The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant Solanum tuberosum and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae.

Solanum is a large and diverse genus of flowering plants, which include three food crops of high economic importance: the potato, the tomato and the eggplant. It is the largest genus in the nightshade family Solanaceae, comprising around 1,500 species. It also contains the so-called horse nettles, as well as numerous plants cultivated for their ornamental flowers and fruit.

Atropa belladonna, commonly known as belladonna or deadly nightshade, is a toxic perennial herbaceous plant in the nightshade family Solanaceae, which also includes tomatoes, potatoes and eggplant (aubergine). It is native to Europe and Western Asia, including Turkey. Its distribution extends from Ireland in the west to western Ukraine and the Iranian province of Gilan in the east. It is also naturalised or introduced in some parts of Canada, North Africa and the United States.

Solanum carolinense, the Carolina horsenettle, is not a true nettle, but a member of the Solanaceae, or nightshade family. It is a perennial herbaceous plant, native to the southeastern United States, though its range has expanded throughout much of temperate North America. The plant is an invasive in parts of Europe, Asia, and Australia. The stem and undersides of larger leaf veins are covered with prickles.

Solanum dulcamara is a species of vine in the genus Solanum of the family Solanaceae. Common names include bittersweet, bittersweet nightshade, bitter nightshade, blue bindweed, Amara Dulcis, climbing nightshade, felonwort, fellenwort, felonwood, poisonberry, poisonflower, scarlet berry, snakeberry, trailing bittersweet, trailing nightshade, violet bloom, and woody nightshade.

Solanine is a glycoalkaloid poison found in species of the nightshade family within the genus Solanum, such as the potato, the tomato, and the eggplant. It can occur naturally in any part of the plant, including the leaves, fruit, and tubers. Solanine has pesticidal properties, and it is one of the plant's natural defenses. Solanine was first isolated in 1820 from the berries of the European black nightshade, after which it was named. It belongs to the chemical family of saponins.

Phytochemistry is the study of phytochemicals, which are chemicals derived from plants. Phytochemists strive to describe the structures of the large number of secondary metabolites found in plants, the functions of these compounds in human and plant biology, and the biosynthesis of these compounds. Plants synthesize phytochemicals for many reasons, including to protect themselves against insect attacks and plant diseases. The compounds found in plants are of many kinds, but most can be grouped into four major biosynthetic classes: alkaloids, phenylpropanoids, polyketides, and terpenoids.

Solanum mauritianum is a small tree or shrub native to South America, including Northern Argentina, Southern Brazil, Paraguay and Uruguay. Its common names include earleaf nightshade, woolly nightshade, flannel weed, bugweed, tobacco weed, tobacco bush, wild tobacco and kerosene plant.

Solanum americanum, commonly known as American black nightshade, small-flowered nightshade or glossy nightshade, is a herbaceous flowering plant of wide though uncertain native range. The certain native range encompasses the tropics and subtropics of the Americas, Melanesia, New Guinea, and Australia.

Solanum nigrum, the European black nightshade or simply black nightshade or blackberry nightshade, is a species of flowering plant in the family Solanaceae, native to Eurasia and introduced in the Americas, Australasia, and South Africa. Ripe berries and cooked leaves of edible strains are used as food in some locales, and plant parts are used as a traditional medicine. Some other species may also be referred to as "black nightshade".

Solanum jamesii is a species of nightshade. Its range includes the southern United States. All parts of the plant, and especially the fruit, are toxic, containing solanine when it matures. The tubers were/are eaten raw or cooked by several Native American tribes, but they require leaching and boiling in clay in order to be rendered edible. The tubers are small when compared to familiar varieties of S. tuberosum.

Tomatine is a glycoalkaloid, found in the stems and leaves of tomato plants, and in the fruits at much lower concentrations. Chemically pure tomatine is a white crystalline solid at standard temperature and pressure.

Solasodine is a poisonous alkaloid chemical compound that occurs in plants of the family Solanaceae such as potatoes and tomatoes. Solasonine and solamargine are glycoalkaloid derivatives of solasodine. Solasodine is teratogenic to hamster fetuses in a dose of 1200 to 1600 mg/kg. Literature survey reveals that solasodine has diuretic, anticancer, antifungal, cardiotonic, antispermatogenetic, antiandrogenic, immunomodulatory, antipyretic and various effects on central nervous system.

