
All Quiet on the Western Front is a semi-autobiographical novel by Erich Maria Remarque, a German veteran of World War I. The book describes the German soldiers' extreme physical and mental trauma during the war as well as the detachment from civilian life felt by many upon returning home from the war. It is billed by some as "the greatest war novel of all time".

A bayonet is a knife, dagger, sword, or spike-shaped melee weapon designed to be mounted on the end of the barrel of a rifle, carbine, musket or similar long firearm, allowing the gun to be used as an improvised spear in close combats.

Erich Maria Remarque was a German-born novelist. His landmark novel All Quiet on the Western Front (1928), based on his experience in the Imperial German Army during World War I, was an international bestseller which created a new literary genre of veterans writing about conflict. The book was adapted to film several times. Remarque's anti-war themes led to his condemnation by Nazi propaganda minister Joseph Goebbels as "unpatriotic". He was able to use his literary success and fame to relocate to Switzerland as a refugee, and to the United States, where he became a naturalized citizen.

Trench warfare is a type of land warfare using occupied lines largely comprising military trenches, in which combatants are well-protected from the enemy's small arms fire and are substantially sheltered from artillery. It became archetypically associated with World War I (1914–1918), when the Race to the Sea rapidly expanded trench use on the Western Front starting in September 1914.

The Gallipoli campaign, the Dardanelles campaign, the Defence of Gallipoli or the Battle of Gallipoli was a military campaign in the First World War on the Gallipoli peninsula from 19 February 1915 to 9 January 1916. The Entente powers, Britain, France and the Russian Empire, sought to weaken the Ottoman Empire, one of the Central Powers, by taking control of the Ottoman straits. This would expose the Ottoman capital at Constantinople to bombardment by Entente battleships and cut it off from the Asian part of the empire. With the Ottoman Empire defeated, the Suez Canal would be safe and the Bosphorus and Dardanelles straits would be open to Entente supplies to the Black Sea and warm-water ports in Russia.

The Battle of the Nek was a minor battle that took place on 7 August 1915, during the Gallipoli campaign of World War I. "The Nek" was a narrow stretch of ridge on the Gallipoli Peninsula. The name derives from the Afrikaans word for a "mountain pass" but the terrain itself was a perfect bottleneck and easy to defend, as had been proven during an Ottoman attack in June. It connected Australian and New Zealand trenches on the ridge known as "Russell's Top" to the knoll called "Baby 700" on which the Ottoman defenders were entrenched.

The Christmas truce was a series of widespread unofficial ceasefires along the Western Front of the First World War around Christmas 1914.

The Battle of Lone Pine was fought between Australian and New Zealand Army Corps (ANZAC) and Ottoman Empire forces during the Gallipoli Campaign of the First World War, between 6 and 10 August 1915. The battle was part of a diversionary attack to draw Ottoman attention away from the main assaults being conducted by British, Indian and New Zealand troops around Sari Bair, Chunuk Bair and Hill 971, which became known as the August Offensive.
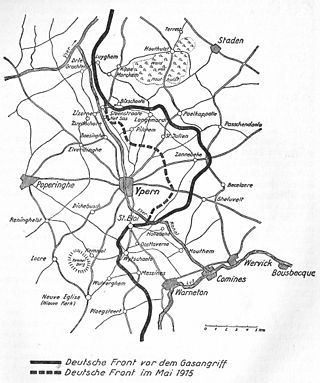
During the First World War, the Second Battle of Ypres was fought from 22 April – 25 May 1915 for control of the tactically important high ground to the east and south of the Flemish town of Ypres in western Belgium. The First Battle of Ypres had been fought the previous autumn. The Second Battle of Ypres was the first mass use by Germany of poison gas on the Western Front.
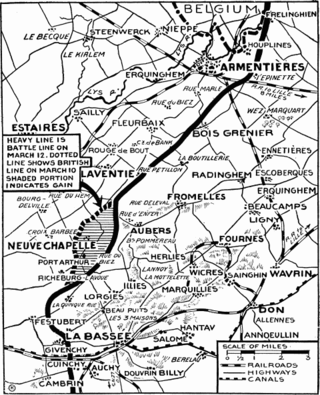
The Attack at Fromelles (French pronunciation:[fʁɔmɛl] 19–20 July 1916, was a military operation on the Western Front during the First World War. The attack was carried out by British and Australian troops and was subsidiary to the Battle of the Somme. General Headquarters of the British Expeditionary Force had ordered the First Army and Second Army to prepare attacks to support the Fourth Army on the Somme, 50 mi to the south, to exploit any weakening of the German defences opposite. The attack took place 9.9 mi from Lille, between the Fauquissart–Trivelet road and Cordonnerie Farm, an area overlooked from Aubers Ridge to the south. The ground was low-lying and much of the defensive fortification by both sides consisted of building breastworks, rather than trenches.

