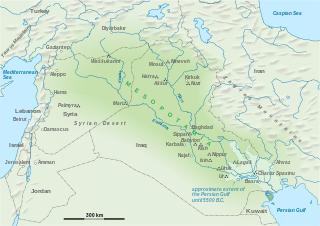
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq. In the broader sense, the historical region of Mesopotamia also includes parts of present-day Iran, Turkey, Syria and Kuwait.

Sumer is the earliest known civilization, located in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia, emerging during the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. Like nearby Elam, it is one of the cradles of civilization, along with Egypt, the Indus Valley, the Erligang culture of the Yellow River valley, Caral-Supe, the Cucuteni–Trypillia culture of the Carpathian Mountains, and Mesoamerica. Living along the valleys of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, Sumerian farmers grew an abundance of grain and other crops, a surplus which enabled them to form urban settlements. The world's earliest known texts come from the Sumerian cities of Uruk and Jemdet Nasr, and date to between c. 3350 – c. 2500 BC, following a period of proto-writing c. 4000 – c. 2500 BC.
Uruk, known today as Warka, was an ancient city in the Near East, located east of the current bed of the Euphrates River, on an ancient, now-dried channel of the river. The site lies 93 kilometers northwest of ancient Ur, 108 kilometers southeast of ancient Nippur, and 24 kilometers southeast of ancient Larsa. It is 30 km (19 mi) east of modern Samawah, Al-Muthannā, Iraq.
Kish is an important archaeological site in Babil Governorate (Iraq), located 80 km (50 mi) south of Baghdad and 12 km (7.5 mi) east of the ancient city of Babylon. The Ubaid period site of Ras al-Amiyah is 8 km (5.0 mi) away. It was occupied from the Ubaid period to the Hellenistic period. In Early Dynastic times the city's patron deity was Ishtar with her consort Ea. Her temple, at Tell Ingharra, was (E)-hursag-kalama. By Old Babylonian times the patron deities had become Zababa, along with his consort, the goddess Bau and Istar. His temple Emeteursag was at Uhaimir.

Dilmun, or Telmun, was an ancient East Semitic-speaking civilization in Eastern Arabia mentioned from the 3rd millennium BC onwards. Based on contextual evidence, it was located in the Persian Gulf, on a trade route between Mesopotamia and the Indus Valley civilisation, close to the sea and to artesian springs. Dilmun encompassed Bahrain, Kuwait, and eastern Saudi Arabia. This area is certainly what is meant by references to "Dilmun" among the lands conquered by King Sargon II and his descendants.

The Ubaid period is a prehistoric period of Mesopotamia. The name derives from Tell al-'Ubaid where the earliest large excavation of Ubaid period material was conducted initially in 1919 by Henry Hall and later by Leonard Woolley.
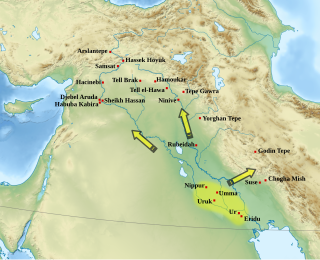
The Uruk period existed from the protohistoric Chalcolithic to Early Bronze Age period in the history of Mesopotamia, after the Ubaid period and before the Jemdet Nasr period. Named after the Sumerian city of Uruk, this period saw the emergence of urban life in Mesopotamia and the Sumerian civilization. The late Uruk period saw the gradual emergence of the cuneiform script and corresponds to the Early Bronze Age; it has also been described as the "Protoliterate period".

Tell Brak was an ancient city in Syria; its remains constitute a tell located in the Upper Khabur region, near the modern village of Tell Brak, 50 kilometers north-east of Al-Hasaka city, Al-Hasakah Governorate. The city's original name is unknown. During the second half of the third millennium BC, the city was known as Nagar and later on, Nawar.
Hamoukar is a large archaeological site located in the Jazira region of northeastern Syria, near the Iraqi and Turkish borders. The early settlement dates back to the 5th millennium BCE, and it existed simultaneously with the Ubaid and the early Uruk cultures. It was a big centre of obsidian production. In the 3rd millennium, this was one of the largest cities of Northern Mesopotamia, and extended to 105 ha.

