
Chamblee is a city in northern DeKalb County, Georgia, United States, northeast of Atlanta. The population was 30,164 as of the 2020 census.

Dunwoody is a city located in DeKalb County, Georgia, United States. As a northern suburb of Atlanta, Dunwoody is part of the Atlanta metropolitan area. It was incorporated as a city on December 1, 2008 but its area establishment dates back to the early 1830s. As of 2020, the city had a population of 51,683.

Sandy Springs is a city in northern Fulton County, Georgia, United States, and a suburb of Atlanta. The city's population was 108,080 at the 2020 census, making it Georgia's 7th most populous city. It is the site of several corporate headquarters, including UPS, Newell Brands, Inspire Brands, Focus Brands, Cox Enterprises, and Mercedes-Benz USA's corporate offices.
Milton County was a county of the U.S. state of Georgia from 1857 to 1931. It was created on December 18, 1857, from parts of northeastern Cobb, southeastern Cherokee, and southwestern Forsyth counties. The county was named for John Milton, Secretary of State of Georgia from 1777 to 1799. Alpharetta was the county seat until the end of 1931, when Milton was merged with Fulton County to save it from bankruptcy during the Great Depression. At that time, Campbell County, which had already gone bankrupt, was also ceded to Fulton, giving it its 70-mile (110 km) long irregular shape along the Chattahoochee River.

The Metropolitan Atlanta Rapid Transit Authority is the principal public transport operator in the Atlanta metropolitan area. Formed in 1971 as strictly a bus system, MARTA operates a network of bus routes linked to a rapid transit system consisting of 48 miles (77 km) of rail track with 38 subway stations. MARTA's rapid transit system is the eighth-largest rapid transit system in the United States by ridership.

The Georgia General Assembly is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Georgia. It is bicameral, consisting of the Senate and the House of Representatives.

The National Voter Registration Act of 1993 (NVRA), also known as the Motor Voter Act, is a United States federal law signed into law by President Bill Clinton on May 20, 1993, that came into effect on January 1, 1995. The law was enacted under the Elections Clause of the United States Constitution and advances voting rights in the United States by requiring state governments to offer simplified voter registration processes for any eligible person who applies for or renews a driver's license or applies for public assistance, and requiring the United States Postal Service to mail election materials of a state as if the state is a nonprofit. The law requires states to register applicants that use a federal voter registration form, and prohibits states from removing registered voters from the voter rolls unless certain criteria are met.

Perimeter College at Georgia State University is a college of Georgia State University in Atlanta, Georgia. Georgia Perimeter College was originally a public community college founded by an Atlanta area county board of education before merging with Georgia State University in 2016 to create one of the largest universities in the United States with over 50,000 students. The Perimeter College (PC) campuses became components of Georgia State University, still maintaining their own mission, degrees, and admittance requirements, separate from those of the main campus. Before merging with GSU, PC served metro Atlanta with five campus locations and offered more than 40 programs of study, including Arts, Music, Theatre, Nursing, Business Administration, Education, Dental Hygiene, Criminal Justice, and Sign Language Interpreting.

The DeKalb County School District (DCSD) is a school district headquartered at 1701 Mountain Industrial Boulevard in unincorporated DeKalb County, Georgia, United States, near Stone Mountain and in the Atlanta metropolitan area. DCSD operates public schools in areas of DeKalb County that are not within the city limits of Atlanta and Decatur. It served a portion of Atlanta annexed by that city in 2018 until 2024, when that portion was re-assigned to Atlanta Public Schools (APS).

Dunwoody High School is a public high school in Dunwoody, an incorporated city in DeKalb County, Georgia, United States.
Electoral reform in Virginia refers to efforts to change the electoral system in the Commonwealth of Virginia. Virginia has undergone much electoral change since its settling in 1607, many of which were required by federal legislation. However, it remains a relatively conservative state in this respect compared to California and others which have experimented with various alternative systems.
In the United States, the term constitutional carry, also called permitless carry, unrestricted carry, or Vermont carry, refers to the legal public carrying of a handgun, either openly or concealed, without a license or permit. The phrase does not typically refer to the unrestricted carrying of a long gun, a knife, or other weapons. The scope and applicability of constitutional carry may vary by state.

