
Siegfried Fred Singer was an Austrian-born American physicist and emeritus professor of environmental science at the University of Virginia, trained as an atmospheric physicist. He was known for rejecting the scientific consensus on several issues, including climate change, the connection between UV-B exposure and melanoma rates, stratospheric ozone loss being caused by chlorofluoro compounds, often used as refrigerants, and the health risks of passive smoking.

Global warming potential (GWP) is a measure of how much heat a greenhouse gas traps in the atmosphere over a specific time period, relative to carbon dioxide (CO2). It is expressed as a multiple of warming caused by the same mass of carbon dioxide (CO2). Therefore, by definition CO2 has a GWP of 1. For other gases it depends on how strongly the gas absorbs thermal radiation, how quickly the gas leaves the atmosphere, and the time frame considered.

Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause harm. Pollution can take the form of any substance or energy. Pollutants, the components of pollution, can be either foreign substances/energies or naturally occurring contaminants.

The Club of Rome is a nonprofit, informal organization of intellectuals and business leaders whose goal is a critical discussion of pressing global issues. The Club of Rome was founded in 1968 at Accademia dei Lincei in Rome, Italy. It consists of one hundred full members selected from current and former heads of state and government, UN administrators, high-level politicians and government officials, diplomats, scientists, economists, and business leaders from around the globe. It stimulated considerable public attention in 1972 with the first report to the Club of Rome, The Limits to Growth. Since 1 July 2008, the organization has been based in Winterthur, Switzerland.

A refrigerant is a working fluid used in cooling, heating or reverse cooling and heating of air conditioning systems and heat pumps where they undergo a repeated phase transition from a liquid to a gas and back again. Refrigerants are heavily regulated because of their toxicity and flammability and the contribution of CFC and HCFC refrigerants to ozone depletion and that of HFC refrigerants to climate change.
A green economy is an economy that aims at reducing environmental risks and ecological scarcities, and that aims for sustainable development without degrading the environment. It is closely related with ecological economics, but has a more politically applied focus. The 2011 UNEP Green Economy Report argues "that to be green, an economy must not only be efficient, but also fair. Fairness implies recognizing global and country level equity dimensions, particularly in assuring a Just Transition to an economy that is low-carbon, resource efficient, and socially inclusive."
An environmental factor, ecological factor or eco factor is any factor, abiotic or biotic, that influences living organisms. Abiotic factors include ambient temperature, amount of sunlight, air, soil, water and pH of the water soil in which an organism lives. Biotic factors would include the availability of food organisms and the presence of biological specificity, competitors, predators, and parasites.
Environmental issues in Iraq are greatly attributed to the government, politics, and region. Iraq is the fifth most vulnerable country to the effects of climate change, subject to oil spills, pollution, land degradation, and poor management of upstream water sources.
Energy & Environment is an academic journal "covering the direct and indirect environmental impacts of energy acquisition, transport, production and use". Under its editor-in-chief from 1998 to 2017, Sonja Boehmer-Christiansen, it was known for easygoing peer-review and publishing climate change denial papers. Yiu Fai Tsang became its editor-in-chief in May 2017.
Cambridge Scientific Abstracts was a division of Cambridge Information Group and provider of online databases, based in Bethesda, Maryland, before merging with ProQuest of Ann Arbor, Michigan, in 2007. CSA hosted databases of abstracts and developed taxonomic indexing of scholarly articles. These databases were hosted on the CSA Illumina platform and were available alongside add-on products like CSA Illustrata. The company produced numerous bibliographic databases in different fields of the arts and humanities, natural and social sciences, and technology. Thus, coverage included materials science, environmental sciences and pollution management, biological sciences, aquatic sciences and fisheries, biotechnology, engineering, computer science, sociology, linguistics, and other areas.
Richard S. J. Tol is a professor of economics at the University of Sussex. He is also professor of the economics of climate change at the Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam. He is a member of the Academia Europaea.
Energy subsidies are measures that keep prices for customers below market levels, or for suppliers above market levels, or reduce costs for customers and suppliers. Energy subsidies may be direct cash transfers to suppliers, customers, or related bodies, as well as indirect support mechanisms, such as tax exemptions and rebates, price controls, trade restrictions, and limits on market access.

Global Environmental Politics (GEP) is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal which examines the relationship between global political forces and environmental change. It covers such topics as the role of states, international finance, science and technology, and grass roots movements. Issues of Global Environmental Politics are divided into three types of articles: short commentaries for a section called Current Debates/Forum, full-length research articles, and book review articles.
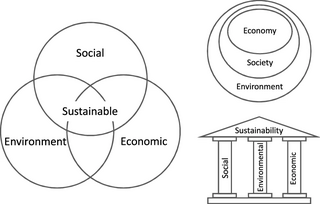
Sustainability is a social goal for people to co-exist on Earth over a long period of time. Definitions of this term are disputed and have varied with literature, context, and time. Sustainability usually has three dimensions : environmental, economic, and social. Many definitions emphasize the environmental dimension. This can include addressing key environmental problems, including climate change and biodiversity loss. The idea of sustainability can guide decisions at the global, national, organizational, and individual levels. A related concept is that of sustainable development, and the terms are often used to mean the same thing. UNESCO distinguishes the two like this: "Sustainability is often thought of as a long-term goal, while sustainable development refers to the many processes and pathways to achieve it."

Energy & Environmental Science, also known as EES, is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal publishing original (primary) research and review articles. The journal covers agenda-setting work of an interdisciplinary nature relating to energy science. Energy & Environmental Science is published by the Royal Society of Chemistry.

Planetary boundaries are a framework to describe limits to the impacts of human activities on the Earth system. Beyond these limits, the environment may not be able to self-regulate anymore. This would mean the Earth system would leave the period of stability of the Holocene, in which human society developed. The framework is based on scientific evidence that human actions, especially those of industrialized societies since the Industrial Revolution, have become the main driver of global environmental change. According to the framework, "transgressing one or more planetary boundaries may be deleterious or even catastrophic due to the risk of crossing thresholds that will trigger non-linear, abrupt environmental change within continental-scale to planetary-scale systems."

Media coverage of climate change has had effects on public opinion on climate change, as it conveys the scientific consensus on climate change that the global temperature has increased in recent decades and that the trend is caused by human-induced emissions of greenhouse gases.

Climate change and poverty are deeply intertwined because climate change disproportionally affects poor people in low-income communities and developing countries around the world. The impoverished have a higher chance of experiencing the ill-effects of climate change due to the increased exposure and vulnerability. Vulnerability represents the degree to which a system is susceptible to, or unable to cope with, adverse effects of climate change including climate variability and extremes.

Cowspiracy: The Sustainability Secret is a 2014 American documentary film produced and directed by Kip Andersen and Keegan Kuhn. The film explores the impact of animal agriculture on the environment—examining such environmental concerns as climate change, water use, deforestation, and ocean dead zones—and investigates the policies of several environmental organizations on the issue.

Climate security is a political and policy framework that looks at the impacts of climate on security. Climate security often refers to the national and international security risks induced, directly or indirectly, by changes in climate patterns. It is a concept that summons the idea that climate-related change amplifies existing risks in society that endangers the security of humans, ecosystems, economy, infrastructure and societies. Climate-related security risks have far-reaching implications for the way the world manages peace and security. Climate actions to adapt and mitigate impacts can also have a negative effect on human security if mishandled.












