Related Research Articles
Politics in the Philippines are governed by a three-branch system of government. The country is a democracy, with a president who is directly elected by the people and serves as both the head of state and the head of government. The president serves as the leader of the executive branch and is a powerful political figure. A president may only hold office for one six-year term. The bicameral Congress consists of two separate bodies: the Senate, with members elected at-large across the country, and the larger House of Representatives, with members chosen mostly from specific geographic districts. The Congress performs legislative functions. The judiciary is overseen by the Supreme Court of the Philippines and has extensive review jurisdiction over judgments issued by other governmental and administrative institutions.

Ferdinand Emmanuel Edralin Marcos Sr. was a Filipino politician and kleptocrat who served as the tenth president of the Philippines from 1965 to 1986. Marcos ruled the country as a dictator under martial law from 1972 to 1981, and with vastly expanded powers under the 1973 Constitution until he was deposed by a nonviolent revolution in 1986. Marcos described his rule's philosophy as "constitutional authoritarianism" under his Kilusang Bagong Lipunan. One of the most controversial figures in Filipino history, Marcos's regime was infamous for its corruption, extravagance, and brutality.

Maria Gloria Macaraeg Macapagal-Arroyo, often referred to by her initials PGMA and GMA, is a Filipino academic and politician who previously served as the 14th President of the Philippines from 2001 to 2010. She is the longest serving president of the Philippines since Ferdinand Marcos. Before her accession to the presidency, she served as the 10th Vice President of the Philippines from 1998 to 2001 under President Joseph Ejercito Estrada, making her the country's first female vice president, despite having run on an opposing ticket. She was also a Senator from 1992 to 1998. After her presidency, she was elected as the Representative of Pampanga's 2nd district in 2010 and later became the Speaker of the House of Representatives on 2018 to 2019. She was also serving in the congress as a Deputy Speaker from 2016 to 2017 and from 2022 until 2023. She is one of the only 2 Filipinos to hold at least three of the four highest offices in the country: vice president, president, and house speaker, alongside former President Sergio Osmeña.

Ferdinand "Bongbong" Romualdez Marcos Jr., commonly referred to by the initials PBBM or BBM, is a Filipino politician who is the 17th and current president of the Philippines. He previously served as a senator from 2010 to 2016. He is the second child and only son of tenth president, kleptocrat and dictator Ferdinand Marcos and former first lady Imelda Marcos.
The Progressive Party of the Philippines (PPP), also known as the Party for Philippine Progress, was a reformist political party that existed in the late 1950s and the 1960s. It is considered to be the earliest Filipino form of a genuine alternative party to the then-dominant political pair of the Nacionalista Party and the Liberal Party. The party ceased to exist by 1969.

The history of the Philippines, from 1965 to 1986, covers the presidency of Ferdinand Marcos. The Marcos era includes the final years of the Third Republic (1965–1972), the Philippines under martial law (1972–1981), and the majority of the Fourth Republic (1981–1986). By the end of the Marcos dictatorial era, the country was experiencing a debt crisis, extreme poverty, and severe underemployment.

The 1992 Philippine presidential and vice presidential elections were held on May 11, 1992. This was the first general election held under the 1987 Constitution. An estimated 80,000 candidates ran for 17,000 posts from the presidency down to municipal councilors.
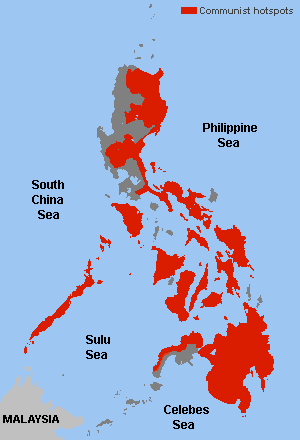
The New People's Army rebellion is an ongoing conflict between the government of the Philippines and the New People's Army (NPA), the armed wing of the Marxist–Leninist–Maoist Communist Party of the Philippines (CPP). It is the world's longest ongoing communist insurgency and the largest, most prominent communist armed conflict in the Philippines, with more than 43,000 insurgency-related fatalities between 1969 and 2008. Due to the involvement of the National Democratic Front of the Philippines (NDFP), the legal wing of the CPP, in the conflict, it is also called the CPP–NPA–NDF conflict, or simply the C/N/N conflict, especially in the context of peace talks with the Philippine government.

José "Peping" Sumulong Cojuangco Jr. is a Filipino politician, sports administrator, and businessman. He served as the 9th president of the Philippine Olympic Committee (POC) from 2004 to 2018. He previously served as the Representative of Tarlac's 1st district from 1961 to 1969 and 1987 to 1998. He began his political career in Paniqui, Tarlac where he served as councilor, vice mayor, and then mayor. A member of the Cojuangco political dynasty, President Corazon Cojuangco Aquino was his sister and President Benigno Aquino III was his nephew.