Charles Yale Harrison was a Canadian-American writer and journalist, best known for his 1930 anti-war novella Generals Die in Bed.

Passchendaele is a 2008 Canadian war film, written, co-produced, directed by, and starring Paul Gross. The film, which was shot in Calgary, Alberta, Fort Macleod, Alberta, and in Belgium, focuses on the experiences of a Canadian soldier, Michael Dunne, at the Battle of Passchendaele, also known as the Third Battle of Ypres, inspired by stories that Gross heard from his grandfather, a First World War soldier.

All Quiet on the Western Front is an epic anti-war television film produced by ITC Entertainment. It was released on November 14, 1979. Based on the 1929 book of the same name by Erich Maria Remarque, it stars Richard Thomas and Ernest Borgnine. Directed by Delbert Mann, this film is a joint British and American production for which most of the filming took place in Czechoslovakia.

Major-General Malcolm Smith Mercer was a Canadian general, barrister and art patron who practiced law in Toronto and led the Canadian Contingent, then later the 3rd Canadian Division, during the first two years of the First World War before he was killed in action at Mount Sorrel in Belgium. Mercer was an experienced Canadian Militia commander and had demonstrated a great flair with training and organising the raw Canadian recruits during the opening months of the war. He also demonstrated courage under fire, visiting the front lines on numerous occasions at the height of battle and personally directing his forces in the face of poison gas attacks and heavy shellfire.

The Crucified Soldier was the widespread story of an Allied soldier serving in the Canadian Corps who may have been crucified with bayonets on a barn door or a tree, while fighting on the Western Front during World War I. Three witnesses said they saw an unidentified crucified Canadian soldier near the battlefield of Ypres, Belgium, on or around 24 April 1915, but eyewitness accounts were somewhat contradictory, no crucified body was recovered and the identity of the alleged crucified soldier was not discovered at the time.

The First World War, which was fought between 1914 and 1918, had an immediate impact on popular culture. In the over a hundred years since the war ended, the war has resulted in many artistic and cultural works from all sides and nations that participated in the war. This included artworks, books, poems, films, television, music, and more recently, video games. Many of these pieces were created by soldiers who took part in the war.

The use of horses in World War I marked a transitional period in the evolution of armed conflict. Cavalry units were initially considered essential offensive elements of a military force, but over the course of the war, the vulnerability of horses to modern machine gun, mortar, and artillery fire reduced their utility on the battlefield. This paralleled the development of tanks, which ultimately replaced cavalry in shock tactics. While the perceived value of the horse in war changed dramatically, horses still played a significant role throughout the war.

The Battle of Krivolak was a World War I battle, fought between 21 October and 22 November 1915. It was fought in the initial stage of the Macedonian campaign, in the Balkans Theatre. On 21 October, Bulgarian troops attacked the French-held positions near the Strumica rail station, at the time part of the Kingdom of Serbia, starting the battle. Fighting continued until 22 November, when two Serbian divisions failed to capture Skopje, thus rendering the continuation of Entente offensive operations dangerous and forcing the French to evacuate their forces from the region.

The Battle of Kosturino was a World War I battle fought between 6 and 12 December 1915. It was fought in the initial stage of the Macedonian campaign, in the Balkans Theatre. On 6 December, Bulgarian troops attacked the French and British-held trenches in Kosturino, at the time part of the Kingdom of Serbia. Though the early offensive was held in check, on 8 December, Bulgaria managed to infiltrate the Memesli ravine. Bulgaria then seized Crete Simonet, thus threatening to outflank the Allies. The Entente defeat at Kosturino led to the complete withdrawal of Allied forces from Serbia, thus enabling the Central Powers to build the Berlin to Constantinople rail line. In the meantime, the Allies concentrated on solidifying their defenses in Greece.

All Quiet on the Western Front is a 2022 German epic anti-war film based on the 1929 novel by Erich Maria Remarque. It is the third film adaptation of the book, after the 1930 and 1979 versions. Co-written, directed and co-produced by Edward Berger, it stars Felix Kammerer, Albrecht Schuch, Daniel Brühl, Sebastian Hülk, Aaron Hilmer, Edin Hasanovic, and Devid Striesow.



















