Related Research Articles

The Gdańsk Voivodeship was a voivodeship (province) of the Polish People's Republic from 1975 to 1989, and the Third Republic of Poland from 1989 to 1998. Its capital was Gdańsk, and it was centered on the region of Pomerelia. It was established on 1 June 1975, from the parts of the voivodeships of Gdańsk, and Bydgoszcz, and existed until 31 December 1998, when it was incorporated into then-established Pomeranian Voivodeship.

The Bielsko Voivodeship was a voivodeship (province) of the Polish People's Republic from 1975 to 1989, and the Third Republic of Poland from 1989 to 1998. Its capital was Bielsko-Biała. It was established on 1 June 1975, from the parts of the voivodeships of Katowice, and Kraków, and existed until 31 December 1998, when it was partitioned between then-established Lesser Poland, and Silesian Voivodeships.
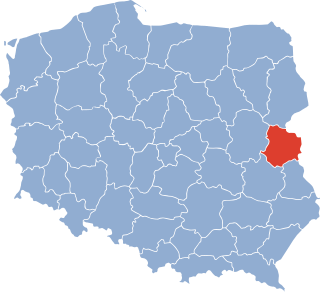
The Biała Podlaska Voivodeship was a voivodeship (province) of the Polish People's Republic from 1975 to 1989, and the Third Republic of Poland from 1989 to 1998. Its capital was Biała Podlaska. It was established on 1 June 1975, from the parts of the voivodeships of Lublin, and Warsaw Voivodeship, and existed until 31 December 1998, when it was partitioned between then-established Lublin, and Masovian Voivodeships.

The Warsaw Voivodeship, between 1975 and 1990 known as the Warsaw Capital Voivodeship, was a voivodeship (province) of the Polish People's Republic from 1975 to 1989, and the Third Republic of Poland from 1989 to 1998. Its capital was Warsaw, and it was located in the central Masovia. It was established on 1 June 1975, from the part of the Warsaw Voivodeship, and a city voivodeship of Warsaw, and existed until 31 December 1998, when it was incorporated into then-established Masovian Voivodeship.

Dziennik Ustaw or Dziennik Ustaw Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej is the most important Polish publication of legal acts. It is the only official source of law for promulgation of Polish laws. The publication of this journal is solely the responsibility of the Prime Minister of the Republic of Poland. 'Dziennik Ustaw' traces its history to the 1918 'Dziennik Praw Królestwa Polskiego' and has changed its name several times during its existence.

A sołtys is a head of a sołectwo elected by its permanent citizens in a village meeting. According to data from 2010, Poland had 40 thousand sołtys, 30.7% of which were women.
Gromada is a Polish word meaning "gathering", "group", or "assembly". In the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, the term referred to a village organization which embraced all the inhabitants of a village and acted as a local authority, as well as overseeing tax payments. In this sense, the gromada developed between the 16th and 18th centuries, and continued to function in Congress Poland. Their chiefs took the title of sołtys and were elected by the local population.

Białystok Voivodeship was a unit of administrative division and local government in Poland from 1944 to 1975, when its purview was separated into eastern Suwałki Voivodeship, Łomża Voivodeship and Białystok Voivodeship (1975–1998). Its capital city was Białystok. The establishment of Podlaskie Voivodeship in 1999 was essentially a reunion of the areas of Białystok Voivodeship (1945–1975).
Mucharzew is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Osiek, within Staszów County, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, in south-central Poland. It lies approximately 7 kilometres (4 mi) west of Osiek, 15 km (9 mi) south-east of Staszów, and 67 km (42 mi) south-east of the regional capital Kielce.
Ossala is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Osiek, within Staszów County, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, in southern Poland. It lies approximately 7 kilometres (4 mi) south-west of Osiek, 17 km (11 mi) south-east of Staszów, and 69 km (43 mi) south-east of the regional capital Kielce.
Ossala-Lesisko is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Osiek, within Staszów County, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, in south-central Poland. It lies approximately 9 kilometres (6 mi) west of Osiek, 14 km (9 mi) south-east of Staszów, and 67 km (42 mi) south-east of the regional capital Kielce.
Trzcianka-Kolonia is a colony in the administrative district of Gmina Osiek, within Staszów County, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, in south-central Poland. It lies approximately 6 kilometres (4 mi) south-west of Osiek, 20 km (12 mi) south-east of Staszów, and 72 km (45 mi) south-east of the regional capital Kielce.
Tursko Wielkie is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Osiek, within Staszów County, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, in south-central Poland. It lies approximately 9 kilometres (6 mi) south-west of Osiek, 19 km (12 mi) south-east of Staszów, and 72 km (45 mi) south-east of the regional capital Kielce.

