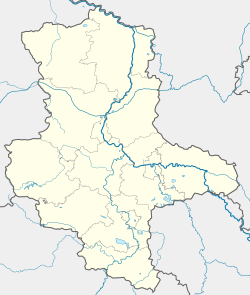
The Saale, also known as the Saxon Saale and Thuringian Saale, is a river in Germany and a left-bank tributary of the Elbe. It is not to be confused with the smaller Franconian Saale, a right-bank tributary of the Main, or the Saale in Lower Saxony, a tributary of the Leine.
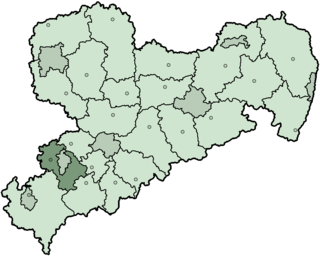
Zwickauer Land is a former Kreis (district) in the south-west of the Free State of Saxony, Germany. Neighboring districts were Chemnitzer Land, Stollberg, Aue-Schwarzenberg, Vogtlandkreis, and the districts Greiz and Altenburger Land in Thuringia. The district-free city of Zwickau was located in the center of the district and nearly completely surrounded by it.

Naumburg is a town in the district Burgenlandkreis, in the state of Saxony-Anhalt, Central Germany. It has a population of around 33,000. The Naumburg Cathedral became a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2018. This UNESCO designation recognizes the processes that shaped the European continent during the High Middle Ages between 1000 and 1300: Christianization, the so-called "Landesausbau" and the dynamics of cultural exchange and transfer characteristic for this very period.
Wethautal is a Verbandsgemeinde in the Burgenlandkreis district in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Before 1 January 2010, it was a Verwaltungsgemeinschaft. It is situated along the small river Wethau, a tributary of the Saale, southeast of Naumburg. The seat of the Verbandsgemeinde is in Osterfeld.

Freyburg is a town in the Burgenlandkreis district, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It is situated on the river Unstrut, 9 km northwest of Hanseatic Naumburg, 63 km from Leipzig and 231 km from Berlin. It is part of the Verwaltungsgemeinschaft Unstruttal. On 1 July 2009 it absorbed the former municipalities Pödelist, Schleberoda, Weischütz and Zeuchfeld. Freyburg consists of the Ortsteile (divisions) Dobichau, Freyburg, Nißmitz, Pödelist, Schleberoda, Weischütz, Zeuchfeld and Zscheiplitz.

Bergstadt Lößnitz, sometimes also called Muhme (“Aunt”) for its age, is a town in the district of Erzgebirgskreis, Saxony, Germany, and belongs to the Town League of Silberberg. Its name comes from the Slavic lesnice, meaning “forest place”.

Schönburg is a municipality in the Burgenlandkreis district, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It is situated 5 km east of Naumburg, on the river Saale. It is part of the Verbandsgemeinde Wethautal.

Bärenbach is an Ortsgemeinde – a municipality belonging to a Verbandsgemeinde, a kind of collective municipality – in the Bad Kreuznach district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It belongs to the Verbandsgemeinde Kirner Land, whose seat is in the town of Kirn.

Becherbach bei Kirn is an Ortsgemeinde – a municipality belonging to a Verbandsgemeinde, a kind of collective municipality – in the Bad Kreuznach district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It belongs to the Verbandsgemeinde Kirner Land, whose seat is in the town of Kirn. Becherbach bei Kirn should not be confused with Becherbach. Becherbach bei Kirn has borne the tag “bei Kirn” since 1 July 1969, at which time both municipalities found themselves in the same district as a result of administrative reform.
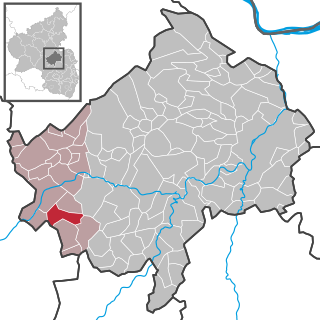
Heimweiler is an Ortsgemeinde – a municipality belonging to a Verbandsgemeinde, a kind of collective municipality – in the Bad Kreuznach district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It belongs to the Verbandsgemeinde Kirner Land, whose seat is in the town of Kirn.
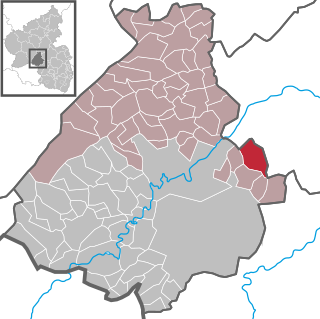
Schmidthachenbach is an Ortsgemeinde – a municipality belonging to a Verbandsgemeinde, a kind of collective municipality – in the Birkenfeld district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It belongs to the Verbandsgemeinde Herrstein-Rhaunen, whose seat is in Herrstein.

Riegenroth is an Ortsgemeinde – a municipality belonging to a Verbandsgemeinde, a kind of collective municipality – in the Rhein-Hunsrück-Kreis (district) in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It belongs to the Verbandsgemeinde Simmern-Rheinböllen, whose seat is in Simmern. Riegenroth is a recognized recreational resort (Erholungsort).
Joachim, Count of Schönburg-Glauchau was the nominal successor head of the former mediatised German Counts of Schönburg-Glauchau until 1945. Dispossessed and expelled from his homeland in 1945, he and his family migrated to the Rhineland, where he was an author and journalist. After the fall of the Berlin Wall, he returned to his homeland, represented the district in the Bundestag, and served in local government.

Schönburg is an old European noble family of princely and historically sovereign rank. It formerly owned large properties in present-day Saxony, Thuringia and Bohemia. As a former ruling and mediatized family, it belongs to the Hochadel. The family today includes a princely and a comital branch.

Stein Castle is a Saxon castle located southeast of Zwickau in the village of Stein in the municipality of Hartenstein on the rocky banks of the Zwickauer Mulde in the east German state of Saxony.

The Naumburg Cathedral and the High Medieval Cultural Landscape of the Rivers Saale and Unstrut is situated in the state of Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Naumburg Cathedral and the surrounding cultural landscape were proposed by Germany as a World Heritage Site. On July 1, 2018, only Naumburg Cathedral was designated by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site. This article discusses the cathedral and its cultural landscape based on the submissions in 1998 (cathedral) and 2005.

Schönburg Castle, is in the municipality of Schönburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It has been proposed by Germany as a World Heritage Site.

Saaleck is a village in the former municipality of Bad Kösen, since 2010 part of the town of Naumburg in the district of Burgenlandkreis in the German state of Saxony-Anhalt.

The village of Flemmingen is one of the eleven components of the cultural landscape Naumburg Cathedral and the High Medieval Cultural Landscape of the Rivers Saale and Unstrut that has been proposed by the Federal Republic of Germany for inscription in the List of World Heritage. The World Heritage nomination is representative for the processes that shaped the continent during the High Middle Ages between 1000 and 1300: Christianization, the so-called “Landesausbau” and the dynamics of cultural exchange and transfer characteristic for this very period.