
Essential tremor (ET), also called benign tremor, familial tremor, and idiopathic tremor, is a medical condition characterized by involuntary rhythmic contractions and relaxations of certain muscle groups in one or more body parts of unknown cause. It is typically symmetrical, and affects the arms, hands, or fingers; but sometimes involves the head, vocal cords, or other body parts. Essential tremor is either an action (intention) tremor—it intensifies when one tries to use the affected muscles during voluntary movements such as eating and writing—or it is a postural tremor, present with sustained muscle tone. This means that it is distinct from a resting tremor, such as that caused by Parkinson's disease, which is not correlated with movement.

Botulinum toxin, or botulinum neurotoxin, is a highly potent neurotoxic protein produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum and related species. It prevents the release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine from axon endings at the neuromuscular junction, thus causing flaccid paralysis. The toxin causes the disease botulism. The toxin is also used commercially for medical and cosmetic purposes.
Spasticity is a feature of altered skeletal muscle performance with a combination of paralysis, increased tendon reflex activity, and hypertonia. It is also colloquially referred to as an unusual "tightness", stiffness, or "pull" of muscles.
Hereditary spastic paraplegia (HSP) is a group of inherited diseases whose main feature is a progressive gait disorder. The disease presents with progressive stiffness (spasticity) and contraction in the lower limbs. HSP is also known as hereditary spastic paraparesis, familial spastic paraplegia, French settlement disease, Strumpell disease, or Strumpell-Lorrain disease. The symptoms are a result of dysfunction of long axons in the spinal cord. The affected cells are the primary motor neurons; therefore, the disease is an upper motor neuron disease. HSP is not a form of cerebral palsy even though it physically may appear and behave much the same as spastic diplegia. The origin of HSP is different from cerebral palsy. Despite this, some of the same anti-spasticity medications used in spastic cerebral palsy are sometimes used to treat HSP symptoms.

Torticollis, also known as wry neck, is a painful, dystonic condition defined by an abnormal, asymmetrical head or neck position, which may be due to a variety of causes. The term torticollis is derived from the Latin words tortus, meaning "twisted", and collum, meaning "neck".
Writer's cramp or focal hand dystonia (FHD) is an idiopathic movement disorder of adult onset, characterized by abnormal posturing and movement of the hand and/or forearm during tasks requiring skilled hand use, such as writing. Overcontraction of affected muscles, cocontraction of agonist and antagonist pairs, and activation of muscles inappropriate to a task all impair use of the affected hand.
Dystonia is a neurological hyperkinetic movement disorder in which sustained or repetitive muscle contractions occur involuntarily, resulting in twisting and repetitive movements or abnormal fixed postures. The movements may resemble a tremor. Dystonia is often intensified or exacerbated by physical activity, and symptoms may progress into adjacent muscles.
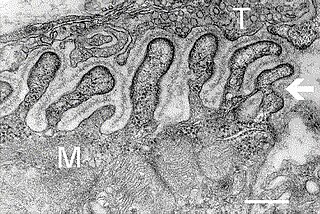
A neuromuscular junction is a chemical synapse between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber.
Hyperkinesia refers to an increase in muscular activity that can result in excessive abnormal movements, excessive normal movements, or a combination of both. Hyperkinesia is a state of excessive restlessness which is featured in a large variety of disorders that affect the ability to control motor movement, such as Huntington's disease. It is the opposite of hypokinesia, which refers to decreased bodily movement, as commonly manifested in Parkinson's disease.
Palatal myoclonus is a rare condition in which there are rhythmic jerky movements or a rapid spasm of the palatal muscles. Chronic clonus is often due to lesions of the central tegmental tract.
Hemifacial spasm (HFS) is a rare neuromuscular disease characterized by irregular, involuntary muscle contractions (spasms) on one side (hemi-) of the face (-facial). The facial muscles are controlled by the facial nerve, which originates at the brainstem and exits the skull below the ear where it separates into five main branches.

