
The United Kingdom straddles the higher mid-latitudes between 49° and 61°N on the western seaboard of Europe. Since the UK is always in or close to the path of the polar front jet stream, frequent changes in pressure and unsettled weather are typical. Many types of weather can be experienced in a single day.

The 2003 European heat wave saw the hottest summer recorded in Europe since at least 1540. France was hit especially hard. The heat wave led to health crises in several countries and combined with drought to create a crop shortfall in parts of Southern Europe. The death toll has been estimated at more than 70,000.

Adelaide has a Mediterranean climate, with mild wet winters and hot dry summers.

The climate of the city of Sydney, Australia is humid subtropical, shifting from mild and cool in winter to warm and hot in the summer, with no extreme seasonal differences as the weather is moderated by proximity to the ocean, although more contrasting temperatures are recorded in the inland western suburbs. Despite the fact that there is no distinct dry or wet season, rainfall peaks in the first few months of the year and is at its lowest just around the middle of the year, though precipitation can be erratic throughout the year. Precipitation varies across the region, with areas adjacent to the coast being the wettest. According to the Bureau of Meteorology, Sydney falls in the temperate climate zone which has warm to hot summers and no dry season. Sydney's plant hardiness zone ranges from zone 11a to 9b throughout the metropolitan area. Under the Holdridge Life Zones classification, eastern Sydney falls in the Subtropical Moist Forest zone and the western suburbs in the Subtropical Dry Forest zone.
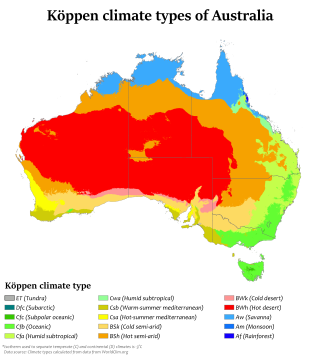
Australia's climate is governed mostly by its size and by the hot, sinking air of the subtropical high pressure belt. This moves north-west and north-east with the seasons. The climate is variable, with frequent droughts lasting several seasons, thought to be caused in part by the El Niño-Southern Oscillation. Australia has a wide variety of climates due to its large geographical size. The largest part of Australia is desert or semi-arid. Only the south-east and south-west corners have a temperate climate and moderately fertile soil. The northern part of the country has a tropical climate, varying between grasslands and desert. Australia holds many heat-related records: the continent has the hottest extended region year-round, the areas with the hottest summer climate, and the highest sunshine duration.

The climate of Italy is the long-term weather pattern in the territory of the Italian Republic. The climate of Italy is influenced by the large body of water of the Mediterranean Seas that surrounds Italy on every side except the north. These seas constitute a reservoir of heat and humidity for Italy. Within the southern temperate zone, they determine a particular climate called Mediterranean climate with local differences due to the geomorphology of the territory, which tends to make its mitigating effects felt, especially in high pressure conditions.

Tasmania has a cool temperate climate with four distinct seasons. The highest recorded maximum temperature in Tasmania is 42.2 °C (108.0 °F) at Scamander on 30 January 2009, during the 2009 southeastern Australia heat wave. Tasmania's lowest recorded minimum temperature is −14.2 °C (6.4 °F) on 7 August 2020, at Central Plateau.
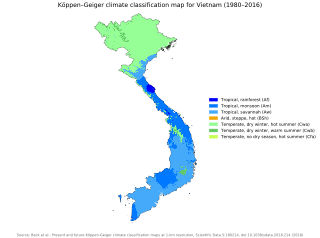
Vietnam has a monsoon-influenced climate typical of that of mainland Southeast Asia. The diverse topography, long latitude, and influences from the South China Sea lead to climatic conditions varying significantly between regions. The northern region experiences a monsoonal and temperate climate (Cfa) with four distinct seasons with winters typically dry and summers ranging from hot to mild. In southern area, the climate is tropical monsoon (Aw) with only two seasons. In addition, a temperate climate exists in mountainous areas, which are found in Sa Pa and Da Lat, while a more continental climate exists in Lai Châu Province and Sơn La Province.
The province of Sindh is situated in a tropical region, with subtropical regions in the northern sections; it is hot, humid and very rainy in the summer and cold and dry in winter. Temperatures frequently rise above 46 °C (115 °F) between May and August, and the minimum average temperature of 2 °C (36 °F) occurs during December and January. The annual rainfall averages about nearly 14 inches (360 mm), falling mainly during June and September. The southwesterly monsoon wind begins to blow in mid-February and continues until the end of September, whereas the cool northerly wind blows during the winter months from October to January.
Extreme weather events in Melbourne, Australia have occurred on multiple occasions. The city has experienced a number of highly unusual weather events and extremes of weather. An increase in heat waves and record breaking temperatures in the 21st century has led to much discussion over the effects of climate change in the country.

