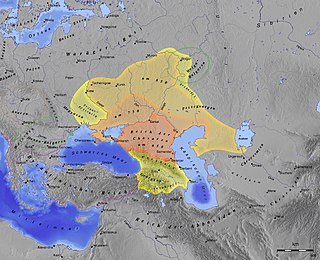
The Khazars were a nomadic Turkic people that, in the late 6th century CE, established a major commercial empire covering the southeastern section of modern European Russia, southern Ukraine, Crimea, and Kazakhstan. They created what, for its duration, was the most powerful polity to emerge from the break-up of the Western Turkic Khaganate. Astride a major artery of commerce between Eastern Europe and Southwestern Asia, Khazaria became one of the foremost trading empires of the early medieval world, commanding the western marches of the Silk Road and playing a key commercial role as a crossroad between China, the Middle East, and Kievan Rus'. For some three centuries, the Khazars dominated the vast area extending from the Volga-Don steppes to the eastern Crimea and the northern Caucasus.

Sarkel was a large limestone-and-brick fortress in what is now Rostov Oblast of Russia, on the left bank of the lower Don River.

Sviatoslav or Svyatoslav I Igorevich was Prince of Kiev from 945 until his death in 972. He is known for his persistent campaigns in the east and south, which precipitated the collapse of two great powers in Eastern Europe, Khazaria and the First Bulgarian Empire. He conquered numerous East Slavic tribes, defeated the Alans and attacked the Volga Bulgars, and at times was allied with the Pechenegs and Magyars (Hungarians).

Atil, also Itil, was the capital of the Khazar Khaganate from the mid-8th century to the late 10th century. It is known historically to have been situated along the Silk Road, on the northern coast of the Caspian Sea, in the Volga Delta region of modern Southern Russia. Its precise location has long been unknown.
The Grand Prince of Kiev was the title of the monarch of Kievan Rus', residing in Kiev from the 10th to 13th centuries. In the 13th century, Kiev became an appanage principality first of the grand prince of Vladimir and the Mongol Golden Horde governors, and later was taken over by the Grand Duchy of Lithuania.
The Khazar Correspondence is a set of documents, which are alleged to date from the 950s or 960s, and to be letters between Hasdai ibn Shaprut, foreign secretary to the Caliph of Cordoba, and Joseph Khagan of the Khazars. The correspondence is one of only a few documents attributed to a Khazar author, and potentially one of only a small number of primary sources on Khazar history.
Bulan was a Khazar king who led the conversion of the Khazars to Judaism. His name means "elk" or "hart" in Old Turkic. The date of his reign is unknown, as the date of the conversion is hotly disputed, though it is certain that Bulan reigned some time between the mid-8th and the mid-9th centuries. Nor is it settled whether Bulan was the Bek or the Khagan of the Khazars.
The Schechter Letter, also called the Genizah Letter or Cambridge Document, was discovered in the Cairo Geniza by Solomon Schechter in 1912. It is an anonymous Khazar letter discussing several matters including the wars of the early 940s, involving the Byzantine Empire, the Khazar Khaganate, and Kievan Rus'. Scholars have debated its authenticity.
Arsiyah was the name used for a group of Muslim mercenaries in the service of the Khazar Khaganate. Whether the Arsiyah were a single tribe or composed of Muslims from a number of different tribes is unclear. Also unclear is their origin; many historians regard them as deriving from Khwarazm, but some scholars point to the fact that "As" is the Turkic term for Alans and believe that the Arsiyah were Alanic in origin. Other scholars derive the name from the Iranian Auruša (white).
Joseph ben Aaron was king of the Khazars during the 950s and 960s. Joseph was the son of Aaron II, a Khazar ruler who defeated a Byzantine-inspired war against Khazaria on numerous fronts. Joseph's wife was the daughter of the king of the Alans.
The Chalyzians or Khalyzians were the people mentioned in various Medieval sources of Halych.
A Khazar ruler during the early 10th century CE, Aaron ben Benjamin was the son of the Khazar king Benjamin. Whether Aaron, like the rest of the Bulanids, was a Khagan or a Bek is an unresolved issue.
The Bulanids were the ruling dynasty of the Khazar Khaganate during the 9th century and 10th century CE.
A purported Khazar ruler of the late tenth century CE who ruled over a Khazar successor-state in the Taman region. David is mentioned in a single document dated AM 4746 which contains a reference to "our lord David, Prince of the Khazars, who lives in Taman." The document in question is of uncertain authenticity, as it passed through the hands of Abraham Firkovich, who on occasion forged documents and inscriptions. Dan Shapira expressed certainty that the document is a forgery by Firkovich and his viewpoint was adopted by other scholars who cited him including Michael Toch and Kevin Brook.
Pesach or Pesakh was a Khazar Jewish general mentioned in the Schechter Letter.
Hanukkah Khagan was a Khazar Khagan who reigned during the mid to late ninth century CE. Hanukkah was the brother of Obadiah and succeeded his great-nephew Manasseh I to the throne. No contemporary records from his reign survive; however, he is known from the Khazar Correspondence between Hisdai ibn Shaprut and the Khazar king Joseph. Historical authenticity and accuracy of the only document mentioning his name has been questioned.

The Caspian expeditions of the Rus' were military raids undertaken by the Rus' between the late 9th century and c. 1041 on the Caspian Sea shores, of what are nowadays Iran, Dagestan, and Azerbaijan. Initially, the Rus' appeared in Serkland in the 9th century travelling as merchants along the Volga trade route, selling furs, honey, and slaves. The first small-scale Viking raids took place in the late 9th and early 10th century. The Rus' undertook the first large-scale expedition in 913; having arrived on 500 ships, they pillaged in the Gorgan region, in the territory of present-day Iran, and more to the west, in Gilan and Mazandaran, taking slaves and goods. On their return, the northern raiders were attacked and defeated by the Khazars in the Volga Delta, and those who escaped were killed by the local tribes in the middle Volga.

Samosdelka is a fishing village in the Astrakhan Oblast of southern Russia, approximately 40 km south-southwest of the city of Astrakhan, in the Volga River delta area of the Caspian Depression marshlands. In September 2008, Russian archaeologists excavating in Samosdelka announced their discovery of what they claimed were the remains of Atil, the capital of the medieval Khazar kingdom. The claim was considered sensational and, owing to the absence of archaeological evidence, did not meet with widespread acceptance. A 2020 assessment by the Russian Geographic Society concluded that Atil had not been found in Samosdelka, and announced that new excavations were underway at another site.
Rus' Khaganate, or kaganate of Rus is a name applied by some modern historians to a hypothetical polity suggested to have existed during a poorly documented period in the history of Eastern Europe between c. 830 and the 890s.