The mentalis muscle is a paired central muscle of the lower lip, situated at the tip of the chin. It originates from the mentum of the mandible, and inserts into the soft tissue of the chin. It is sometimes referred to as the "pouting muscle" due to it raising the lower lip and causing chin wrinkles.

Blepharospasm is any abnormal contraction of the orbicularis oculi muscle. The condition should be distinguished from the more common, and milder, involuntary quivering of an eyelid, known as myokymia, or fasciculation. In most cases, blepharospasm symptoms last for a few days and then disappear without treatment, but in some cases the twitching is chronic and persistent, causing life-long challenges. In these cases, the symptoms are often severe enough to result in functional blindness. The person's eyelids feel like they are clamping shut and will not open without great effort. People have normal eyes, but for periods of time are effectively blind due to their inability to open their eyelids. In contrast, the reflex blepharospasm is due to any pain in and around the eye.

Spasmodic torticollis is an extremely painful chronic neurological movement disorder causing the neck to involuntarily turn to the left, right, upwards, and/or downwards. The condition is also referred to as "cervical dystonia". Both agonist and antagonist muscles contract simultaneously during dystonic movement. Causes of the disorder are predominantly idiopathic. A small number of patients develop the disorder as a result of another disorder or disease. Most patients first experience symptoms midlife. The most common treatment for spasmodic torticollis is the use of botulinum toxin type A.

Sixth nerve palsy, or abducens nerve palsy, is a disorder associated with dysfunction of cranial nerve VI, which is responsible for causing contraction of the lateral rectus muscle to abduct the eye. The inability of an eye to turn outward, results in a convergent strabismus or esotropia of which the primary symptom is diplopia in which the two images appear side-by-side. Thus, the diplopia is horizontal and worse in the distance. Diplopia is also increased on looking to the affected side and is partly caused by overaction of the medial rectus on the unaffected side as it tries to provide the extra innervation to the affected lateral rectus. These two muscles are synergists or "yoke muscles" as both attempt to move the eye over to the left or right. The condition is commonly unilateral but can also occur bilaterally.
Spasmodic dysphonia, also known as laryngeal dystonia, is a disorder in which the muscles that generate a person's voice go into periods of spasm. This results in breaks or interruptions in the voice, often every few sentences, which can make a person difficult to understand. The person's voice may also sound strained or they may be nearly unable to speak. Onset is often gradual and the condition is lifelong.
Synkinesis is a neurological symptom in which a voluntary muscle movement causes the simultaneous involuntary contraction of other muscles. An example might be smiling inducing an involuntary contraction of the eye muscles, causing a person to squint when smiling. Facial and extraocular muscles are affected most often; in rare cases, a person's hands might perform mirror movements.

Spastic cerebral palsy is the type of cerebral palsy characterized by spasticity or high muscle tone often resulting in stiff, jerky movements. Cases of spastic CP are further classified according to the part or parts of the body that are most affected. Such classifications include spastic diplegia, spastic hemiplegia, spastic quadriplegia, and in cases of single limb involvement, spastic monoplegia.
Congenital distal spinal muscular atrophy (cDSMA), also known as distal hereditary motor neuropathytype VIII (dHMN8), is a hereditary medical condition characterized by muscle wasting (atrophy), particularly of distal muscles in legs and hands, and by early-onset contractures of the hip, knee, and ankle. Affected individuals often have shorter lower limbs relative to the trunk and upper limbs. The condition is a result of a loss of anterior horn cells localized to lumbar and cervical regions of the spinal cord early in infancy, which in turn is caused by a mutation of the TRPV4 gene. The disorder is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. Arm muscle and function, as well as cardiac and respiratory functions are typically well preserved.
Alan Brown Scott was an American ophthalmologist specializing in eye muscles and their disorders, such as strabismus. He is best known for his work in developing and manufacturing the drug that became known as Botox, research described as "groundbreaking" by the ASCRS.












