
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, on the east by the Levant in West Asia, and on the west almost by the Morocco–Spain border. The Mediterranean has played a central role in the history of Western civilization. Geological evidence indicates that around 5.9 million years ago, the Mediterranean was cut off from the Atlantic and was partly or completely desiccated over a period of some 600,000 years during the Messinian salinity crisis before being refilled by the Zanclean flood about 5.3 million years ago.

Malta, officially the Republic of Malta, is an island country in Southern Europe located in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago 80 km (50 mi) south of Italy, 284 km (176 mi) east of Tunisia, and 333 km (207 mi) north of Libya. The two official languages are Maltese and English. The country's capital is Valletta, which is the smallest capital city in the EU by both area and population. With a population of about 542,000 over an area of 316 km2 (122 sq mi), Malta is the world's tenth-smallest country by area and the ninth most densely populated. Various sources consider the country to consist of a single urban region, for which it is often described as a city-state.

Malta has been inhabited since 5900 BC. The first inhabitants were farmers; their agricultural methods degraded the soil until the islands became uninhabitable. The islands were repopulated around 3850 BC by a civilization that at its peak built the Megalithic Temples, which today are among the oldest surviving buildings in the world. Their civilization collapsed in around 2350 BC; the islands were repopulated by Bronze Age warriors soon afterwards.

The Battle of Preveza was a naval engagement that took place on 28 September 1538 near Preveza in the Ionian Sea in northwestern Greece between an Ottoman fleet and that of a Holy League. The battle was an Ottoman victory which occurred in the same area in the Ionian Sea as the Battle of Actium in 31 BC. It was one of the three largest sea battles that took place in the sixteenth century Mediterranean, along with the Battle of Djerba and the Battle of Lepanto.

The mistral is a strong, cold, northwesterly wind that blows from southern France into the Gulf of Lion in the northern Mediterranean. It produces sustained winds averaging 31 miles an hour, sometimes reaching 60 miles an hour. It can last for several days. Periods of the wind exceeding 30 km/h for more than sixty-five hours have been reported. It is most common in the winter and spring, and strongest in the transition between the two seasons.

Lampedusa is the largest island of the Italian Pelagie Islands in the Mediterranean Sea.

Southern Europe is the southern region of Europe. It is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of southern Europe include some or all of these countries and regions: Albania, Andorra, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Gibraltar, Greece, Italy, Malta, Monaco, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Portugal, San Marino, Serbia, Slovenia, southern France, Spain, Turkey, and Vatican City.
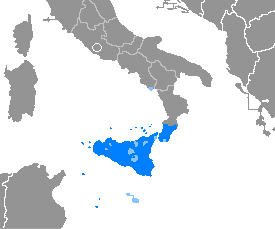
Sicilian is a Romance language that is spoken on the island of Sicily and its satellite islands. It belongs to the broader Extreme Southern Italian language group.

Sirocco or scirocco is a Mediterranean wind that comes from the Sahara and can reach hurricane speeds in North Africa and Southern Europe, especially during the summer season.

Pantelleria, known in ancient times as Cossyra or Cossura, is an Italian island and comune in the Strait of Sicily in the Mediterranean Sea, 106 kilometres southwest of Sicily and 68 km (35 nmi) east of the Tunisian coast. On clear days Tunisia is visible from the island. Administratively Pantelleria's comune belongs to the Sicilian province of Trapani.

The Maltese people are an ethnic group native to Malta who speak Maltese, a Semitic language and share a common culture and Maltese history. Malta, an island country in the Mediterranean Sea, is an archipelago that also includes an island of the same name together with the islands of Gozo and Comino ; people of Gozo, Gozitans are considered a subgroup of the Maltese.

The Battle of the Duisburg Convoy was fought on the night of 8/9 November 1941 between an Italian convoy, its escorts and four British ships. The convoy was named BETA by the Italian naval authorities and carried supplies for the Italian Army civilian colonists and the Afrika Korps in Italian Libya.

Cantareus apertus, commonly known as the green garden snail, is a species of air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusc in the family Helicidae, the typical snails.

Mediterranean tropical-like cyclones, often referred to as Mediterranean cyclones or Mediterranean hurricanes, and shortened as medicanes, are meteorological phenomena occasionally observed over the Mediterranean Sea. On a few rare occasions, some storms have been observed reaching the strength of a Category 1 hurricane, on the Saffir–Simpson scale, and Cyclone Ianos in 2020 was recorded reaching Category 2 intensity. The main societal hazard posed by medicanes is not usually from destructive winds, but through life-threatening torrential rains and flash floods.

Cyclone Qendresa, also known as Medicane Qendresa, was one of the most intense Mediterranean tropical-like cyclones on record, which struck Malta and the Italian island of Sicily in 2014. The storm formed on 5 November and rapidly intensified two days later, reaching peak intensity on 7 November, due to a cold-core low aloft. Qendresa directly hit Malta in the afternoon and then crossed the eastern coast of Sicily on 8 November. Later, the cyclone weakened significantly and dissipated over Crete on 11 November. Academic sources indicate that Qendresa transitioned into a subtropical cyclone, prior to reaching peak intensity. Qendresa caused three fatalities, and at least $250 million in damages in Italy.

Malta was ruled by the Byzantine Empire, from the time of the Byzantine conquest of Sicily in 535-6 to 869-870, when the islands were occupied by Arabs. Evidence for the three centuries of Byzantine rule in Malta is very limited, and at times ambiguous. Historians theorise that Byzantine Malta was exposed to the same phenomena affecting the Central Mediterranean, namely a considerable influx of Greek settlers and Hellenic culture, administrative changes brought about by the reorganisation of Sicily along the lines of a Byzantine theme, and significant naval activity in the Mediterranean following the rise of Islam.

The Maserati Grecale is a front-engine, five-door, five passenger compact luxury crossover SUV (D-segment) manufactured and marketed by the Maserati subdivision of Stellantis, entering production at the company's Cassino Plant in March 2022. Internally designated model M182, the Grecale shares the company's Giorgio platform with the Alfa Romeo Stelvio and the fifth generation Jeep Grand Cherokee.

Cyclone Ianos, also known as Medicane Ianos, was a rare medicane that impacted the eastern Mediterranean on 17 and 18 September 2020, especially Greece. Ianos developed from an area of low pressure over the Gulf of Sidra that quickly began tropical cyclogenesis while moving over warm waters. After receiving various names from different meteorological centers, the storm, dubbed Ianos by the METEO unit of the National Observatory of Athens, rapidly intensified while moving northeastward. After scraping Italy, the storm went on to strike Malta and Crete with tropical storm-force winds. Despite land interaction, the small cyclone reached its peak intensity of 159 km/h (99 mph) with wind gusts up to 195 km/h (121 mph) on 18 September, equivalent to a Category 2 hurricane on the Saffir–Simpson scale, immediately before making landfall in southwestern Greece. After landfall, Ianos turned back out to sea and moved south-southeastward, before dissipating on 21 September.

Cyclone Apollo, also known as Medicane Nearchus, was a powerful Mediterranean tropical-like cyclone that affected many countries on the Mediterranean coast, especially Italy, in 2021. The storm killed 7 people total, due to flooding from the cyclone, in the countries of Tunisia, Algeria, Malta, and Italy, where the worst of the effects have been felt, especially on the island of Sicily. Damage estimates by the Aon Benfield were set at more than $245 million.














