
The California Institute of Technology (branded as Caltech) is a private research university in Pasadena, California. The university is responsible for many modern scientific advances and is among a small group of institutes of technology in the United States that are devoted to the instruction of pure and applied sciences.

The Technion – Israel Institute of Technology is a public research university located in Haifa, Israel. Established in 1912 by Jews under the dominion of the Ottoman Empire, the Technion is the oldest university in the country.

The Fu Foundation School of Engineering and Applied Science is the engineering and applied science school of Columbia University, a private research university in New York City. It was founded as the School of Mines in 1863 and then the School of Mines, Engineering and Chemistry before becoming the School of Engineering and Applied Science. On October 1, 1997, the school was renamed in honor of Chinese businessman Z.Y. Fu, who had donated $26 million to the school.

Nanotechnology education involves a multidisciplinary natural science education with courses such as physics, chemistry, mathematics, and molecular biology. It is being offered by many universities around the world. The first program involving nanotechnology was offered by the University of Toronto's Engineering Science program, where nanotechnology could be taken as an option.

Georgia Tech Europe (GTE) is a campus of the Georgia Institute of Technology in Metz, France and is part of Georgia Tech's International Plan. GTE offers undergraduate and graduate programs in electrical and computer engineering, mechanical engineering, computer science, and liberal arts.
The College of Design at the Georgia Institute of Technology, established in 1908 as the Department of Architecture and also formerly called the College of Architecture, offered the first four-year course of study in architecture in the Southern United States.
The College of Sciences at the Georgia Institute of Technology is one of the six colleges at the institute.

Georgia Tech Savannah is a satellite campus of the Atlanta-based Georgia Institute of Technology. It is located in Savannah, Georgia, near Savannah/Hilton Head International Airport. The campus is the institute's hub for professional and continuing education and is home to the regional offices of the Georgia Tech Enterprise Innovation Institute, the Savannah Advanced Technology Development Center, and the Georgia Logistics Innovation Center.
The Sam Nunn School of International Affairs, at the Georgia Institute of Technology located in Atlanta, Georgia is the only professional school of international affairs at a major technological institution. Founded in 1990, the School was renamed the Sam Nunn School of International Affairs in 1996 in honor of former US Senator and Georgia Tech alumnus Sam Nunn.
The School of Interactive Computing is an academic unit located within the College of Computing at the Georgia Institute of Technology. It conducts both research and teaching activities related to interactive computing at the undergraduate and graduate levels. These activities focus on computing's interaction with users and the environment, as well as how computers impact the quality of people's lives.
The School of Computer Science is an academic unit located within the College of Computing at the Georgia Institute of Technology. It conducts both research and teaching activities related to computer science at the undergraduate and graduate levels. These activities focus on the roots of the computing discipline, including mathematical foundations and system building principles and practices.
The George W. Woodruff School of Mechanical Engineering is the oldest and second largest department in the College of Engineering at the Georgia Institute of Technology. The school offers degree programs in mechanical engineering and nuclear and radiological engineering that are accredited by ABET. In its 2019 ranking list, U.S. News & World Report placed the school ranks 2nd in undergraduate mechanical engineering, 5th in graduate mechanical engineering, and 9th in graduate nuclear and radiological engineering.
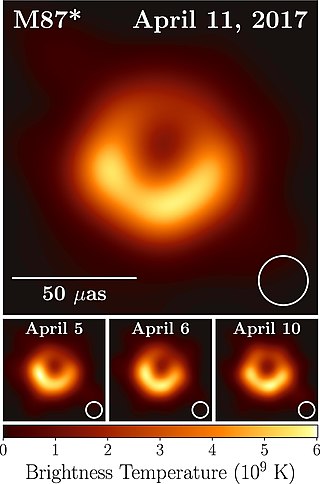
Feryal Özel is a Turkish-American astrophysicist born in Istanbul, Turkey, specializing in the physics of compact objects and high energy astrophysical phenomena. As of 2022, Özel is the Department Chair and a professor at the Georgia Institute of Technology School of Physics in Atlanta. She was previously a professor at the University of Arizona in Tucson, in the Astronomy Department and Steward Observatory.
The School of Engineering at Rutgers University was founded in 1914 as the College of Engineering. It was originally a part of the Rutgers Scientific School, which was founded in 1864. The school has seven academic departments, with a combined undergraduate student enrollment of over 2,400 students. It offers over 25 academic and professional degree programs. These include several interdisciplinary programs, such as Environmental Engineering with the Department of Environmental Science, and the graduate program in mechanics.

The College of Engineering (CoE) is one of the three undergraduate colleges at the University of California, Santa Barbara. The College of Engineering (CoE) at UC Santa Barbara is consistently ranked among the upper echelon of engineering schools globally. The College offers a mid-sized, interdisciplinary environment where innovation drives the development of both fundamental science and applied technology solutions, adding value to the economy locally and globally.
The Irwin and Joan Jacobs School of Engineering is an undergraduate and graduate-level engineering school offering BS, BA, MEng, MS, MAS and PhD degrees at the University of California, San Diego in San Diego, California. The Jacobs School of Engineering is the youngest engineering school of the nation's top ten, the largest by enrollment in the University of California system, as well as the largest engineering school on the West Coast and the ninth-largest in the country. More than thirty faculty have been named members of the National Academies. The current dean of the Jacobs School of Engineering is Albert P. Pisano.

James Emory Boyd was an American physicist, mathematician, and academic administrator. He was director of the Georgia Tech Research Institute from 1957 to 1961, president of West Georgia College from 1961 to 1971, and acting president of the Georgia Institute of Technology from 1971 to 1972.

The Georgia Institute of Technology is a public research university and institute of technology in Atlanta, Georgia. Established in 1885, it is part of the University System of Georgia and has satellite campuses in Savannah, Georgia; Metz, France; Shenzhen, China; and Singapore.
The College of Science at Virginia Tech contains academic programs in eight departments: biology, chemistry, economics, geosciences, mathematics, physics, psychology, and statistics, as well as programs in the School of Neuroscience, the Academy of Integrated Science, and founded in 2020, an Academy of Data Science. For the 2018-209 academic year, the College of Science consisted of 419 faculty members, and 4,305 students, and 600 graduate students The college was established in July 2003 after university restructuring split the College of Arts and Sciences, established in 1963, into two distinct colleges. Lay Nam Chang served as founding dean of the College of Science from 2003 until 2016. In 2016, Sally C. Morton was named dean of the College of Science. Morton served in that role until January 2021, when she departed for Arizona State University and Ronald D. Fricker—senior associate dean and professor in the Department of Statistics—was named interim dean of the College. In February 2022, Kevin T. Pitts was named the third official dean of the College of Science.

Ilia State University ISU is a public university in Tbilisi, Georgia that was founded in 2006 as a result of a merger of six different academic institutions. Currently, ISU is one of the leading research and educational institutions in Georgia.













