The Devonian is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic, spanning 60 million years from the end of the Silurian, 419.2 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, 358.9 Mya. It is named after Devon, England, where rocks from this period were first studied.
The Permian is a geologic period and system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous period 298.9 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic period 251.902 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleozoic era; the following Triassic period belongs to the Mesozoic era. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the region of Perm in Russia.
The Silurian is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at 443.8 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, 419.2 Mya. The Silurian is the shortest period of the Paleozoic Era. As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the exact dates are uncertain by several million years. The base of the Silurian is set at a series of major Ordovician–Silurian extinction events when up to 60% of marine genera were wiped out.

The gastropods, more commonly known as snails and slugs, belong to a large taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca, called Gastropoda. This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, from freshwater, and from the land. There are many thousands of species of sea snails and slugs, as well as freshwater snails, freshwater limpets, and land snails and slugs.

Goniatids, informally Goniatites, are ammonoid cephalopods that form the order Goniatitida, derived from the more primitive Agoniatitida during the Middle Devonian some 390 million years ago. Goniatites (goniatitids) survived the Late Devonian extinction to flourish during the Carboniferous and Permian only to become extinct at the end of the Permian some 139 million years later.
In the geologic timescale, the Bajocian is an age and stage in the Middle Jurassic. It lasted from approximately 170.3 Ma to around 168.3 Ma. The Bajocian age succeeds the Aalenian age and precedes the Bathonian age.
The Late Triassic is the third and final of three epochs of the Triassic Period in the geologic timescale. The Triassic-Jurassic extinction event began during this epoch and is one of the five major mass extinction events of the Earth. The corresponding series is known as the Upper Triassic. In Europe the epoch was called the Keuper, after a German lithostratigraphic group that has a roughly corresponding age. The Late Triassic spans the time between 237 Ma and 201.3 Ma. The Late Triassic is divided into the Carnian, Norian and Rhaetian ages.
The Emsian is one of three faunal stages in the Early Devonian epoch. It lasted from 407 ± 2.8 million years ago to 397.5 ± 2.7 million years ago. It was preceded by the Pragian stage and followed by the Eifelian stage.

Bramerton Pits is a 0.7-hectare (1.7-acre) geological Site of Special Scientific Interest north of the village of Bramerton in Norfolk on the southern banks of the River Yare. It is a Geological Conservation Review site.
Benthamaspis is an extinct genus from a well-known class of fossil marine arthropods, the trilobites. It lived during the early part of the Arenig stage of the Ordovician Period, a faunal stage which lasted from approximately 478 to 471 million years ago.

Megalaspides is an extinct genus from a well-known class of fossil marine arthropods, the trilobites. It lived during the later part of the Arenig stage of the Ordovician Period, approximately 478 to 471 million years ago.
Kingstonia is an extinct genus from a well-known class of fossil marine arthropods, the trilobites. It lived from 501 to 490 million years ago during the Dresbachian faunal stage of the late Cambrian Period.

In geology, the Arenigian refers both to a time interval during the Lower Ordovician period and also to the suite of rocks which were deposited during this interval.

Callawayasaurus is a genus of plesiosaur from the family Elasmosauridae. When the first Callawayasaurus fossil was first discovered by Samuel Paul Welles in 1962, it was described as Alzadasaurus colombiensis before being moved into its current genus by Kenneth Carpenter in 1999.
The Dresbachian is a Maentwrogian regional stage of North America, lasting from 501 to 497 million years ago. It is part of the Upper Cambrian and is defined by four trilobite zones. It overlaps with the ICS-stages Guzhangian, Paibian and the lowest Jiangshanian.

Tarpons are large fish of the genus Megalops; one species is native to the Atlantic, and the other to the Indo-Pacific Seas. They are the only members of the family Megalopidae.

Crustaceans may pass through a number of larval and immature stages between hatching from their eggs and reaching their adult form. Each of the stages is separated by a moult, in which the hard exoskeleton is shed to allow the animal to grow. The larvae of crustaceans often bear little resemblance to the adult, and there are still cases where it is not known what larvae will grow into what adults. This is especially true of crustaceans which live as benthic adults, more-so than where the larvae are planktonic, and thereby easily caught.
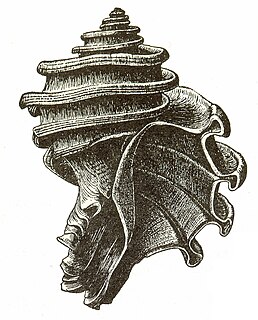
Ecphora is the common name for a group of extinct predatory marine gastropod mollusks within the family Muricidae, the rocks snails or murexes. The common name is based on the first officially described genus, Ecphora. The entire lineage of these ocenebrinid murexes are descended from the Eocene murex, Tritonopsis. Ecphoras are indigenous to the North American Eastern Seaboard, being found in marine strata from the Late Eocene until their extinction during the Pliocene. Many ecphora species are important index fossils.

Crustaceans form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such familiar animals as crabs, lobsters, crayfish, shrimps, prawns, krill, woodlice, and barnacles. The crustacean group is usually treated as a class under subphylum Mandibulata and because of recent molecular studies it is now well accepted that the crustacean group is paraphyletic, and comprises all animals in the Pancrustacea clade other than hexapods. Some crustaceans are more closely related to insects and other hexapods than they are to certain other crustaceans.

Borealopelta is a genus of nodosaurid ankylosaur from the Early Cretaceous of Alberta, Canada. It contains a single species, B. markmitchelli, named in 2017 by Caleb Brown and colleagues from a well-preserved specimen known as the Suncor nodosaur. Discovered at an oil sands mine north of Fort McMurray, Alberta, that is owned by the Suncor Energy company, the specimen is remarkable for being among the best preserved dinosaur fossils of its size ever found. It preserved not only the armor (osteoderms) in their life positions, but also remains of their keratin sheaths, overlying skin, and stomach contents from the animal's last meal. Melanosomes were also found that indicate the animal had a reddish skin tone.












