Related Research Articles

The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) is an independent agency of the United States government that regulates the interstate transmission and wholesale sale of electricity and natural gas and regulates the prices of interstate transport of petroleum by pipeline. FERC also reviews proposals to build interstate natural gas pipelines, natural gas storage projects, and liquefied natural gas (LNG) terminals, in addition to licensing non-federal hydropower projects.
Enbridge Inc. is a Canadian multinational pipeline and energy company headquartered in Calgary, Alberta, Canada. Enbridge owns and operates pipelines throughout Canada and the United States, transporting crude oil, natural gas, and natural gas liquids, and also generates renewable energy. Enbridge's pipeline system is the longest in North America and the largest oil export pipeline network in the world. Its crude oil system consists of 28,661 kilometres of pipelines. Its 38,300 kilometre natural gas pipeline system connects multiple Canadian provinces, several US states, and the Gulf of Mexico. The company was formed by Imperial Oil in 1949 as the Interprovincial Pipe Line Company Limited to transport Alberta oil to refineries. Over time, it has grown through acquisition of other existing pipeline companies and the expansion of their projects.

Columbia Gulf Transmission gathers gas in the Gulf of Mexico and brings it to Columbia Gas Transmission. It is owned by TransCanada Corporation. Its FERC code is 70.
East Tennessee Natural Gas Pipeline is a natural gas pipeline that brings gas from eastern Tennessee to Virginia and North Carolina. It was formerly owned by Duke Energy but is now owned by Enbridge. Its FERC code is 2.

The Garden Banks Pipeline is a 30-inch diameter natural gas transmission pipeline which gathers gas from the offshore Gulf of Mexico and brings it into Enbridge Pipelines UTOS system, which leads into various locations in Louisiana and Texas. One end of the pipeline originates from Cameron, Louisiana, and it spans for 50 miles. Since 2005, the pipeline itself is 100% owned by Enbridge Offshore L.L.C., a subsidiary of the multinational pipeline company Enbridge, which has the longest pipeline system in North America. Its FERC code is 148. According to the FERC website, the company total cost for pipeline operations in the 2022 fiscal year was $60,318, 949.
Gas Transmission Northwest (GTN) is a 1,353 miles (2,177 km) long natural gas pipeline built in 1961 with a capacity of 2,900 million cubic feet per day. It brings gas from Alberta, Canada, beginning at Kingsgate, British Columbia and passing through Washington and terminates at Malin, Oregon then connecting to California, connecting to the Pacific Gas and Electric system. Prior to being purchased by TransCanada Corporation in 2004, it was named Pacific Gas Transmission. TransCanada subsequently sold 25 percent of its interest in GTN to TC PipeLines, LP, which connects via the Tuscarora Gas Pipeline. GTN's FERC code is 86.
Gulfstream Natural Gas Pipeline is a natural gas pipeline that brings gas from Mississippi and Alabama, underwater across the Gulf of Mexico, to Florida. It was owned by Duke Energy, but is now owned by Enbridge and Williams. Its FERC code is 183.
Horizon Pipeline is a natural gas pipeline in northern Illinois, United States. Its FERC code is 178.
Iroquois Gas Transmission System is a natural gas pipeline that brings gas from eastern Canada to the New York City area.

Kern River Pipeline is a 1,679-mile (2,702 km) long natural gas pipeline line extending from southwestern Wyoming to its terminus near Bakersfield, California. The pipeline supplies local gas distribution companies, power plants, and heavy industry in Utah, Nevada, and California. It is owned and operated by the Kern River Gas Transmission Company, a subsidiary of Berkshire Hathaway Energy. Its FERC code is 99.
Kinder Morgan Interstate Gas Transmission was a natural gas pipeline system that brought gas from the Rocky Mountains into Missouri and Nebraska, where it joined other pipes to go on towards the Midwest. Prior to being purchased by Kinder Morgan Energy Partners, it was named KN Energy and Kansas Nebraska Pipeline. Its FERC code is 53.
The North Baja Pipeline is an overall 220-mile (350 km), bidirectional natural gas pipeline that can deliver gas from Arizona, through California, and into Mexico or from Mexico into the United States.
Northern Border Pipeline is a natural gas pipeline which brings gas from Canada through Montana, North Dakota, South Dakota, Minnesota, and Iowa into the Chicago area. It is owned by TC PipeLines, LP and ONEOK Partners and is operated by TC PipeLines, LP. Its FERC code is 89.
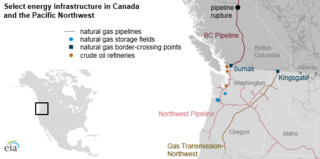
Northwest Pipeline is a natural gas pipeline network which takes gas from western Canada and the Rocky Mountains via the Westcoast Pipeline and brings it into California, either through Gas Transmission Northwest or Kern River. A small amount of gas goes through the San Juan Basin to El Paso Natural Gas. It is owned by the Williams Companies. Its FERC code is 37.
Vector Pipeline L.P. is a 348-mile-long natural gas pipeline which transports approximately 1 billion cubic feet (28,000,000 m3) per day of natural gas from Joliet, Illinois, in the Chicago area, to parts of Indiana and Michigan and into Ontario, Canada. The pipeline is important in the supply and transportation of natural gas from the United States and Western Canada to the Midwest, eastern Canada and the northeastern United States, supplying power generation plants, natural gas distribution companies, and natural gas storage facilities. The pipeline also has interconnections with several other natural gas pipelines along its route.
Viking Gas Transmission is a natural gas pipeline which takes gas from the TransCanada pipeline in Minnesota and brings it to Wisconsin. It is owned by ONEOK Partners. Its FERC code is 82.
Natural gas is a commodity that can be stored for an indefinite period of time in natural gas storage facilities for later consumption.
Southern Star Central Gas Pipeline, Inc, headquartered in Owensboro, Kentucky, is a natural gas transmission system spanning approximately 6,000 miles (9,700 km) in the Midwest and Mid-continent regions of the United States. Southern Star's employees and its pipeline system and facilities are located throughout Kansas, Oklahoma, Missouri, Wyoming, Colorado, Texas, Nebraska, and Kentucky. It serves major markets such as St. Louis, Wichita, and Kansas City. Southern Star is a locally managed, private company owned by Caisse de dépôt et placement du Québec and Ullico, Inc. The company is more commonly referred to as Southern Star. The company's FERC code is 43.

The Natural Gas Act of 1938 was the first occurrence of the United States federal government regulating the natural gas industry. It was focused on regulating the rates charged by interstate natural gas transmission companies. In the years prior to the passage of the Act, concern arose about the monopolistic tendencies of the transmission companies and the fact that they were charging higher than competitive prices. The passage of the Act gave the Federal Power Commission (FPC) control over the regulation of interstate natural gas sales. Later on, the FPC was dissolved and became the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) pursuant to a different act. FERC continues to regulate the natural gas industry to this day.
References
- ↑ "Three Digit Pipeline Code List for Index of Customers (Form 549B)". FERC. Archived from the original on 20 January 2013. Retrieved 25 July 2014.
- ↑ "TC Energy".