The Civilization of Mesopotamia ranges from the earliest human occupation in the Paleolithic period up to Late antiquity. This history is pieced together from evidence retrieved from archaeological excavations and, after the introduction of writing in the late 4th millennium BC, an increasing amount of historical sources. While in the Paleolithic and early Neolithic periods only parts of Upper Mesopotamia were occupied, the southern alluvium was settled during the late Neolithic period. Mesopotamia has been home to many of the oldest major civilizations, entering history from the Early Bronze Age, for which reason it is often called a cradle of civilization.
The dynastic race theory was the earliest thesis to attempt to explain how predynastic Egypt developed into the sophisticated monarchy of Dynastic Egypt. The theory holds that the earliest roots of the ancient Egyptian dynastic civilisation were imported by invaders from Mesopotamia who then founded the First Dynasty and brought culture to the indigenous population. This theory had strong supporters in the Egyptological community in the first half of the 20th century, but has since lost mainstream support.

The Early Dynastic period is an archaeological culture in Mesopotamia that is generally dated to c. 2900 – c. 2350 BC and was preceded by the Uruk and Jemdet Nasr periods. It saw the development of writing and the formation of the first cities and states. The ED itself was characterized by the existence of multiple city-states: small states with a relatively simple structure that developed and solidified over time. This development ultimately led to the unification of much of Mesopotamia under the rule of Sargon, the first monarch of the Akkadian Empire. Despite this political fragmentation, the ED city-states shared a relatively homogeneous material culture. Sumerian cities such as Uruk, Ur, Lagash, Umma, and Nippur located in Lower Mesopotamia were very powerful and influential. To the north and west stretched states centered on cities such as Kish, Mari, Nagar, and Ebla.
Tepe Gawra is an ancient Mesopotamian settlement 15 miles NNE of Mosul in northwest Iraq that was occupied between 5000 and 1500 BC. It is roughly a mile from the site of Nineveh and 2 miles E of the site of Khorsabad. It contains remains from the Halaf period, the Ubaid period, and the Uruk period. Tepe Gawra contains material relating to the Halaf-Ubaid Transitional period c. 5,500–5,000 BC.
Tell es-Sweyhat is the name of a large archaeological site on the Euphrates River in northern Syria. It is located in Raqqa Governorate roughly 95 km northeast of Aleppo and 60 km south of Carchemish. Also, a Uruk site of Jebel Aruda and a Bronze Age site Tell Hadidi (Azu) are located just across the river.

The ancient Near East was the home of early civilizations within a region roughly corresponding to the modern Middle East: Mesopotamia, ancient Egypt, ancient Persia, Anatolia and the Armenian highlands, the Levant and the Arabian Peninsula. The ancient Near East is studied in the fields of ancient Near East studies, Near Eastern archaeology, and ancient history.

Habuba Kabira at Tell Qanas is the site of an Uruk settlement along the Euphrates in Syria, founded during the later part of the Uruk period. It was about 800 mi (1,300 km) from the city of Uruk. The site is now mostly underwater due to the Tabqa Dam project. It consists of Habuba Kabira South, which is protoliterate, and Habuba Kabira North, which is protoliterate, Middle Bronze Age, Late Bronze Age, and Roman.
Choghā Mīsh (Persian language; چغامیش čoġā mīš) dating back to about 6800 BC, is the site of a Chalcolithic settlement located in the Khuzistan Province Iran on the eastern Susiana Plain. It was occupied at the beginning of 6800 BC and continuously from the Neolithic up to the Proto-Literate period, thus spanning the time periods from Archaic through Proto-Elamite period. After the decline of the site about 4400 BC, the nearby Susa, on the western Susiana Plain, became culturally dominant in this area. Chogha Mish is located just to the east of Dez River, and about 25 kilometers to the east from the ancient Susa. The similar, though much smaller site of Chogha Bonut lies six kilometers to the west.

The art of Mesopotamia has survived in the record from early hunter-gatherer societies on to the Bronze Age cultures of the Sumerian, Akkadian, Babylonian and Assyrian empires. These empires were later replaced in the Iron Age by the Neo-Assyrian and Neo-Babylonian empires. Widely considered to be the cradle of civilization, Mesopotamia brought significant cultural developments, including the oldest examples of writing.

Egypt–Mesopotamia relations were the relations between the civilizations of ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia, in the Middle East. They seem to have developed from the 4th millennium BCE, starting in the Uruk period for Mesopotamia and the half a millennium younger Gerzean culture of Prehistoric Egypt, and constituted a largely one way body of influences from Mesopotamia into Egypt.

Ancient Mesopotamia at the Dawn of Civilization: the Evolution of an Urban Landscape is an ancient history monograph by Guillermo Algaze, published in 2008 by University of Chicago Press.











