
A glacier is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as crevasses and seracs, as it slowly flows and deforms under stresses induced by its weight. As it moves, it abrades rock and debris from its substrate to create landforms such as cirques, moraines, or fjords. Although a glacier may flow into a body of water, it forms only on land and is distinct from the much thinner sea ice and lake ice that form on the surface of bodies of water.

A moraine is any accumulation of unconsolidated debris, sometimes referred to as glacial till, that occurs in both currently and formerly glaciated regions, and that has been previously carried along by a glacier or ice sheet. It may consist of partly rounded particles ranging in size from boulders down to gravel and sand, in a groundmass of finely-divided clayey material sometimes called glacial flour. Lateral moraines are those formed at the side of the ice flow, and terminal moraines were formed at the foot, marking the maximum advance of the glacier. Other types of moraine include ground moraines and medial moraines.

Glaciology is the scientific study of glaciers, or, more generally, ice and natural phenomena that involve ice.
Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as their creating process, shape, elevation, slope, orientation, rock exposure, and soil type.
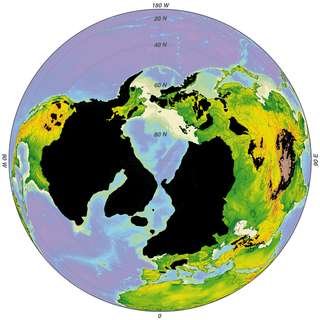
The Wisconsin Glacial Episode, also called the Wisconsin glaciation, was the most recent glacial period of the North American ice sheet complex, peaking more than 20,000 years ago. This advance included the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, which nucleated in the northern North American Cordillera; the Innuitian ice sheet, which extended across the Canadian Arctic Archipelago; the Greenland ice sheet; and the massive Laurentide Ice Sheet, which covered the high latitudes of central and eastern North America. This advance was synchronous with global glaciation during the last glacial period, including the North American alpine glacier advance, known as the Pinedale glaciation. The Wisconsin glaciation extended from approximately 75,000 to 11,000 years ago, between the Sangamonian Stage and the current interglacial, the Holocene. The maximum ice extent occurred approximately 25,000–21,000 years ago during the last glacial maximum, also known as the Late Wisconsin in North America.

A kettle is a depression or hole in an outwash plain formed by retreating glaciers or draining floodwaters. The kettles are formed as a result of blocks of dead ice left behind by retreating glaciers, which become surrounded by sediment deposited by meltwater streams as there is increased friction. The ice becomes buried in the sediment and when the ice melts, a depression is left called a kettle hole, creating a dimpled appearance on the outwash plain. Lakes often fill these kettles; these are called kettle hole lakes. Another source is the sudden drainage of an ice-dammed lake and when the block melts, the hole it leaves behind is a kettle. As the ice melts, ramparts can form around the edge of the kettle hole. The lakes that fill these holes are seldom more than 10 m (33 ft) deep and eventually fill with sediment. In acid conditions, a kettle bog may form but in alkaline conditions, it will be kettle peatland.

An outwash plain, also called a sandur, sandr or sandar, is a plain formed of glaciofluvial deposits due to meltwater outwash at the terminus of a glacier. As it flows, the glacier grinds the underlying rock surface and carries the debris along. The meltwater at the snout of the glacier deposits its load of sediment over the outwash plain, with larger boulders being deposited near the terminal moraine, and smaller particles travelling further before being deposited. Sandurs are common in Iceland where geothermal activity accelerates the melting of ice flows and the deposition of sediment by meltwater.

The Würm glaciation or Würm stage, usually referred to in the literature as the Würm, was the last glacial period in the Alpine region. It is the youngest of the major glaciations of the region that extended beyond the Alps themselves. Like most of the other ice ages of the Pleistocene epoch, it is named after a river, in this case the Würm in Bavaria, a tributary of the Amper.

Till plains are an extensive flat plain of glacial till that forms when a sheet of ice becomes detached from the main body of a glacier and melts in place, depositing the sediments it carried. Ground moraines are formed with melts out of the glacier in irregular heaps, forming rolling hills. Till plains are common in areas such as the Midwestern United States, due to multiple glaciation events that occurred in the Holocene epoch. During this period, the Laurentide Ice Sheet advanced and retreated during the Pleistocene epoch. Till plains formed by the Wisconsin glaciation cover much of the Midwest, including North Dakota, South Dakota, Indiana, Minnesota, Wisconsin, Iowa, Illinois, and northern Ohio.

Glacial landforms are landforms created by the action of glaciers. Most of today's glacial landforms were created by the movement of large ice sheets during the Quaternary glaciations. Some areas, like Fennoscandia and the southern Andes, have extensive occurrences of glacial landforms; other areas, such as the Sahara, display rare and very old fossil glacial landforms.

The Riss glaciation, Riss Glaciation, Riss ice age, Riss Ice Age, Riss glacial or Riss Glacial is the second youngest glaciation of the Pleistocene epoch in the traditional, quadripartite glacial classification of the Alps. The literature variously dates it to between about 300,000 to 130,000 years ago and 347,000 to 128,000 years ago. It coincides with the Saale glaciation of North Germany. The name goes back to Albrecht Penck and Eduard Brückner who named this cold period after the river Riss in Upper Swabia in their three-volume work Die Alpen im Eiszeitalter published between 1901 and 1909.

