macOS is a Unix operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc. since 2001. It is the primary operating system for Apple's Mac computers. Within the market of desktop and laptop computers it is the second most widely used desktop OS, after Microsoft Windows and ahead of ChromeOS.

Adobe Flash is a multimedia software platform used for production of animations, rich web applications, desktop applications, mobile apps, mobile games, and embedded web browser video players. Flash displays text, vector graphics, and raster graphics to provide animations, video games, and applications. It allows streaming of audio and video, and can capture mouse, keyboard, microphone, and camera input.
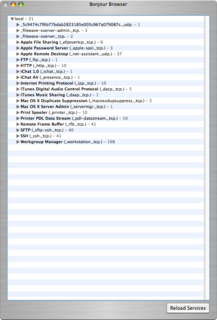
Bonjour is Apple's implementation of zero-configuration networking (zeroconf), a group of technologies that includes service discovery, address assignment, and hostname resolution. Bonjour locates devices such as printers, other computers, and the services that those devices offer on a local network using multicast Domain Name System (mDNS) service records.

iSync is a software application first released by Apple Inc. on Jan 2, 2003. Apple licensed the core technology from fusionOne. It ran only under Mac OS X and was used to synchronize contact and calendar data from Address Book and iCal with many non-Apple SyncML-enabled mobile phones via a Bluetooth or USB connection. Support for many devices was built-in, with newer devices being supported via manufacturer and third-party iSync Plugins. Support for Palm OS organizers and compatible smartphones was removed with the release of iSync 3.1 and Mac OS X 10.6 Snow Leopard. BlackBerry OS, Palm OS, and Windows Mobile devices could not be used with iSync, but were supported by third-party applications. Before the release of Mac OS X 10.4, iSync also synchronized a user's Safari bookmarks with the then .Mac subscription service provided by Apple.

Contacts is a computerized address book included with the Apple operating systems iOS, iPadOS and macOS, previously Mac OS X and OS X. It includes various cloud synchronization capabilities and integrates with other Apple applications and features, including iMessage, FaceTime and the iCloud service.

Quicksilver is a utility app for macOS. Originally developed as proprietary freeware by Nicholas Jitkoff of Blacktree, Inc., it is now an open-source project hosted on GitHub.

Dashboard is a discontinued feature of Apple Inc.'s macOS operating systems, used as a secondary desktop for hosting mini-applications known as widgets. These are intended to be simple applications that do not take time to launch. Dashboard applications supplied with macOS included a stock ticker, weather report, calculator, and notepad; while users could create or download their own.
A menu extra, menu item, menulet, or status item is a graphical control element in macOS. It is a small indicator that appears at the right of the menu bar. They often provide quick ways to use applications or display information, or control system-level variables. There are a number of third-party menu items available. Menu extras are similar to items in the Microsoft Windows notification area but are less common.
The Apple Developer Tools are a suite of software tools from Apple to aid in making software dynamic titles for the macOS and iOS platforms. The developer tools were formerly included on macOS install media, but are now exclusively distributed over the Internet. As of macOS 10.12, Xcode is available as a free download from the Mac App Store.
Apple's Macintosh computer supports a wide variety of fonts. This support was one of the features that initially distinguished it from other systems.

Mac OS X Snow Leopard is the seventh major release of macOS, Apple's desktop and server operating system for Macintosh computers.

Apple Push Notification service is a platform notification service created by Apple Inc. that enables third party application developers to send notification data to applications installed on Apple devices. The notification information sent can include badges, sounds, newsstand updates, or custom text alerts. It was first launched with iOS 3 on June 17, 2009. APNs support for local applications was later added to the Mac OS X API beginning with the release of Mac OS X 10.7 ("Lion"). Support for website notifications was later added with the release of Mac OS X 10.9 ("Mavericks").

Mac OS X Lion, also known as OS X Lion, is the eighth major release of macOS, Apple's desktop and server operating system for Macintosh computers.

The App Store is a digital distribution platform for macOS apps, created and maintained by Apple Inc. The platform was announced on October 20, 2010, at Apple's "Back to the Mac" event. Apple began accepting app submissions from registered developers on November 3, 2010, in preparation for its launch.
Notification Center is a feature in iOS and macOS that provides an overview of alerts from applications. It displays notifications until the user completes an associated action, rather than requiring instant resolution. Users may choose what applications appear in Notification Center, and how they are handled. Initially released with iOS 5 in October 2011, Notification Center was made available on Macs as part of OS X Mountain Lion in July 2012.

OS X Mountain Lion is the ninth major release of macOS, Apple Inc.'s desktop and server operating system for Macintosh computers. OS X Mountain Lion was released on July 25, 2012, for purchase and download through Apple's Mac App Store, as part of a switch to releasing OS X versions online and every year, rather than every two years or so. Named to signify its status as a refinement of the previous OS X version, Lion, Apple's stated aims in developing Mountain Lion were to allow users to more easily manage and synchronise content between multiple Apple devices and to make the operating system more familiar.

OS X Yosemite is the eleventh major release of macOS, Apple Inc.'s desktop and server operating system for Macintosh computers.

macOS Sierra is the thirteenth major release of macOS, Apple Inc.'s desktop and server operating system for Macintosh computers. The name "macOS" stems from the intention to uniform the operating system's name with that of iOS, watchOS and tvOS. Sierra is named after the Sierra Nevada mountain range in California and Nevada. Its major new features concern Continuity, iCloud, and windowing, as well as support for Apple Pay and Siri.

macOS Big Sur is the seventeenth major release of macOS, Apple Inc.'s operating system for Macintosh computers. It was announced at Apple's Worldwide Developers Conference (WWDC) on June 22, 2020, and was released to the public on November 12, 2020.














