
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is a research and development agency of the United States Department of Defense responsible for the development of emerging technologies for use by the military.

FlightGear Flight Simulator is a free, open source multi-platform flight simulator developed by the FlightGear project since 1997.

RoboCup is an annual international robotics competition founded in 1996 by a group of university professors. The aim of the competition is to promote robotics and AI research by offering a publicly appealing – but formidable – challenge.
The DARPA Grand Challenge is a prize competition for American autonomous vehicles, funded by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency, the most prominent research organization of the United States Department of Defense. Congress has authorized DARPA to award cash prizes to further DARPA's mission to sponsor revolutionary, high-payoff research that bridges the gap between fundamental discoveries and military use. The initial DARPA Grand Challenge in 2004 was created to spur the development of technologies needed to create the first fully autonomous ground vehicles capable of completing a substantial off-road course within a limited time. The third event, the DARPA Urban Challenge in 2007, extended the initial Challenge to autonomous operation in a mock urban environment. The 2012 DARPA Robotics Challenge, focused on autonomous emergency-maintenance robots, and new Challenges are still being conceived. The DARPA Subterranean Challenge was tasked with building robotic teams to autonomously map, navigate, and search subterranean environments. Such teams could be useful in exploring hazardous areas and in search and rescue.

James Sacra Albus was an American engineer, Senior NIST Fellow and founder and former chief of the Intelligent Systems Division of the Manufacturing Engineering Laboratory at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).

Microsoft Robotics Developer Studio is a discontinued Windows-based environment for robot control and simulation that was aimed at academic, hobbyist, and commercial developers and handled a wide variety of robot hardware. It requires a Microsoft Windows 7 operating system or later.

The Player Project creates free and open-source software for research into robotics and sensor systems. Its components include the Player network server and the Stage platform robotics simulators. Although accurate statistics are hard to obtain, Player is one of the most popular open-source robot interfaces in research and post-secondary education.

A robotics simulator is a simulator used to create an application for a physical robot without depending on the physical machine, thus saving cost and time. In some case, such applications can be transferred onto a physical robot without modification.
There are a number of competitions and prizes to promote research in artificial intelligence.

Robot Operating System is an open-source robotics middleware suite. Although ROS is not an operating system (OS) but a set of software frameworks for robot software development, it provides services designed for a heterogeneous computer cluster such as hardware abstraction, low-level device control, implementation of commonly used functionality, message-passing between processes, and package management. Running sets of ROS-based processes are represented in a graph architecture where processing takes place in nodes that may receive, post, and multiplex sensor data, control, state, planning, actuator, and other messages. Despite the importance of reactivity and low latency in robot control, ROS is not a real-time operating system (RTOS). However, it is possible to integrate ROS with real-time computing code. The lack of support for real-time systems has been addressed in the creation of ROS 2, a major revision of the ROS API which will take advantage of modern libraries and technologies for core ROS functions and add support for real-time code and embedded system hardware.

The Florida Institute for Human & Machine Cognition (IHMC) is a not-for-profit research institute of the State University System of Florida, with locations in Pensacola and Ocala, Florida. IHMC scientists and engineers investigate a broad range of topics related to building systems aimed at amplifying and extending human cognitive, physical and perceptual capacities.
Vortex Studio is a simulation software platform developed by CM Labs Simulations. It features a real-time physics engine that simulates rigid body dynamics, collision detection, contact determination, and dynamic reactions. It also contains model import and preparation tools, an image generator, and networking tools for distributed simulation which is accessed through a desktop editor via a GUI. Vortex adds accurate physical motion and interactions to objects in visual-simulation applications for operator training, mission planning, product concept validation, heavy machinery and robotics design and testing, haptics devices, immersive and virtual reality (VR) environments.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to robotics:

The RoboCup 2D Simulated Soccer League is the oldest of the RoboCup Soccer Simulation Leagues. It consists of a number of competitions with computer simulated soccer matches as the main event.
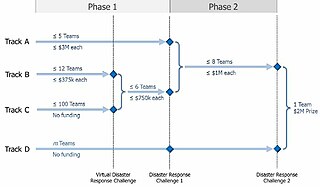
The DARPA Robotics Challenge (DRC) was a prize competition funded by the US Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency. Held from 2012 to 2015, it aimed to develop semi-autonomous ground robots that could do "complex tasks in dangerous, degraded, human-engineered environments." The DRC followed the DARPA Grand Challenge and DARPA Urban Challenge. It began in October 2012 and was to run for about 33 months with three competitions: a Virtual Robotics Challenge (VRC) that took place in June 2013; and two live hardware challenges, the DRC Trials in December 2013 and the DRC Finals in June 2015.
RoboDK is an offline programming and simulation software for industrial robots. The simulation software allows you to program robots outside the production environment, eliminating production downtime caused by shop floor programming.

Diffeo, Inc., is a software company that developed a collaborative intelligence text mining product for defense, intelligence and financial services customers.
Open Robotics is a nonprofit corporation headquartered in Mountain View, California. It is the primary maintainer of the Robot Operating System, and the Gazebo simulator. Its stated mission is to support "the development, distribution and adoption of open source software for use in robotics research, education, and product development".
Over the years, the U.S. Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) has conducted a number of prize competitions to spur innovations. A prize competition allows DARPA to establish an ambitious goal, which makes way for novel approaches from the public that might otherwise appear too risky to undertake by experts in a particular discipline.












