Related Research Articles

Cosmic rays or astroparticles are high-energy particles or clusters of particles that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our own galaxy, and from distant galaxies. Upon impact with Earth's atmosphere, cosmic rays produce showers of secondary particles, some of which reach the surface, although the bulk are deflected off into space by the magnetosphere or the heliosphere.

Jeffrey Alan Hoffman is an American former NASA astronaut and currently a professor of aeronautics and astronautics at MIT.
The Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics is part of the Max Planck Society, located in Garching, near Munich, Germany. In 1991 the Max Planck Institute for Physics and Astrophysics split up into the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics, the Max Planck Institute for Physics and the Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics. The Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics was founded as sub-institute in 1963. The scientific activities of the institute are mostly devoted to astrophysics with telescopes orbiting in space. A large amount of the resources are spent for studying black holes in the Milky Way Galaxy and in the remote universe.

Explorer 11 was a NASA satellite that carried the first space-borne gamma-ray telescope. This marked the beginning of space gamma-ray astronomy. Launched on 27 April 1961 by a Juno II, the satellite returned data until 17 November 1961, when power supply problems ended the science mission. During the spacecraft's seven-month lifespan it detected twenty-two events from gamma-rays and approximately 22,000 events from cosmic radiation.
Astroparticle physics, also called particle astrophysics, is a branch of particle physics that studies elementary particles of astronomical origin and their relation to astrophysics and cosmology. It is a relatively new field of research emerging at the intersection of particle physics, astronomy, astrophysics, detector physics, relativity, solid state physics, and cosmology. Partly motivated by the discovery of neutrino oscillation, the field has undergone rapid development, both theoretically and experimentally, since the early 2000s.

Cornelis A. "Neil" Gehrels was an American astrophysicist specializing in the field of gamma-ray astronomy. He was Chief of the Astroparticle Physics Laboratory at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) from 1995 until his death, and was best known for his work developing the field from early balloon instruments to today's space observatories such as the NASA Swift mission, for which he was the principal investigator. He was leading the WFIRST wide-field infrared telescope forward toward a launch in the mid-2020s. He was a member of the National Academy of Sciences and the American Academy of Arts and Sciences.

The Small Astronomy Satellite 3 was a NASA X-ray astronomy space telescope. It functioned from May 7, 1975 to April 1979. It covered the X-ray range with four experiments on board. The satellite, built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL), was proposed and operated by MIT's Center for Space Research (CSR). It was launched on a Scout vehicle from the Italian San Marco launch platform near Mombasa, Kenya, into a low-Earth, nearly equatorial orbit. It was also known as Explorer 53, as part of NASA's Explorer program.
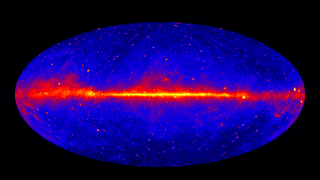
Gamma-ray astronomy is the astronomical observation of gamma rays, the most energetic form of electromagnetic radiation, with photon energies above 100 keV. Radiation below 100 keV is classified as X-rays and is the subject of X-ray astronomy.

OSO 3, or Third Orbiting Solar Observatory was launched on March 8, 1967, into a nearly circular orbit of mean altitude 550 km, inclined at 33° to the equatorial plane. Its on-board tape recorder failed on June 28, 1968, allowing only the acquisition of sparse real-time data during station passes thereafter; the last data were received on November 10, 1969. OSO 3 reentered the Earth's atmosphere and burned up on April 4, 1982.

The history of X-ray astronomy begins in the 1920s, with interest in short wave communications for the U.S. Navy. This was soon followed by extensive study of the earth's ionosphere. By 1927, interest in the detection of X-ray and ultraviolet (UV) radiation at high altitudes inspired researchers to launch Goddard's rockets into the upper atmosphere to support theoretical studies and data gathering. The first successful rocket flight equipped with instrumentation able to detect solar ultraviolet radiation occurred in 1946. X-ray solar studies began in 1949. By 1973 a solar instrument package orbited on Skylab providing significant solar data.

Alan Andrew Watson, FRS, is a physicist and an emeritus professor at the University of Leeds, England.

Dr. Thomas A. Prince is the Ira S. Bowen Professor of Physics at the California Institute of Technology and holds a joint appointment with Caltech’s NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) as a senior research scientist. Between May 2001 and June 2006, Prince was the chief scientist at JPL. He is currently the director and Allen V.C. Davis and Lenabelle Davis Leadership Chair for the W. M. Keck Institute for Space Studies at Caltech.

Hakkı Boran Ögelman was a Turkish physicist and astrophysicist. He was an expert on gamma ray astronomy, the physics of neutron stars, and solar energy and worked on several key topics in modern astrophysics. He made many contributions to high energy astrophysics. In his early professional career he engaged in the SAS-II Small Gamma Ray Astronomy Satellite experiment development, data analysis, and first detection and imaging of our universe in gamma rays with his NASA colleagues, as well as in other fields of physics. His main interests in the field of astrophysics were the study of gamma ray astronomy and compact objects such as neutron stars and pulsars. Ögelman worked at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Middle East Technical University (METU) in Ankara, Turkey, Çukurova University in Adana, Turkey, Max Planck Institute (MPI) at Garching, Germany and the University of Wisconsin.

The High Altitude Water Cherenkov Experiment or High Altitude Water Cherenkov Observatory is a gamma-ray and cosmic ray observatory located on the flanks of the Sierra Negra volcano in the Mexican state of Puebla at an altitude of 4100 meters, at 18°59′41″N97°18′30.6″W. HAWC is the successor to the Milagro gamma-ray observatory in New Mexico, which was also a gamma-ray observatory based around the principle of detecting gamma-rays indirectly using the water Cherenkov method.
Charles James "Chuck" Hailey is an experimental astrophysicist and Pupin Professor of Physics at Columbia University. He earned his BA in physics from Cornell University in 1977 and his PhD from Columbia in 1983, with a thesis entitled "The Development of an Imaging Gas Scintillation Proportional Counter for Use in X-ray Astronomy." He received tenure from Columbia University in 1995. Hailey's research focuses on high energy astrophysics and experimental particle physics. He is co-director of the Columbia Astrophysics Laboratory, where he works on gamma-ray and X-ray research.
María Magdalena González Sánchez is a Mexican astrophysicist, nuclear physicist, researcher, and professor best known for her contributions in gamma ray research and for being the head of the High Altitude Water Cherenkov Experiment (HAWC). She has published 90 articles about her field of study in indexed journals. In 2015 she received the Sor Juana Inés de la Cruz Recognition from the National Autonomous University of Mexico (UNAM).

Péter István Mészáros is a Hungarian-American theoretical astrophysicist, best known for the Mészáros effect in cosmology and for his work on gamma-ray bursts.
Lucy Frear Fortson is an American astronomer known for her work on gamma-ray astronomy and Galaxy morphological classification and for her leadership of citizen science projects including the Galaxy Zoo and Zooniverse. She is a professor in the School of Physics and Astronomy at the University of Minnesota.
Stefan Funk is a German astroparticle physicist. He is a professor at the Erlangen Centre for Astroparticle Physics at the FAU Erlangen-Nuernberg in Germany and an elected a fellow of the American Physical Society.
References
- ↑ ""The John Simon Guggenheim Memorial Foundation, All Fellows"". Archived from the original on 2013-01-14. Retrieved 2010-08-11.