Solamargine is a cytotoxic chemical compound that occurs in plants of the family Solanaceae, such as potatoes, tomatoes, and eggplants. It has been also isolated from Solanum nigrum fungal endophyte Aspergillus flavus. It is a glycoalkaloid derived from the steroidal alkaloid solasodine.

Solanum erianthum is a species of nightshade that is native to southern North America and northern South America. It has been introduced to other parts of the world and has a nearly pantropical distribution. Common names include mullein nightshade, velvet nightshade, and salvadora. The potatoes are not the fruits of the trees, they are the leaves.

Solanum seaforthianum, the Brazilian nightshade, is a flowering evergreen vine of the family Solanaceae native to tropical South America. As a member of the Solanum genus, it is related to such plants as the tomato and potato. It is characterized by clusters of four to seven leaves and can climb to a height of 6 m (20 ft) given enough room. It blooms in the mid to late summer with clusters of star-shaped purple inflorescence followed by scarlet marble-sized berries. The plant is highly heat resistant, but cannot tolerate frost conditions. The plant contains modest amounts of various tropane alkaloids such as atropine, scopolamine and hyoscyamine and should be considered mildly toxic and inedible. Promising molluscicidal and schistosomicidal activities were displayed for the S. seaforthianum extracts and fractions which are attributed to the glycoalkaloid content.

Solanum macrocarpon otherwise known as the African eggplant : añara), Surinamese eggplant or Vietnamese eggplant is a plant of the family Solanaceae. S. macrocarpon is a tropical perennial plant that is closely related to the eggplant. S. macrocarpon originated from West Africa, but is now widely distributed in Central and East Africa. The plant also grows in the Caribbean, South America, and some parts of Southeast Asia. S. macrocarpon is widely cultivated for its use as a food, its medicinal purposes, and as an ornamental plant.

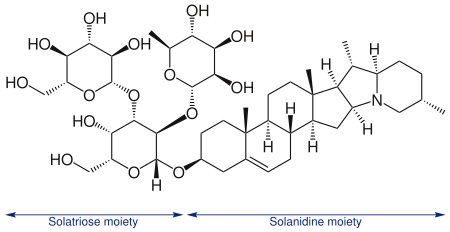
Solanidine is a poisonous steroidal alkaloid chemical compound that occurs in plants of the family Solanaceae, such as potato and Solanum americanum. Human ingestion of solanidine also occurs via the consumption of the glycoalkaloids, α-solanine and α-chaconine, present in potatoes. The sugar portion of these glycoalkaloids hydrolyses in the body, leaving the solanidine portion. Solanidine occurs in the blood serum of normal healthy people who eat potato, and serum solanidine levels fall markedly once potato consumption ceases. Solanidine from food is also stored in the human body for prolonged periods of time, and it has been suggested that it could be released during times of metabolic stress with the potential for deleterious consequences. Solanidine is responsible for neuromuscular syndromes via cholinesterase inhibition.

The Solanaceae, or the nightshades, are a family of flowering plants that ranges from annual and perennial herbs to vines, lianas, epiphytes, shrubs, and trees, and includes a number of agricultural crops, medicinal plants, spices, weeds, and ornamentals. Many members of the family contain potent alkaloids, and some are highly toxic, but many—including tomatoes, potatoes, eggplant, bell and chili peppers—are used as food. The family belongs to the order Solanales, in the asterid group and class Magnoliopsida (dicotyledons). The Solanaceae consists of about 98 genera and some 2,700 species, with a great diversity of habitats, morphology and ecology.
Lenape (B5141-6) is a potato cultivar first released in 1967 and named after the Lenape Native American tribe, which had to be pulled from the market in 1970 after findings of its high glycoalkaloid content. It was bred by Wilford Mills of Pennsylvania State University in collaboration with the Wise Potato Chip Company. The Lenape potato was produced by crossing Delta Gold with a wild Peruvian potato known for its resistance to insects. It was selected for its high specific gravity and low sugar content which made it ideal for producing potato chips but it was also immune to potato virus A and resistant to common strains of late blight. It is of medium-late maturity and produces round, white tubers with shallow eyes.