
The Council of Europe is an international organisation whose stated aim is to uphold human rights, democracy and the rule of law in Europe. Founded in 1949, it has 47 member states, with a population of approximately 820 million, and operates with an annual budget of approximately 500 million euros.

The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) is a historic document that was adopted by the United Nations General Assembly at its third session on 10 December 1948 as Resolution 217 at the Palais de Chaillot in Paris, France. Of the then 58 members of the United Nations, 48 voted in favor, none against, eight abstained, and two did not vote.

Title IX is a federal civil rights law in the United States of America that was passed as part of the Education Amendments of 1972. This is Public Law No. 92‑318, 86 Stat. 235, codified at 20 U.S.C. §§ 1681–1688. It was co-authored and introduced by Senator Birch Bayh in the U.S. Senate, and Congresswoman Patsy Mink in the House. It was later renamed the Patsy T. Mink Equal Opportunity in Education Act following Mink's death in 2002.
A domestic partnership is an interpersonal relationship between two individuals who live together and share a common domestic life, but are not married. People in domestic partnerships receive benefits that guarantee right of survivorship, hospital visitation, and others.
In sociology, a minority group refers to a category of people who experience relative disadvantage as compared to members of a dominant social group. Minority group membership is typically based on differences in observable characteristics or practices, such as: ethnicity, race, religion, sexual orientation, or disability. Utilizing the framework of intersectionality, it is important to recognize that an individual may simultaneously hold membership in multiple minority groups. Likewise, individuals may also be part of a minority group in regard to some characteristics, but part of a dominant group in regard to others.

Proposition 59 was an amendment of the Constitution of California that introduced freedom of information or "sunshine" provisions. It was proposed by the California Legislature and overwhelmingly approved by the voters in an initiative held as part of the November 2004 elections.

The Convention on the Elimination of all Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW) is an international treaty adopted in 1979 by the United Nations General Assembly. Described as an international bill of rights for women, it was instituted on 3 September 1981 and has been ratified by 189 states. Over fifty countries that have ratified the Convention have done so subject to certain declarations, reservations, and objections, including 38 countries who rejected the enforcement article 29, which addresses means of settlement for disputes concerning the interpretation or application of the Convention. Australia's declaration noted the limitations on central government power resulting from its federal constitutional system. The United States and Palau have signed, but not ratified the treaty. The Holy See, Iran, Somalia, Sudan, and Tonga are not signatories to CEDAW.

Elaine McCoy, is a Canadian senator from Alberta and formerly served as the first Facilitator of the Independent Senators Group. She was the last remaining member of the Canadian Senate to sit as a Progressive Conservative following the retirement of Senator Lowell Murray on September 26, 2011. On February 11, 2013 she changed her designation to Independent Progressive Conservative, before changing it once again, to Independent, on February 17, 2016.

The Fundamental Rights, Directive Principles of State Policy and Fundamental Duties are sections of the Constitution of India that prescribe the fundamental obligations of the states to its citizens and the duties and the rights of the citizens to the State. These sections comprise a constitutional bill of rights for government policy-making and the behaviour and conduct of citizens. These sections are considered vital elements of the constitution, which was developed between 1947 and 1949 by the Constituent Assembly of India.

UNESCO's Memory of the World Programme is an international initiative launched to safeguard the documentary heritage of humanity against collective amnesia, neglect, the ravages of time and climatic conditions, and willful and deliberate destruction. It calls for the preservation of valuable archival holdings, library collections, and private individual compendia all over the world for posterity, the reconstitution of dispersed or displaced documentary heritage, and increased accessibility to, and dissemination of, these items.
Corpus separatum was the Jerusalem area in the 1947 United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine. According to the plan, the city would be placed under an international regime, conferring it a special status due to its shared religious importance. The corpus separatum was one of the main issues of the Lausanne Conference of 1949, besides the other borders and the question of the right of return of Palestinian refugees. The plan was adopted by the General Assembly with a two-thirds majority, although its implementation failed and nowadays, the view that Jerusalem should be the capital of both Israel and Palestine is widely supported internationally.