A terminal moraine, also called an end moraine, is a type of moraine that forms at the terminal (edge) of a glacier, marking its maximum advance. At this point, debris that has accumulated by plucking and abrasion, has been pushed by the front edge of the ice, is driven no further and instead is deposited in an unsorted pile of sediment. Because the glacier acts very much like a conveyor belt, the longer it stays in one place, the greater the amount of material that will be deposited. The moraine is left as the marking point of the terminal extent of the ice.
A subaqueous fan is a fan-shaped deposit formed beneath water, that is commonly related to glaciers and crater lakes.

The glacial history of Minnesota is most defined since the onset of the last glacial period, which ended some 10,000 years ago. Within the last million years, most of the Midwestern United States and much of Canada were covered at one time or another with an ice sheet. This continental glacier had a profound effect on the surface features of the area over which it moved. Vast quantities of rock and soil were scraped from the glacial centers to its margins by slowly moving ice and redeposited as drift or till. Much of this drift was dumped into old preglacial river valleys, while some of it was heaped into belts of hills at the margin of the glacier. The chief result of glaciation has been the modification of the preglacial topography by the deposition of drift over the countryside. However, continental glaciers possess great power of erosion and may actually modify the preglacial land surface by scouring and abrading rather than by the deposition of the drift.
Fluvioglacial landforms or glaciofluvial landforms are those that result from the associated erosion and deposition of sediments caused by glacial meltwater. Glaciers contain suspended sediment loads, much of which is initially picked up from the underlying landmass. Landforms are shaped by glacial erosion through processes such as glacial quarrying, abrasion, and meltwater. Glacial meltwater contributes to the erosion of bedrock through both mechanical and chemical processes. Fluvio-glacial processes can occur on the surface and within the glacier. The deposits that happen within the glacier are revealed after the entire glacier melts or partially retreats. Fluvio-glacial landforms and erosional surfaces include: outwash plains, kames, kame terraces, kettle holes, eskers, varves, and proglacial lakes.

The Kankakee Outwash Plain is a flat plain interspersed with sand dunes in the Kankakee River valley in northwestern Indiana and northeastern Illinois of the United States. It is just south of the Valparaiso Moraine and was formed during the Wisconsin Glaciation. As the glacier stopped at the Valparaiso Moraine, its meltwater was carried away to the outwash plain. On the south side of the moraine, where the elevation drops, the meltwaters eroded away valleys, carrying sand and mud with them. As the muddy meltwater reached the valley where the slope lessened, the water slowed, depositing the sand on the outwash plain. This created a smooth, flat, and sandy plain. Before its draining, the Kankakee Marsh, located on the outwash plain, was one of the largest freshwater marshes in the United States.
An urstromtal is a type of broad glacial valley, for example, in northern Central Europe, that appeared during the ice ages, or individual glacial periods of an ice age, at the edge of the Scandinavian ice sheet and was formed by meltwaters that flowed more or less parallel to the ice margin. Urstromtäler are an element of the glacial series. The term is German and means "ancient stream valley". Although often translated as "glacial valley", it should not be confused with a valley carved out by a glacier. More accurately some sources call them "meltwater valleys" or "ice-marginal valleys".

A Zungenbecken, also called a tongue basin or tongue-basin, is part of a succession of ice age geological landforms, known as a glacial series. It is a hollow that is left behind by the ice mass, as the snout of the glacier recedes, which initially fills with meltwater, forming a proglacial lake, and later may be filled with surface water from streams or precipitation. When the glacier has more fully retreated this produces a finger lake or glacial piedmont lake. The term Zungenbecken is of German origin, but used in English language sources.
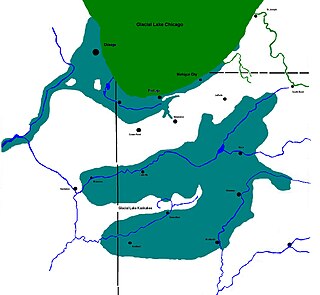
Lake Kankakee formed 14,000 years before present (YBP) in the valley of the Kankakee River. It developed from the outwash of the Michigan Lobe, Saginaw Lobe, and the Huron-Erie Lobe of the Wisconsin glaciation. These three ice sheets formed a basin across Northwestern Indiana. It was a time when the glaciers were receding, but had stopped for a thousand years in these locations. The lake drained about 13,000 YBP, until reaching the level of the Momence Ledge. The outcropping of limestone created an artificial base level, holding water throughout the upper basin, creating the Grand Kankakee Marsh.

The Munich gravel plain is an outwash plain in Upper Bavaria, Germany, formed during Late Pleistocene glacial periods. Characterized by its very wide extension, it comprises sandur terraces and the floodplain of the Isar river. These most recent deposits overlie the Neogene Molasse basin of the Alpine Foreland, which in contrast comprises fine-grained fluviatile and lacustrine facies.

















