An ecumenical council, also called general council, is a meeting of bishops and other church authorities to consider and rule on questions of Christian doctrine, administration, discipline, and other matters in which those entitled to vote are convoked from the whole world (oikoumene) and which secures the approbation of the whole Church.

Worcester College is one of the constituent colleges of the University of Oxford in England. The college was founded in 1714 by the benefaction of Sir Thomas Cookes, 2nd Baronet (1648–1701) of Norgrove, Worcestershire, whose coat of arms was adopted by the college. Its predecessor, Gloucester College, had been an institution of learning on the same site since the late 13th century until the Dissolution of the Monasteries in 1539. Founded as a men's college, Worcester has been coeducational since 1979. The provost is David Isaac, CBE who took office on 1 July 2021
Greek Orthodox Church is a term that can refer to any one of three classes of Christian churches, each associated in some way with Greek Christianity, Levantine Arabic-speaking Christians or more broadly the rite used in the Eastern Roman Empire.

The Catholic Church is the fourth largest religious congregation in Bulgaria, after Eastern Orthodoxy, Islam and Protestantism. Its roots in the country date to the Middle Ages and are part of the worldwide Catholic Church, under the spiritual leadership of the Pope in Rome.

The Autocephalous Orthodox Church of Albania, commonly known as the Albanian Orthodox Church or the Orthodox Church of Albania, is an autocephalous Eastern Orthodox church. It declared its autocephaly in 1922 through its Congress of 1922, and gained recognition from the Patriarch of Constantinople in 1937.

Beaumont Palace, built outside the north gate of Oxford, was intended by Henry I about 1130 to serve as a royal palace conveniently close to the royal hunting-lodge at Woodstock. Its former presence is recorded in Beaumont Street, Oxford. Set into a pillar on the north side of the street, near Walton Street, is a stone with the inscription: "Near to this site stood the King's Houses later known as Beaumont Palace. King Richard I was born here in 1157 and King John in 1166." The "King's House" was the range of the palace that contained the king's lodgings.

The Imperial University of Constantinople, sometimes known as the University of the Palace Hall of Magnaura, was an Eastern Roman educational institution that could trace its corporate origins to 425 AD, when the emperor Theodosius II founded the Pandidacterium.
Greeks in the United Kingdom are British residents and citizens of full or partial Greek heritage, or Greeks who emigrated to and reside in the United Kingdom.

English Baroque is a term used to refer to modes of English architecture that paralleled Baroque architecture in continental Europe between the Great Fire of London (1666) and roughly 1720, when the flamboyant and dramatic qualities of Baroque art were abandoned in favour of the more chaste, rule-based Neo-classical forms espoused by the proponents of Palladianism.

Gloucester College, Oxford, was a Benedictine institution of the University of Oxford in Oxford, England, from the late 13th century until the dissolution of the monasteries in the 16th century. It was never a typical college of the University; in that there was an internal division in the college, by staircase units, into parts where the monasteries sending monks had effective authority. The overall head was a Prior, later changed to a Prior Studentium, and finally a Principal.
The history of the Eastern Orthodox Church is the formation, events, and transformation of the Eastern Orthodox Church through time. According to the Eastern Orthodox tradition, the history of the Eastern Orthodox Church is traced back to Jesus Christ and the Apostles. The Apostles appointed successors, known as bishops, and they in turn appointed other bishops in a process known as Apostolic succession. Over time, five Patriarchates were established to organize the Christian world, and four of these ancient patriarchates remain Orthodox today. Orthodox Christianity reached its present form in late antiquity, when the ecumenical councils were held, doctrinal disputes were resolved, the Fathers of the Church lived and wrote, and Orthodox worship practices settled into their permanent form.

The Russian Orthodox Church is traditionally said to have been founded by Andrew the Apostle, who is thought to have visited Scythia and Greek colonies along the northern coast of the Black Sea. According to one of the legends, St. Andrew reached the future location of Kiev and foretold the foundation of a great Christian city. The spot where he reportedly erected a cross is now marked by St. Andrew's Cathedral.

John Nost was a Flemish sculptor who worked in England in the late 17th and early 18th centuries.
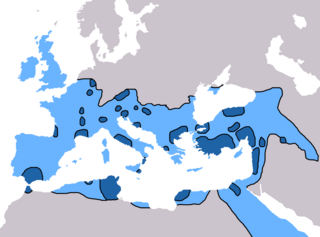
In the 5th century in Christianity, there were many developments which led to further fracturing of the State church of the Roman Empire. Emperor Theodosius II called two synods in Ephesus, one in 431 and one in 449, that addressed the teachings of Patriarch of Constantinople Nestorius and similar teachings. Nestorius had taught that Christ's divine and human nature were distinct persons, and hence Mary was the mother of Christ but not the mother of God. The Council rejected Nestorius' view causing many churches, centered on the School of Edessa, to a Nestorian break with the imperial church. Persecuted within the Roman Empire, many Nestorians fled to Persia and joined the Sassanid Church thereby making it a center of Nestorianism. By the end of the 5th century, the global Christian population was estimated at 10-11 million. In 451 the Council of Chalcedon was held to clarify the issue further. The council ultimately stated that Christ's divine and human nature were separate but both part of a single entity, a viewpoint rejected by many churches who called themselves miaphysites. The resulting schism created a communion of churches, including the Armenian, Syrian, and Egyptian churches, that is today known as Oriental Orthodoxy. In spite of these schisms, however, the imperial church still came to represent the majority of Christians within the Roman Empire.

Sir Thomas Cookes, 2nd Baronet was an English philanthropist who was the benefactor of Worcester College, Oxford and Bromsgrove School.
The history of Eastern Orthodox Christian theology begins with the life of Jesus and the forming of the Christian Church. Major events include the Chalcedonian schism of 451 with the Oriental Orthodox miaphysites, the Iconoclast controversy of the 8th and 9th centuries, the Photian schism (863-867), the Great Schism between East and West, and the Hesychast controversy. The period after the end of the Second World War in 1945 saw a re-engagement with the Greek, and more recently Syriac Fathers that included a rediscovery of the theological works of St. Gregory Palamas, which has resulted in a renewal of Orthodox theology in the 20th and 21st centuries.

Rūm millet was the name of the Eastern Orthodox Christian community in the Ottoman Empire. Despite being subordinated within the Ottoman political system, the community maintained a certain internal autonomy.
This is a timeline of the presence of Eastern Orthodoxy in Greece. The history of Greece traditionally encompasses the study of the Greek people, the areas they ruled historically, as well as the territory now composing the modern state of Greece.

Benjamin Woodroffe (1638–1711) was an English cleric and college head.

Perpendicular Gothic architecture was the third and final style of English Gothic architecture developed in the Kingdom of England during the Late Middle Ages, typified by large windows, four-centred arches, straight vertical and horizontal lines in the tracery, and regular arch-topped rectangular panelling. Perpendicular was the prevailing style of Late Gothic architecture in England from the 14th century to the 17th century. Perpendicular was unique to the country: no equivalent arose in Continental Europe or elsewhere in the British-Irish Isles. Of all the Gothic architectural styles, Perpendicular was the first to experience a second wave of popularity from the 18th century on in Gothic Revival architecture.


