The 2010 Philippine presidential and vice presidential elections were held on Monday, May 10, 2010. The incumbent President of the Philippines, Gloria Macapagal Arroyo, was ineligible to seek re-election as per the 1987 Constitution.
The 2010 presidential campaign of Benigno Aquino III, then Philippine Senator, began when he announced his candidacy for the presidency of the Philippines at the Club Filipino, Greenhills, San Juan, Metro Manila, on September 9, 2009, 40 days after the death of his mother, former President Corazon Aquino. On September 21, 2009, Aquino's campaign announced that Senator Mar Roxas would be his vice presidential nominee.

The Solid North refers to the regional voting bloc of the northern provinces of the Philippines for politicians of Ilocano descent, more particularly the Marcos family and their allies, and also economic issues affecting the Ilocanos in general such as the tobacco industry. Often included in Solid North are the provinces in the Ilocos Region, Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR), and Cagayan Valley. The regions are considered to be a conservative/right-wing bastion for the country.

A general election in the Philippines took place on May 9, 2016, for executive and legislative branches for all levels of government – national, provincial, and local, except for the barangay officials.
Gun law in the Philippines is regulated by the Firearms and Explosives Division of the Philippine National Police. In order to possess a firearm in the Philippines, a person must be at a minimum age of 21 years and pass a background check to be issued a Possession License. They must also take a firearms training and safety course. Any history of mental illnesses or domestic violence within the individual or the family will cause an applicant to have their request rejected.

Banta ng Kahapon is a 1977 Philippine action film directed by Eddie Romero and starring Vic Vargas, Rafael Roco, Jr., Roland Dantes, and Chanda Romero.

Ferdinand Marcos was inaugurated to his first term as the 10th president of the Philippines on December 30, 1965. His inauguration marked the beginning of his two-decade long stay in power, even though the 1935 Philippine Constitution had set a limit of only two four-year terms of office. Marcos had won the Philippine presidential election of 1965 against the incumbent president, Diosdado Macapagal.
The 1969 reelection campaign of Ferdinand Marcos, the 10th president of the Philippines, started in July 1969 when incumbent President Ferdinand Marcos was unanimously nominated as the Presidential candidate of the Nacionalista Party, and concluded when the 1969 Philippine presidential election concluded with Marcos winning an unprecedented second full term as President of the Philippines. With Fernando Lopez as his vice president, he ran against the Liberal Party slate of Sergio Osmena Jr. and Genaro Magsaysay.

Ferdinand Marcos' second term as President of the Philippines began on December 30, 1969, as a result of his winning the 1969 Philippine presidential election on November 11, 1969. Marcos was the first and last president of the Third Philippine Republic to win a second full term. The end of Marcos' second term was supposed to be in December 1973, which would also have been the end of his presidency because the 1935 Constitution of the Philippines allowed him to have only two four-year terms. However, Marcos issued Proclamation 1081 in September 1972, placing the entirety of the Philippines under Martial Law and effectively extending his term indefinitely. He would only be removed from the presidency in 1986, as a result of the People Power Revolution.

The 2022 Philippine general election took place on May 9, 2022, for the executive and legislative branches of government at every level – national, provincial, and local – except for the barangay officials.
The 1969 Philippine balance of payments crisis was a currency crisis experienced by the Philippine economy as a result of heavy government spending linked to Ferdinand Marcos' campaign for his second presidential term in 1969. It was notable for being the first major economic crisis of the Marcos Administration, and for triggering the social unrest which was the rationalization for the proclamation of martial law in 1972.
References
- ↑ "Elections 2007: 3Gs rear hideous head on campaign's Day 3". GMA News Online. Retrieved 2018-07-21.
- ↑ DROGIN, BOB (1992-02-10). "'Guns, Goons, Gold' Time in Philippines : Elections: Authorities brace for traditional violence and cheating as campaigns get under way". Los Angeles Times. ISSN 0458-3035 . Retrieved 2018-07-21.
- ↑ An anarchy of families : state and family in the Philippines. Madison, Wis.: University of Wisconsin Press. 2009. ISBN 9780299229849. OCLC 223848773.
- ↑ Morallo, Audrey. "Sabotaging the System | 31 years of amnesia". The Philippine Star. Retrieved 2018-07-21.
- ↑ "Protecting the vote". Sun Star Philippines. 2016-02-29. Retrieved 2018-07-21.
- ↑ Smith, Tom (2010-05-05). "Philippine election plays more like a soap opera". The Guardian. Retrieved 2018-07-21.
- ↑ Rood, Steven (2010-05-12). "Philippine Election Update: Results Reported in Record Time, Largely Peaceful, Now What? - The Asia Foundation". The Asia Foundation. Retrieved 2018-07-21.
- ↑ "In Focus: Edie Romero's "Passionate Strangers" Opens Festival of Restored Filipino Films". National Commission for Culture and the Arts . July 12, 2004. Archived from the original on July 21, 2018. Retrieved April 26, 2017.