Related Research Articles
The Wisconsin Range is a major mountain range of the Horlick Mountains in Antarctica, comprising the Wisconsin Plateau and numerous glaciers, ridges and peaks bounded by the Reedy Glacier, Shimizu Ice Stream, Horlick Ice Stream and the interior ice plateau.

James Ross Island is a large island off the southeast side and near the northeastern extremity of the Antarctic Peninsula, from which it is separated by Prince Gustav Channel. Rising to 1,630 metres (5,350 ft), it is irregularly shaped and extends 64 km in a north–south direction. It was charted in October 1903 by the Swedish Antarctic Expedition under Otto Nordenskiöld, who named it for Sir James Clark Ross, the leader of a British expedition to this area in 1842 that discovered and roughly charted a number of points along the eastern side of the island. The style, "James" Ross Island is used to avoid confusion with the more widely known Ross Island in McMurdo Sound.
Martin Glacier is a glacier, 3 nautical miles (6 km) wide and 9 nautical miles (17 km) long, which flows west and then northwest from the south side of Mount Lupa to the southeast corner of Rymill Bay where it joins Bertrand Ice Piedmont, on the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. It was first surveyed in 1936 by the British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE) under John Riddoch Rymill, and was resurveyed in 1948–1949 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey. The glacier was named for James Hamilton Martin, a member of the British Australian and New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (1929–1931) under Sir Douglas Mawson, and first mate of the Penola during the BGLE.

The Prince Charles Mountains are a major group of mountains in Mac. Robertson Land in Antarctica, including the Athos Range, the Porthos Range, and the Aramis Range. The highest peak is Mount Menzies, with a height of 3,228 m (10,591 ft). Other prominent peaks are Mount Izabelle and Mount Stinear. These mountains, together with other scattered peaks, form an arc about 420 km (260 mi) long, extending from the vicinity of Mount Starlight in the north to Goodspeed Nunataks in the south.
Athos Range is the northernmost range in the Prince Charles Mountains of Mac. Robertson Land, Antarctica. The range consists of many individual mountains and nunataks that trend east–west for 40 miles (64 km) along the north side of Scylla Glacier.
The Porthos Range is the second range south in the Prince Charles Mountains of Antarctica, extending for about 30 miles in an east-to-west direction between Scylla Glacier and Charybdis Glacier. First visited in December 1956 by the Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions (ANARE) southern party under W.G. Bewsher (1956-57) and named after Porthos, a character in Alexandre Dumas, père's novel The Three Musketeers, the most popular book read on the southern journey.

Bachstrom Point is a headland on the northeast side of Beascochea Bay, 8 nautical miles (15 km) southeast of Cape Perez on the southwest coast of Kyiv Peninsula in Graham Land, Antarctica. It was first charted by the British Graham Land Expedition, 1934–37, under John Rymill, and named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1959 for Johann Bachstrom, the author in 1734 of a classic pamphlet recognizing scurvy as a nutritional deficiency disease and prescribing the necessary measures for its prevention and cure.

Barilari Bay is a bay 12 nautical miles (22 km) long and 6 nautical miles (11 km) wide, between Cape Garcia and Loqui Point on the west coast of Graham Land. The glaciers Birley, Lawrie, Weir and Bilgeri feed the bay.

Belgica Glacier is a glacier 8 nautical miles (15 km) long, flowing into Trooz Glacier to the east of Lancaster Hill on Kyiv Peninsula, on the west coast of Graham Land. It was first charted by the British Graham Land Expedition under John Rymill, 1934–37, and named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1959 after the RV Belgica, the ship of the Belgian Antarctic Expedition under Gerlache which explored this area in 1897–99.