The states parties to the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court are those sovereign states that have ratified, or have otherwise become party to, the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court. The Rome Statute is the treaty that established the International Criminal Court, an international court that has jurisdiction over certain international crimes, including genocide, crimes against humanity, and war crimes that are committed by nationals of states parties or within the territory of states parties. States parties are legally obligated to co-operate with the Court when it requires, such as in arresting and transferring indicted persons or providing access to evidence and witnesses. States parties are entitled to participate and vote in proceedings of the Assembly of States Parties, which is the Court's governing body. Such proceedings include the election of such officials as judges and the Prosecutor, the approval of the Court's budget, and the adoption of amendments to the Rome Statute.
Employment discrimination law in the United States derives from the common law, and is codified in numerous state and federal laws, particularly the Civil Rights Act of 1964, as well as in the ordinances of counties and municipalities. These laws prohibit discrimination based on certain characteristics or protected categories. The United States Constitution also prohibits discrimination by federal and state governments against their public employees. Discrimination in the private sector is not directly constrained by the Constitution, but has become subject to a growing body of federal and state law. Federal law prohibits discrimination in a number of areas, including recruiting, hiring, job evaluations, promotion policies, training, compensation and disciplinary action. State laws often extend protection to additional categories or employers.

The Constitution of Kosovo, refers to the supreme law of the Republic of Kosovo. Article four of the constitution establishes the rules and separate powers of the three branches of the government. The unicameral Assembly of the Republic exercises the legislative power, the executive branch led by the President and the Prime Minister which are responsible for implementing laws and the judicial system headed by the Supreme Court.

The Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities is an international human rights treaty of the United Nations intended to protect the rights and dignity of people with disabilities. Parties to the Convention are required to promote, protect, and ensure the full enjoyment of human rights by people with disabilities and ensure that they enjoy full equality under the law. The Convention has served as the major catalyst in the global movement from viewing people with disabilities as objects of charity, medical treatment and social protection towards viewing them as full and equal members of society, with human rights. It is also the only UN human rights instrument with an explicit sustainable development dimension. The Convention was the first human rights treaty of the twenty-first century.

Pirate Parties International (PPI) is a not-for-profit international non-governmental organisation with its headquarters in Brussels, Belgium. Formed in 2010, it serves as a worldwide organisation for Pirate Parties, currently representing members from 42 countries. The Pirate Parties are political incarnations of the freedom of expression movement, trying to achieve their goals by the means of the established political system rather than through activism. In 2017 PPI had been granted special consultative status to the United Nations Economic and Social Council.
The FIMCAP, which is short for Fédération Internationale des Mouvements Catholiques d’Action Paroissiale, is an umbrella organization for Catholic youth organizations. Its 31 member organizations are based in 28 countries. The FIMCAP was founded in 1962 and is recognised as an official Catholic organization by the Dicastery for Laity, Family and Life. FIMCAP is also a full member of the European Youth Forum.
The regulation of LGBT employment discrimination in the United States varies by jurisdiction. Many states and localities prohibit bias in hiring, promotion, job assignment, termination, and compensation, as well as harassment on the basis of one's sexual orientation. Fewer extend those protections to cover gender identity. Some cover government employees, but do not extend their protections to the private sector. Protections at the national level are limited. There is no federal statute explicitly addressing employment discrimination based on sexual orientation or gender identity. However, the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) interprets Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 to cover discrimination against LGBT employees, as "allegations of discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation necessarily state a claim of discrimination on the basis of sex". This interpretation in essence bars employment discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation in accordance with the Civil Rights Act of 1964. In 2012 the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission ruled that Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 does not allow gender identity-based employment discrimination because it is a form of sex discrimination. Then in 2015, the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission concluded that Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 does not allow sexual orientation discrimination in employment because it is a form of sex discrimination. However, these rulings, while persuasive, may not be binding in courts.
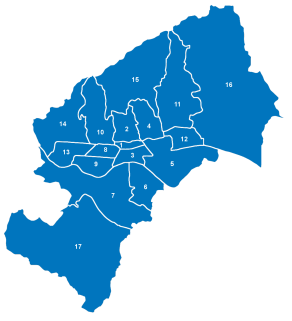
Zagreb is split into seventeen administrative divisions called city districts. The city district, along with a local committee, is a form of local self-government in the City of Zagreb through which citizens participate in the decision-making process in a self-governing areas of the City and local affairs that directly affect their lives. The city district is established for an area that represents urban, economic and social entity, which is linked to the common interests of citizens. The current division was established by the Statute of the City of Zagreb on 14 December 1999. Legally, a city district is a legal person who has its own governing bodies.














