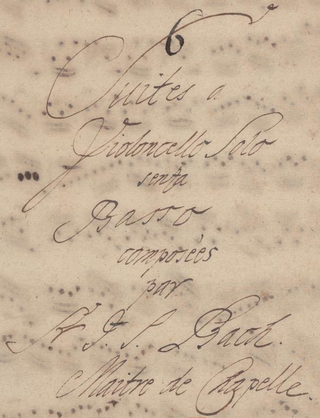Baroque dance is dance of the Baroque era, closely linked with Baroque music, theatre, and opera.
A scherzo, in western classical music, is a short composition – sometimes a movement from a larger work such as a symphony or a sonata. The precise definition has varied over the years, but scherzo often refers to a movement that replaces the minuet as the third movement in a four-movement work, such as a symphony, sonata, or string quartet. The term can also refer to a fast-moving humorous composition that may or may not be part of a larger work.
Ternary form, sometimes called song form, is a three-part musical form consisting of an opening section (A), a following section (B) and then a repetition of the first section (A). It is usually schematized as A–B–A. Prominent examples include the da capo aria "The trumpet shall sound" from Handel's Messiah, Chopin's Prelude in D-Flat Major "Raindrop", and the opening chorus of Bach's St John Passion.

A suite, in Western classical music, is an ordered set of instrumental or orchestral/concert band pieces. It originated in the late 14th century as a pairing of dance tunes and grew in scope to comprise up to five dances, sometimes with a prelude, by the early 17th century. The separate movements were often thematically and tonally linked. The term can also be used to refer to similar forms in other musical traditions, such as the Turkish fasıl and the Arab nuubaat.
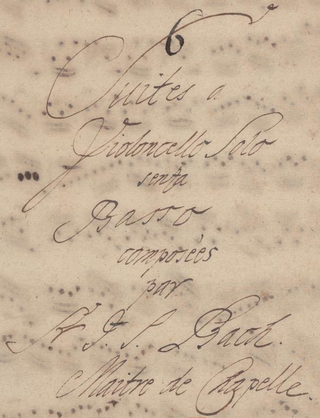
The six Cello Suites, BWV 1007–1012, are suites for unaccompanied cello by Johann Sebastian Bach (1685–1750). They are some of the most frequently performed solo compositions ever written for cello. Bach most likely composed them during the period 1717–1723, when he served as Kapellmeister in Köthen. The title given on the cover of the Anna Magdalena Bach manuscript was Suites à Violoncello Solo senza Basso.

The gavotte is a French dance, taking its name from a folk dance of the Gavot, the people of the Pays de Gap region of Dauphiné in the southeast of France, where the dance originated, according to one source. According to another reference, the word gavotte is a generic term for a variety of French folk dances, and most likely originated in Lower Brittany in the west, or possibly Provence in the southeast or the French Basque Country in the southwest of France. It is notated in 4
4 or 2
2 time and is usually of moderate tempo, though the folk dances also use meters such as 9
8 and 5
8.

The sarabande is a dance in triple metre, or the music written for such a dance.

The sonatas and partitas for solo violin are a set of six works composed by Johann Sebastian Bach. They are sometimes referred to in English as the sonatas and partias for solo violin in accordance with Bach's headings in the autograph manuscript: "Partia" was commonly used in German-speaking regions during Bach's time, whereas the Italian "partita" was introduced to this set in the 1879 Bach Gesellschaft edition, having become standard by that time. The set consists of three sonatas da chiesa in four movements and three partitas in dance-form movements. The 2nd Partita is widely known for its Chaconne, considered one of the most masterly and expressive works ever written for solo violin.

The Partitas, BWV 825–830, are a set of six keyboard suites written by Johann Sebastian Bach, published individually beginning in 1726, then together as Clavier-Übung I in 1731, the first of his works to be published under his own direction. They were, however, among the last of his keyboard suites to be composed, the others being the six English Suites, BWV 806-811 and the six French Suites, BWV 812-817, as well as the Overture in the French style, BWV 831.

The English Suites, BWV 806–811, are a set of six suites written by the German composer Johann Sebastian Bach for harpsichord and generally thought to be the earliest of his 19 suites for keyboard, the others being the six French Suites, the six Partitas and the Overture in the French style. They probably date from around 1713 or 1714.