Birley Glacier is a glacier, at least 10 nautical miles (19 km) long, flowing west into the eastern extremity of Barilari Bay north of Vardun Point, on the west coast of Graham Land. First seen and roughly surveyed in 1909 by the French Antarctic Expedition under Jean-Baptiste Charcot, it was re-surveyed in 1935–36 by the British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE) under John Rymill, and later named for Kenneth P. Birley, who contributed toward the cost of the BGLE, 1934–37.
Comrie Glacier is a glacier 13 nautical miles (24 km) long, flowing west to enter the head of Bigo Bay on the west coast of Graham Land. It was first sighted and roughly surveyed by the French Antarctic Expedition in 1909. It was resurveyed in 1935–36 by the British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE), and later named for Leslie J. Comrie, founder and first director of the Scientific Computing Service Ltd, London, who, as superintendent of HM Nautical Almanac Office in 1934, greatly assisted the BGLE, 1934–37, by providing advance copies of The Nautical Almanac up to 1937.
Darboux Island is an island 1 nautical mile (2 km) long rising to 270 metres (900 ft), lying 3 nautical miles (6 km) west of Cape Perez off the west coast of Graham Land. It was discovered by the French Antarctic Expedition, 1903–05, and named by Jean-Baptiste Charcot for Jean Gaston Darboux, the noted French mathematician.
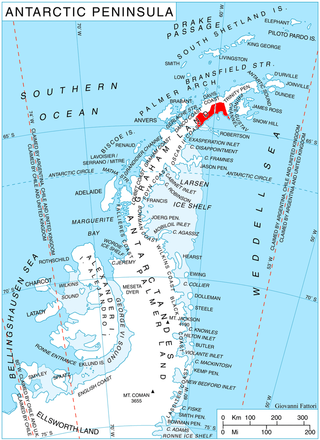
Edgeworth Glacier is a glacier 12 nautical miles (22 km) long, flowing south-southwestwards from the edge of Detroit Plateau below Wolseley Buttress and Paramun Buttress between Trave Peak and Chipev Nunatak into Mundraga Bay west of Sobral Peninsula, on the Nordenskjöld Coast of Graham Land. It was mapped from surveys by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (1960–61), and was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for Richard Lovell Edgeworth, the British inventor of the "portable railway," the first track-laying vehicle, in 1770.
Erskine Glacier is a glacier 16 nautical miles (30 km) long on the west coast of Graham Land, flowing west into Darbel Bay to the north of Hopkins Glacier. It was first surveyed by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) in 1946–47, and named "West Gould Glacier". With East Gould Glacier it was reported to fill a transverse depression across Graham Land, but further survey in 1957 showed no close topographical alignment between the two. The name Gould has been limited to the east glacier and an entirely new name, for Angus B. Erskine, leader of the first FIDS party to travel down the glacier and to survey it in detail, has been approved for the west glacier.
Forel Glacier is a glacier 1.5 nautical miles (3 km) wide and 4 nautical miles (7 km) long, flowing southwest into Blind Bay, on the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. It was first roughly surveyed in 1936 by the British Graham Land Expedition under John Rymill. Its lower reaches were surveyed in 1949 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey, and the glacier named by them for François-Alphonse Forel, a noted Swiss glacier physicist and author, and first President of the International Commission of Glaciers in 1894.
The Gaunt Rocks are a small group of rocks lying 2 nautical miles (4 km) west of the Barros Rocks, in the Wilhelm Archipelago. They were roughly charted by the British Graham Land Expedition under John Rymill, 1934–37, and more accurately positioned by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey from photos taken by Hunting Aerosurveys Ltd in 1956–57. The name, given by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1959, is descriptive of these desolate, grim-looking rocks.
The Gedges Rocks are a group of rocks located 3 nautical miles (6 km) north-northwest of Grim Rock and 10 nautical miles (19 km) west-southwest of Cape Tuxen, off the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. They were discovered by the British Graham Land Expedition, 1934–37, and named "Gedges Reef" after The Gedges, a dangerous reef off the mouth of the Helford River in Cornwall, England. In 1971 the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee reported that the term rocks is more appropriate for this feature.

Luke Glacier is a glacier at least 15 nautical miles (28 km) long, flowing northwest into the head of Leroux Bay on the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. It is surmounted by Mount Chevreux on the south, Mount Perchot on the southwest and Mount Radotina on the northeast. The glacier was first sighted and roughly surveyed in 1909 by the Fourth French Antarctic Expedition. It was resurveyed in 1935–36 by the British Graham Land Expedition and later named for George Lawson Johnston, 1st Baron Luke of Pavenham, Chairman of Bovril Ltd, who contributed toward the cost of the expedition.

Leroux Bay is a bay 9 nautical miles (17 km) long in a northwest–southeast direction and averaging 5 nautical miles (9 km) wide, between Nunez Point and the narrow Magnier Peninsula surmounted by the Magnier Peaks and Lisiya Ridge, along the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. The glaciers Chernomen, Luke and Muldava feed the bay.
References
- ↑ "Grim Rock". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior . Retrieved 2012-05-08.
- ↑ Alberts, Fred G., ed. (June 1995). Geographic Names of the Antarctic (PDF) (second ed.). United States Board on Geographic Names. p. 297. Retrieved 2012-04-05.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from "Grim Rock". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from "Grim Rock". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.