Cecil Ivan Bell Jr. is a Republican member of the Texas House of Representatives for District 3, which initially encompassed Waller County and is now entirely a portion of populous Montgomery County in Southeast Texas.
A six-week abortion ban, also called a "fetal heartbeat bill" by proponents, is a law in the United States which makes abortion illegal as early as six weeks gestational age, which is when proponents claim that a "fetal heartbeat" can be detected. Medical and reproductive health experts, including the American Medical Association and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, say that the reference to a fetal heartbeat is medically inaccurate and misleading, for a conceptus is not called a fetus until eight weeks after fertilization, as well as that at four weeks after fertilization, the embryo has no heart, only a group of cells which will become a heart. Medical professionals advise that a true fetal heartbeat cannot be detected until around 17 to 20 weeks of gestation when the chambers of the heart have become sufficiently developed.
William Stone Cowsert is an American politician from the state of Georgia. A member of the Republican Party, Cowsert serves in the Georgia State Senate, representing the 46th district. He is the most senior member of the Senate Republican Caucus.

The John R. Lewis Voting Rights Advancement Act of 2023 is proposed voting rights legislation named after civil rights activist John Lewis. The bill would restore and strengthen parts of the Voting Rights Act of 1965, most notably its requirement for states and jurisdictions with a history of voting rights violations to seek federal approval before enacting certain changes to their voting laws. The bill was written in response to the Supreme Court decision in Shelby County v. Holder in 2013, which struck down the system that was used to determine which jurisdictions were subject to that requirement.
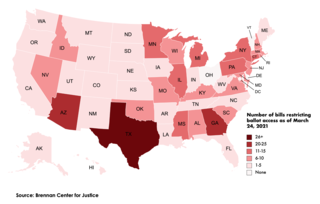
Following the 2020 United States presidential election and the unsuccessful attempts by Donald Trump and various other Republican officials to overturn it, Republican lawmakers initiated a sweeping effort to make voting laws more restrictive within several states across the country. According to the Brennan Center for Justice, as of October 4, 2021, more than 425 bills that would restrict voting access have been introduced in 49 states—with 33 of these bills enacted across 19 states so far. The bills are largely centered around limiting mail-in voting, strengthening voter ID laws, shortening early voting, eliminating automatic and same-day voter registration, curbing the use of ballot drop boxes, and allowing for increased purging of voter rolls. Republicans in at least eight states have also introduced bills that would give lawmakers greater power over election administration after they were unsuccessful in their attempts to overturn election results in swing states won by Democratic candidate Joe Biden in the 2020 election. The efforts garnered press attention and public outrage from Democrats, and by 2023 Republicans had adopted a more "under the radar" approach to achieve their goals.
The Election Integrity Act of 2021, originally known as the Georgia Senate Bill 202, is a law in the U.S. state of Georgia overhauling elections in the state. It replaced signature matching requirements on absentee ballots with voter identification requirements, limits the use of ballot drop boxes, expands in-person early voting, bars officials from sending out unsolicited absentee ballot request forms, reduces the amount of time people have to request an absentee ballot, increases voting stations or staff and equipment where there have been long lines, makes it a crime for outside groups to give free food or water to voters waiting in line, gives the Georgia General Assembly greater control over election administration, and shortens runoff elections, among other provisions.

Sherry Boston serves as the district attorney for DeKalb County, Georgia, which includes a portion of Atlanta, as well as several smaller metro-area cities. Boston was first elected to the position in 2016 after defeating incumbent DA Robert James, a fellow Democrat, in the primary. Boston ran on an anti-corruption platform. She is the second woman to serve as DA in DeKalb County.