The French Suites, BWV 812–817, are six suites which Johann Sebastian Bach wrote for the clavier between the years of 1722 and 1725. Although Suites Nos. 1 to 4 are typically dated to 1722, it is possible that the first was written somewhat earlier.
Robert de Visée was a French lutenist, guitarist, theorbist and viol player at the court of the kings Louis XIV and Louis XV, as well as a singer and composer for lute, theorbo and guitar.

The four orchestral suites BWV 1066–1069 are four suites by Johann Sebastian Bach from the years 1724–1731. The name ouverture refers only in part to the opening movement in the style of the French overture, in which a majestic opening section in relatively slow dotted-note rhythm in duple meter is followed by a fast fugal section, then rounded off with a short recapitulation of the opening music. More broadly, the term was used in Baroque Germany for a suite of dance-pieces in French Baroque style preceded by such an ouverture. This genre was extremely popular in Germany during Bach's day, and he showed far less interest in it than was usual: Robin Stowell writes that "Telemann's 135 surviving examples [represent] only a fraction of those he is known to have written"; Christoph Graupner left 85; and Johann Friedrich Fasch left almost 100. Bach did write several other ouverture (suites) for solo instruments, notably the Cello Suite no. 5, BWV 1011, which also exists in the autograph Lute Suite in G minor, BWV 995, the Keyboard Partita no. 4 in D, BWV 828, and the Overture in the French style, BWV 831 for keyboard. The two keyboard works are among the few Bach published, and he prepared the lute suite for a "Monsieur Schouster," presumably for a fee, so all three may attest to the form's popularity.
The Overture in the French style, BWV 831, original title Ouvertüre nach Französischer Art, also known as the French Overture and published as the second half of the Clavier-Übung II in 1735, is a suite in B minor for a two-manual harpsichord written by Johann Sebastian Bach.

The Minuets in G major and G minor, BWV Anh. 114 and 115, are a pair of movements from a suite for harpsichord by Christian Petzold, which, through their appearance in the 1725 Notebook for Anna Magdalena Bach, used to be attributed to Johann Sebastian Bach. These minuets, which are suitable for beginners on the piano, are among the best known pieces of music literature. The 1965 pop song "A Lover's Concerto", of which millions of copies were sold, is based on the first of these Minuets.

The Partita No. 3 in E major for solo violin, BWV 1006.1, is the last work in Johann Sebastian Bach's set of Sonatas and Partitas. It consists of the following movements:
- Preludio
- Loure
- Gavotte en Rondeau
- Menuets
- Bourrée
- Gigue
Sophocles Papas was a Greek classical guitar pedagogue and music publisher.

Baroque music refers to the period or dominant style of Western classical music composed from about 1600 to 1750. The Baroque style followed the Renaissance period, and was followed in turn by the Classical period after a short transition. The Baroque period is divided into three major phases: early, middle, and late. Overlapping in time, they are conventionally dated from 1580 to 1650, from 1630 to 1700, and from 1680 to 1750. Baroque music forms a major portion of the "classical music" canon, and is widely studied, performed, and listened to. The term "baroque" comes from the Portuguese word barroco, meaning "misshapen pearl". The works of George Frideric Handel and Johann Sebastian Bach are considered the pinnacle of the Baroque period. Other key composers of the Baroque era include Claudio Monteverdi, Domenico Scarlatti, Alessandro Scarlatti, Alessandro Stradella, Tomaso Albinoni, Johann Pachelbel, Henry Purcell, Antonio Vivaldi, Georg Philipp Telemann, Jean-Baptiste Lully, Jean-Philippe Rameau, Marc-Antoine Charpentier, Arcangelo Corelli, François Couperin, Johann Hermann Schein, Heinrich Schütz, Samuel Scheidt, Dieterich Buxtehude, Gaspar Sanz, José de Nebra, Antonio Soler, Carlos Seixas and others.
Suite in E minor, BWV 996, is a musical composition written by Johann Sebastian Bach (1685–1750) between 1708 and 1717. It is probable that this suite was intended for Lautenwerck (lute-harpsichord). Because the lautenwerk is an uncommon instrument, it is in modern times often performed on the guitar or the lute.

The bourrée is a dance of French origin and the words and music that accompany it. The bourrée resembles the gavotte in that it is in double time and often has a dactylic rhythm. However, it is somewhat quicker, and its phrase starts with a quarter-bar anacrusis or "pick-up", whereas a gavotte has a half-bar anacrusis.