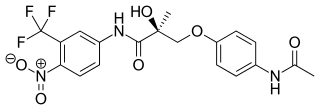
Andarine is a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) which was developed by GTX, Inc for the treatment of conditions such as muscle wasting, osteoporosis, and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), using the nonsteroidal antiandrogen bicalutamide as a lead compound. Development of andarine for all indications has been discontinued, in favor of the structurally related and improved compound enobosarm.

LGD-4033, also known by the developmental code name VK5211 and by the black-market name Ligandrol, is a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) which is under development for the treatment of muscle atrophy in people with hip fracture. It was also under development for the treatment of cachexia, hypogonadism, and osteoporosis, but development for these indications was discontinued. LGD-4033 has been reported to dose-dependently improve lean body mass and muscle strength in preliminary clinical trials, but is still being developed and has not been approved for medical use. The drug is taken by mouth.

Vosilasarm, also known by the development codes RAD140 and EP0062 and by the black-market name Testolone or Testalone, is a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) which is under development for the treatment of hormone-sensitive breast cancer. It is specifically under development for the treatment of androgen receptor-positive, estrogen receptor-negative, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer. Vosilasarm was also previously under development for the treatment of sarcopenia, osteoporosis, and weight loss due to cancer cachexia, but development for these indications was discontinued. The drug is taken by mouth.

Acetothiolutamide is a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) derived from the nonsteroidal antiandrogen bicalutamide that was described in 2002 and was one of the first SARMs to be discovered and developed. It is a high-affinity, selective ligand of the androgen receptor (AR), where it acts as a full agonist in vitro, and has in vitro potency comparable to that of testosterone. However, in vivo, acetothiolutamide displayed overall negligible androgenic effects, though significant anabolic effects were observed at high doses. In addition, notable antiandrogen effects were observed in castrated male rats treated with testosterone propionate. The discrepancy between the in vitro and in vivo actions of acetothiolutamide was determined to be related to rapid plasma clearance and extensive hepatic metabolism into a variety of metabolites with differing pharmacological activity, including AR partial agonism and antagonism. In accordance with its poor metabolic stability, acetothiolutamide is not orally bioavailable, and shows activity only via injected routes such as subcutaneous and intravenous.

GTx-758 is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen which was under development by GTx, Inc. for the treatment of advanced prostate cancer. As of 2016, it had completed two phase II clinical trials.
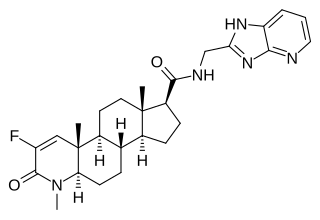
MK-0773, also known as PF-05314882, is a steroidal, orally active selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) that was under development by Merck and GTx for the treatment of sarcopenia in women and men. Clinical trials for sarcopenia began in late 2007 but the collaboration between Merck and GTx ended in early 2010 and GTx terminated development of MK-0773 shortly thereafter. MK-0773 was developed as a more advanced version of the related compound TFM-4AS-1.
A sex-hormonal agent, also known as a sex-hormone receptor modulator, is a type of hormonal agent which specifically modulates the effects of sex hormones and of their biological targets, the sex hormone receptors. The sex hormones include androgens such as testosterone, estrogens such as estradiol, and progestogens such as progesterone. Sex-hormonal agents may be either steroidal or nonsteroidal in chemical structure and may serve to either enhance, inhibit, or have mixed effects on the function of the sex hormone systems.

β-LGND2, also known as ERβ-selective ligand 2 or as GTx-878, is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen and selective ERβ agonist which was under development by GTx for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia, prostatitis, and rheumatoid arthritis but was never marketed. It shows approximately 25-fold selectivity for activation of the ERβ over the ERα (EC50Tooltip half-maximal effective concentration = 2 nM and 52 nM, respectively). β-LGND2 is an isoquinolinone derivative.
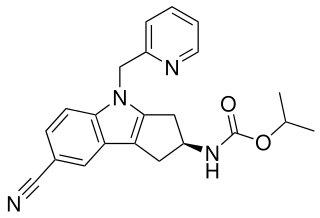
OPK-88004 is a non-steroidal indole derivative which acts as a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM). It has been investigated by OPKO Health for the treatment of erectile dysfunction and symptoms associated with benign prostate hyperplasia.

Pimicotinib (ABSK021), an oral, highly potent and selective small molecule blocker of the colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF-1R) independently discovered by Abbisko Therapeutics. A number of studies have shown that blocking the CSF-1R signaling pathway could effectively modulate and change macrophage functions, and potentially treat many macrophage-dependent human diseases.

JNJ-37654032 is a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) which was developed by Johnson & Johnson for the potential treatment of muscular atrophy but was never marketed.

GTx-027 is a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) which was under development for or of potential interest in the treatment of breast cancer and stress urinary incontinence (SUI) but was never marketed. It is taken by mouth.














