Related Research Articles

Belarus, officially the Republic of Belarus, and historically Byelorussia, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Covering an area of 207,600 square kilometres (80,200 sq mi) and with a population of 9.3 million, Belarus is the thirteenth-largest and the twentieth-most populous country in Europe. The country is administratively divided into seven regions. Minsk is the capital and largest city.

The Commonwealth of Independent States is a regional intergovernmental organization in Eurasia. It was formed following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. It covers an area of 20,368,759 km2 (7,864,422 sq mi) and has an estimated population of 239,796,010. The CIS encourages cooperation in economic, political and military affairs and has certain powers relating to the coordination of trade, finance, lawmaking, and security. It has also promoted cooperation on cross-border crime prevention.

This article describes the history of Belarus. The Belarusian ethnos is traced at least as far in time as other East Slavs.
The history of the Jews in the Soviet Union is inextricably linked to much earlier expansionist policies of the Russian Empire conquering and ruling the eastern half of the European continent already before the Bolshevik Revolution of 1917. "For two centuries – wrote Zvi Gitelman – millions of Jews had lived under one entity, the Russian Empire and [its successor state] the USSR. They had now come under the jurisdiction of fifteen states, some of which had never existed and others that had passed out of existence in 1939." Before the revolutions of 1989 which resulted in the end of communist rule in Central and Eastern Europe, a number of these now sovereign countries constituted the component republics of the Soviet Union.

The Belarus national football team represents Belarus in international football and is controlled by the Football Federation of Belarus, the governing body for football in Belarus. Belarus' home ground is Dinamo Stadium in Minsk. Since independence in 1991, Belarus has not yet qualified for a FIFA World Cup or UEFA European Championship.
A raion is a type of administrative unit of several post-Soviet states. The term is from the French "rayon", which is both a type of a subnational entity and a division of a city, and is commonly translated in English as "district".
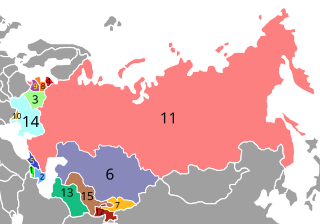
The post-Soviet states, also known as the former Soviet Union (FSU), the former Soviet Republics and in Russia as the near abroad, are the 15 sovereign states that were union republics of the Soviet Union; that emerged and re-emerged from the Soviet Union following its dissolution in 1991.

The Constitution of the Republic of Belarus is the ultimate law of Belarus. The Constitution is composed of a preamble and nine sections divided into 146 articles.

The Collective Security Treaty Organization is an intergovernmental military alliance in Eurasia that consists of selected post-Soviet states. The treaty had its origins to the Soviet Armed Forces, which was gradually replaced by the United Armed Forces of the Commonwealth of Independent States. However, on 15 May 1992, six post-Soviet states belonging to the Commonwealth of Independent States—Russia, Armenia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan—signed the Collective Security Treaty. Three other post-Soviet states—Azerbaijan, Belarus, and Georgia—signed the next year and the treaty took effect in 1994. Five years later, six of the nine—all but Azerbaijan, Georgia, and Uzbekistan—agreed to renew the treaty for five more years, and in 2002 those six agreed to create the Collective Security Treaty Organization as a military alliance.

The history of the Jews in Azerbaijan dates back many centuries. Today, Jews in Azerbaijan mainly consist of three distinct groups: Mountain Jews, the most sizable and most ancient group; Ashkenazi Jews, who settled in the area during the late 19th-early 20th centuries, and during World War II; and Georgian Jews who settled mainly in Baku during the early part of the 20th century.

The Republic of Abkhazia (Abkhazia) is a self-proclaimed state that declared soon after a catastrophic war as residual effect of Soviet Union dissolution in early 1990s, well known as Abkhazian War 1992–1993 between Abkhazian and Georgian. As the new born countries, Abkhazia struggle to gain international community recognition, but no one countries has been recognizing Abkhazia as an independent state after this war. Firstly, Transnistria recognizing each other with Abkhazia on 22 January 1993. This is the first step to Abkhazia for looking forward recognition. After a decades, on 20 September 2005, the second countries was recognizing each other with Abkhazia is South Ossetia. Third, Nagorno-Karabakh also follows two other countries to recognizing Abkhazia on 14 November 2006.
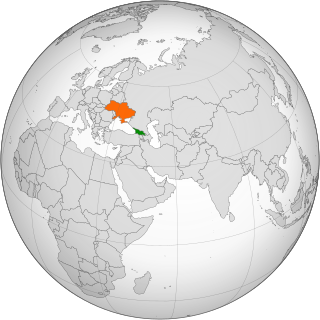
Georgian-Ukrainian relations are the relations between Georgia and Ukraine and between the Georgian and Ukrainian people in particular which lasts from the Middle Ages. Since their independence from the Soviet Union, both countries consider each other as strategic partners and have forged close political and cultural relations. The diplomatic relations between the two nations are realized at the level of embassies and consulates. The current Ambassadors Extraordinary and Plenipotentiary are Ukraine's Mykola Spys and Georgia's Grigol Katamadze.

There is a small Russian population in Georgia of less than 0.5% of the total population. For many years, Georgia was a part of the Russian Empire, and later the Soviet Union. As the two countries share a border, many Russians settled in various regions of Georgia. In recent years, the number of Russians living in Georgia has sharply declined.
Armenians in Belarus refers to ethnic Armenians living in Belarus. They numbered 8,512 as of the 2009 census and mainly live in Minsk.
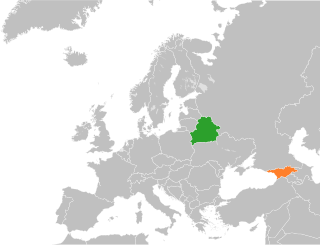
Belarus–Georgia relations are foreign relations between Belarus and Georgia. Before 1918, both countries were part of the Russian Empire and both were part of the USSR until 1991. Both countries established diplomatic relations in 1992.

The Belarusian diaspora refers to emigrants from the territory of Belarus as well as to their descendants.

The Euronest Parliamentary Assembly is the inter-parliamentary forum in which members of the European Parliament and the national parliaments of Ukraine, Moldova, Armenia, Azerbaijan and Georgia participate and forge closer political and economic ties with the European Union. It was established in 2011 by the European Commission as a component of the Eastern Partnership. After the elections in Belarus in 2010 were declared as flawed by the OSCE, the membership of Belarus in Euronest was automatically suspended. Belarus is welcome to re-join the Assembly once political requirements have been fulfilled. In 2015, Azerbaijan's membership was suspended due to the European Union's criticism of human rights abuses by the government. In September 2016, it was announced that Azerbaijan would take the necessary steps towards restoring ties. As of 2017, the combined population of Euronest members stands at 61,927,521 people.

Energy in Belarus describes energy and electricity production, consumption and import in Belarus. Belarus is a net energy importer. According to IEA, the energy import vastly exceeded the energy production in 2015, describing Belarus as one of the world's least energy sufficient countries in the world. Belarus is very dependent on Russia.
Belarusian Australians refers to Australians of full or partial Belarusian national background or descent, or Belarusian citizens living in Australia.

Belarus–Mexico relations refers to the foreign relations between Belarus and Mexico. Both nations are members of the United Nations.