Brodnica Górna is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Kartuzy, within Kartuzy County, Pomeranian Voivodeship, in northern Poland. It lies approximately 11 kilometres (7 mi) south-west of Kartuzy and 38 km (24 mi) west of the regional capital Gdańsk. It is located within the ethnocultural region of Kashubia in the historic region of Pomerania.
Gromada Osiek is a group of several Polish villages, constituted at the lowest tier of local government. They take over the role previously played by Gmina Osiek at a smaller scale than Gmina Osiek. In communist Poland between September 29, 1954 to December 31, 1972 these villages were introduced as a Polish word meaning “Osiek”. These units are created by the Communist Polish Law and have legal effect.
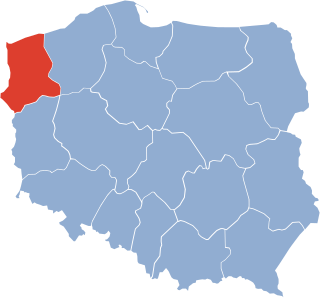
The Szczecin Voivodeship was a voivodeship (province) with its capital in Szczecin, that was centered on the Farther Pomerania. It existed from 1946 to 1975. Until 19 February 1947 it was under the administration of Provisional Government of National Unity, which then was replaced by the Polish People's Republic. It was established on 28 June 1946, when it was carved out of the territory of the District of the Western Pomerania, and parts of the Gdańsk, and Pomeranian Voivodeships. On 6 July 1950, its eastern half was incorporated into then-established Koszalin Voivodeship, and the voivodeship ceased to exist on 31 May 1975, when it was replaced by then-established Szczecin and Gorzów Voivodeships.

The Kraków Voivodeship, from 1975 to 1984 known as the Kraków Metropolitan Voivodeship, was a voivodeship (province) of the Polish People's Republic from 1975 to 1989, and the Republic of Poland from 1989 to 1998. Its territory included its capital, Kraków and the surrounding municipalities. It was established on 1 June 1975 from the part of the Kraków Voivodeship, and the city of Kraków, which until then acted as a separate administrative division. It existed until 31 December 1998, when it got incorporated into then-established Lesser Poland Voivodeship.

The Koszalin Voivodeship was a voivodeship (province) of the Polish People's Republic, with capital in Koszalin, that existed from 1950 to 1975. It was established on 6 July 1950, from the eastern half of the Szczecin Voivodeship, and existed until 31 May 1975, when it was partitioned between then-established voivodeships of Koszalin, Słupsk, and Piła.

The Koszalin Voivodeship was a voivodeship (province) of the Polish People's Republic from 1975 to 1989, and the Third Republic of Poland from 1989 to 1998. Its capital was Koszalin, and it was centered on the eastern Farther Pomerania. It was established on 1 June 1975, from the part of the Koszalin Voivodeship, and existed until 31 December 1998, when it was incorporated into then-established West Pomeranian Voivodeship.
References
- ↑ "Dz.U. 1954 nr 43 poz. 191" [Journal of the Laws of 1954, No. 43, item 191]. Ustawa z dnia 25 września 1954 r. o reformie podziału administracyjnego wsi i powołaniu gromadzkich rad narodowych[Act of September 25, 1954 on the reform of administrative division and the establishment of village and the constituent Gromadzka National Councils] (in Polish). They signed under this act: Zawadzki, Aleksander — President of Council of State of the Republic of Poland; Rybicki, Marian — Secretary Council of State. Warsaw, Poland: Lower house of the Polish parliament. 25 September 1954. pp. 349–353.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: others (link) - ↑ "Dz.U. 1972 nr 49 poz. 312" [Journal of the Laws of 1972, No. 49, item 312]. Ustawa z dnia 29 listopada 1972 r. o utworzeniu gmin i zmianie ustawy o radach narodowych[Act of November 29, 1972 on the establishment of gminas and amending the law on National Councils] (in Polish). They signed under this act: Jabłoński, Henryk — President of Council of State of the Republic of Poland; Stasiak, Ludomir — Secretary Council of State. Warsaw, Poland: Lower house of the Polish parliament. 29 November 1972. pp. 474–480. Archived from the original on 26 January 2013. Retrieved 17 January 2012.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: others (link) - 1 2 Cf. Kaczmarek, Leon (ed.); Taszycki, Witold (1970). Urzędowe nazwy miejscowości i obiektów fizjograficznych. 33. Powiat staszowski województwo kieleckie[Official Names of Localities and Physiographic Objects. 33. Staszów County Kielce Voivodeship] (in Polish). Commission for Establishing Names of Localities and Physiographic Objects (to business use). Vol. 33. Warsaw, Poland: Council of Ministers' Office. Cabinet Office for bureaux of the Supervisory Boards. pp. 62–67, 77–96.
{{cite book}}:|first1=has generic name (help) - ↑ Cf. Wykaz Gromad Polskiej Rzeczypospolitej Ludowej według stanu z dnia 1 VII 1952 r.[List of Gromadas of the Polish People’s Republic according to of July 1, 1952] (in Polish). Warsaw: Polish People’s Republic. Central Statistical Office. 1952.