A gallery grave is a form of megalithic tomb built primarily during the Neolithic Age in Europe in which the main gallery of the tomb is entered without first passing through an antechamber or hallway. There are at least four major types of gallery grave, and they may be covered with an earthen mound or rock mound.

Klekkende Høj is a megalithic tomb on the island of Møn in Denmark. It takes its name from its location near the village of Klekkende. "Høj" stems from the Old Norse word haugr, meaning hill, mound or barrow.

Denghoog is a Neolithic passage grave dating from around 3000 BC on the northern edge of Wenningstedt-Braderup on the German island of Sylt. The name Denghoog derives from the Söl'ring Deng (Thing) and Hoog (Hill).

Pentre Ifan is the name of an ancient manor in the community and parish of Nevern, Pembrokeshire, Wales. It contains and gives its name to the largest and best preserved neolithic dolmen in Wales. The Pentre Ifan monument is a Scheduled Ancient Monument and was one of three Welsh monuments to receive legal protection under the Ancient Monuments Protection Act 1882.

The dolmens of Jersey are neolithic sites, including dolmens, in Jersey. They range over a wide period, from around 4800 BC to 2250 BC, these dates covering the periods roughly designated as Neolithic, or “new stone age”, to Chalcolithic, or “copper age”.

Tinkinswood or its full name Tinkinswood Burial Chamber, also known as Castell Carreg, Llech-y-Filiast and Maes-y-Filiast, is a megalithic burial chamber, built around 6,000 BP, during the Neolithic period, in the Vale of Glamorgan, near Cardiff, Wales.

The dolmen on a low elevation between the villages of Dohnsen and Siddernhausen near the town of Bergen in North Germany, was originally 500 m further north. It was excavated in 1977 and reconstructed in its present location. This dolmen from the New Stone Age is believed to have been destroyed in the 17th or 18th century, because its large stones lay scattered on the fields. Several of the stones were sunk into the ground, others had been carried away. As a result a considerable amount of the original material has been lost.

The Oldendorfer Totenstatt is a group of six burial mounds and megalith sites in Oldendorf north of Amelinghausen in the valley of the River Luhe in Lüneburg district in the German state of Lower Saxony. It consists of dolmens and tumuli.

The Lancken-Granitz dolmens are a group of seven megalith tombs in the Lancken-Granitz municipality on Rügen, northern Germany. Erected during the middle Neolithic, when they were used by the Funnelbeaker culture, at least some were in use until the early Bronze Age. Three of them are encircled by solitary rocks forming either rectangles or a stone circle, one has a solitary "guardian stone" on its eastern side.

In the area of present-day Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany, up to 5,000 megalith tombs were erected as burial sites by people of the Neolithic Funnelbeaker (TRB) culture. More than 1,000 of them are preserved today and protected by law. Though varying in style and age, megalith structures are common in Western Europe, with those in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern belonging to the youngest and easternmost—further east, in the modern West Pomeranian Voivodeship of Poland, monuments erected by the TRB people did not include lithic structures, while they do in the south (Brandenburg), west and north (Denmark).

Nobbin is a village in the municipality of Putgarten on the Wittow peninsula on the German Baltic Sea island of Rügen. The village, comprising just a few houses, lies between the road from Altenkirchen to Arkona and the bay of Tromper Wiek. As a result of its attractive location between Cape Arkona and the broad, over 10 km long beach of the Schaabe, the village is dominated by tourism.

The Great dolmen of Dwasieden, is a great dolmen in the borough of Sassnitz, on the Jasmund peninsula of Germany's largest island, Rügen. It was excavated in 1970 by Ewald Schuldt and is designated a Sprockhoff No. 472. The megalithic site of the Funnelbeaker culture (TBK) was constructed between 3500 and 2800 B. C.

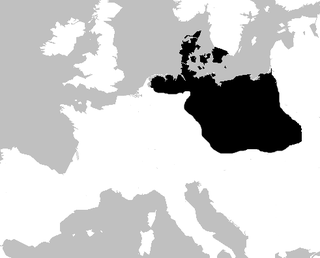
Nordic megalith architecture is an ancient architectural style found in Northern Europe, especially Scandinavia and North Germany, that involves large slabs of stone arranged to form a structure. It emerged in northern Europe, predominantly between 3500 and 2800 BC. It was primarily a product of the Funnelbeaker culture. Amongst its researchers, Ewald Schuldt in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania excavated over 100 sites of different types - simple dolmens, extended dolmens – also called rectangular dolmens – passage graves, great dolmens, unchambered long barrows and stone cists - between 1964 and 1974. In addition, there are polygonal dolmens and types that emerged later, for example, the Grabkiste and Röse. This nomenclature, which specifically derives from the German, is not used in Scandinavia where these sites are categorised by other, more general, terms, as dolmens, passage graves and stone cists . Neolithic monuments are a feature of the culture and ideology of Neolithic communities. Their appearance and function serves as an indicator of their social development.

The Harhoog is a dolmen, a rectangular megalithic tomb from the Funnelbeaker culture, located near Keitum on the island of Sylt in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. Discovered in 1925, it was moved to the present site in 1954 when a new airport was developed.

The various types of megalithic monuments in northeastern Germany were last compiled by Ewald Schuldt in the course of a project to excavate megalithic tombs from the Neolithic Era, which was conducted between 1964 and 1972 in the area of the northern districts of East Germany. His aim was to provide a "classification and naming of the objects present in this field of research". In doing so it utilised a classification by Ernst Sprockhoff, which in turn was based on an older Danish model.

The Necropolis of Soderstorf is a prehistoric cemetery in the valley of the Luhe river valley near Soderstorf in the Lüneburg district of Lower Saxony, Germany. The site was used for more than 2000 years. It includes a megalithic tomb, a tumulus tomb, a stone circle, paving stones, funerary urns and a flat grave.

Tŷ Newydd Burial Chamber is a Neolithic dolmen located northeast of the village of Llanfaelog on the Isle of Anglesey in Wales. It is located near Tŷ Newydd farm, and is in the care of Cadw.

Borkowo megalithic cemetery is a prehistoric burial ground situated in the county of Sławno, in Western Pomerania, Poland.