Launceston, Tasmania has a cool, temperate climate, with four distinct seasons. The city is located in the Tamar Valley in Northern Tasmania and is surrounded by many large hills and mountains. With this type of topography, Launceston's weather patterns can change considerably in a short period.

Dubai has a hot arid climate. Dubai has 2 seasons – winter and summer. Summer in Dubai begins around the last week of April and ends around the first week of October. This period is characterized by extremely hot weather, hot winds and high humidity. Due to the city's close proximity to the sea, the temperatures in Dubai are slightly milder in summer in comparison to other Gulf cities such as Kuwait City and Riyadh. However, this means the city has high humidity which can make the weather extremely unpleasant in summer. Rainfall is scarce during the summer months, but the windy conditions ensure there are frequent dust storms. Temperatures regularly rise above 38 °C (100 °F) during this period and fall to around 26 °C (79 °F) overnight. Winter in Dubai begins around the last week of October and lasts until the middle of April. Most of the precipitation takes place during this season. Strong thunderstorms are not uncommon in the city during this period, these are accompanied by strong north-westerly winds and lower temperatures. The average daytime high during January, the coolest month, is around 22 °C (72 °F) with overnight lows of 12 °C (54 °F). Rainfall has been increasing over the past few decades in the city accumulating to more than 130 mm (5.12 in) per year.
The climate of Uttar Pradesh (U.P.) is primarily defined as humid subtropical with dry winter (Cwa) type with parts of Western U.P. as hot semi-arid (BSh) type. Alternatively, some authors refer to it as tropical monsoon. Variations do exist in different parts of the large state, however the uniformity of the vast Indo-Gangetic Plain forming bulk of the state gives a predominantly single climatic pattern to the state with minor regional variations. U.P. has a climate of extremes. With temperatures fluctuating anywhere from 0 °C or 32 °F to 50 °C or 122 °F in several parts of the state and cyclical droughts and floods due to unpredictable rains, the summers are extremely hot, winters are cold and the rainy season can be either very wet or very dry.

The climate in Spain varies across continental Spain. Spain is the most climatically diverse country in Europe with 17 different Köppen climates, excluding the Canary Islands, and is within the 10 most climatically diverse countries in the world. The country is dominated by five major climate regions, with the other regions including smaller portions of the country. The Mediterranean environment and location in Europe mean that it will experience greater heatwaves and dry weather due to climate change.
The Australian summer of 2012–2013, known as the Angry Summer or Extreme Summer, resulted in 123 weather records being broken over a 90-day period, including the hottest day ever recorded for January on record, the hottest summer average on record, and a record seven days in a row when the whole country averaged above 39 °C (102 °F). Single-day temperature records were broken in dozens of towns and cities, as well as single-day rainfall records, and several rivers flooded to new record highs.
Perth, the capital city of the state of Western Australia, has a Mediterranean climate, with hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. February is the hottest month of the year, with an average high of 31.6 °C (88.9 °F), and July is the coldest month of the year, with an average low of 7.9 °C (46.2 °F). 77% of rain in Perth falls between May and September. Perth has an average of 8.8 hours of sunshine per day, which equates to around 3,200 hours of annual sunshine, and 138.7 clear days annually, making it the sunniest capital city in Australia.

The 1995 British Isles heatwave occurred between late July and late August. It was part of one of the warmest summers recorded in the UK, and one of the warmest Augusts ever recorded in many locations around the UK, as well as being one of the driest summers ever recorded in the UK; many weather stations recorded the summer of 1995 as drier than, or comparable with, the summer of 1976. Ireland was also widely affected by the heatwave with temperatures reaching over 30 °C (86 °F) in some locations, as well as exceptionally low rainfall throughout the summer.

The 2018 Britain and Ireland heatwave was a period of unusually hot weather that took place in June, July and August. It caused widespread drought, hosepipe bans, crop failures, and a number of wildfires. These wildfires worst affected northern moorland areas around the Greater Manchester region, the largest was at Saddleworth Moor and another was at Winter Hill, together these burned over 14 square miles (36 km2) of land over a period of nearly a month.













