
A sextant is a doubly reflecting navigation instrument that measures the angular distance between two visible objects. The primary use of a sextant is to measure the angle between an astronomical object and the horizon for the purposes of celestial navigation. The estimation of this angle, the altitude, is known as sighting or shooting the object, or taking a sight. The angle, and the time when it was measured, can be used to calculate a position line on a nautical or aeronautical chart—for example, sighting the Sun at noon or Polaris at night to estimate latitude. Sighting the height of a landmark can give a measure of distance off and, held horizontally, a sextant can measure angles between objects for a position on a chart. A sextant can also be used to measure the lunar distance between the moon and another celestial object in order to determine Greenwich Mean Time and hence longitude. The principle of the instrument was first implemented around 1731 by John Hadley (1682–1744) and Thomas Godfrey (1704–1749), but it was also found later in the unpublished writings of Isaac Newton (1643–1727). Additional links can be found to Bartholomew Gosnold (1571–1607) indicating that the use of a sextant for nautical navigation predates Hadley's implementation. In 1922, it was modified for aeronautical navigation by Portuguese navigator and naval officer Gago Coutinho.

A multimeter or a multitester, also known as a VOM (volt-ohm-milliammeter), is an electronic measuring instrument that combines several measurement functions in one unit. A typical multimeter can measure voltage, current, and resistance. Analog multimeters uses a microammeter with a moving pointer to display readings. Digital multimeters have a numeric display, and may also show a graphical bar representing the measured value. Digital multimeters are now far more common due to their cost and precision, but analog multimeters are still preferable in some cases, for example when monitoring a rapidly varying value.
In measurement technology and metrology, calibration is the comparison of measurement values delivered by a device under test with those of a calibration standard of known accuracy. Such a standard could be another measurement device of known accuracy, a device generating the quantity to be measured such as a voltage, a sound tone, or a physical artefact, such as a metre ruler.

A cleanroom or clean room is a laboratory facility ordinarily utilized as a part of specialized industrial production or scientific research, including the manufacture of pharmaceutical items and microprocessors. Cleanrooms are designed to maintain extremely low levels of particulates, such as dust, airborne organisms, or vaporized particles. Cleanrooms typically have a cleanliness level quantified by the number of particles per cubic meter at a predetermined molecule measure. The ambient outdoor air in a typical urban area contains 35,000,000 particles for each cubic meter in the size range 0.5 μm and bigger in measurement, equivalent to an ISO 9 cleanroom, while by comparison an ISO 1 cleanroom permits no particles in that size range and just 12 particles for each cubic meter of 0.3 μm and smaller.

A nephelometer is an instrument for measuring the concentration of suspended particulates in a liquid or gas colloid. A nephelometer measures suspended particulates by employing a light beam and a light detector set to one side of the source beam. Particle density is then a function of the light reflected into the detector from the particles. To some extent, how much light reflects for a given density of particles is dependent upon properties of the particles such as their shape, color, and reflectivity. Nephelometers are calibrated to a known particulate, then use environmental factors (k-factors) to compensate lighter or darker colored dusts accordingly. K-factor is determined by the user by running the nephelometer next to an air sampling pump and comparing results. There are a wide variety of research-grade nephelometers on the market as well as open source varieties.

Geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GD&T) is a system for defining and communicating engineering tolerances. It uses a symbolic language on engineering drawings and computer-generated three-dimensional solid models that explicitly describe nominal geometry and its allowable variation. It tells the manufacturing staff and machines what degree of accuracy and precision is needed on each controlled feature of the part. GD&T is used to define the nominal geometry of parts and assemblies, to define the allowable variation in form and possible size of individual features, and to define the allowable variation between features.

A monochromator is an optical device that transmits a mechanically selectable narrow band of wavelengths of light or other radiation chosen from a wider range of wavelengths available at the input. The name is from the Greek roots mono-, "single", and chroma, "colour", and the Latin suffix -ator, denoting an agent.

In various contexts of science, technology, and manufacturing, an indicator is any of various instruments used to accurately measure small distances and angles, and amplify them to make them more obvious. The name comes from the concept of indicating to the user that which their naked eye cannot discern; such as the presence, or exact quantity, of some small distance.
Surface metrology is the measurement of small-scale features on surfaces, and is a branch of metrology. Surface primary form, surface fractality and surface roughness are the parameters most commonly associated with the field. It is important to many disciplines and is mostly known for the machining of precision parts and assemblies which contain mating surfaces or which must operate with high internal pressures.

A coordinate measuring machine (CMM) is a device that measures the geometry of physical objects by sensing discrete points on the surface of the object with a probe. Various types of probes are used in CMMs, including mechanical, optical, laser, and white light. Depending on the machine, the probe position may be manually controlled by an operator or it may be computer controlled. CMMs typically specify a probe's position in terms of its displacement from a reference position in a three-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system. In addition to moving the probe along the X, Y, and Z axes, many machines also allow the probe angle to be controlled to allow measurement of surfaces that would otherwise be unreachable.
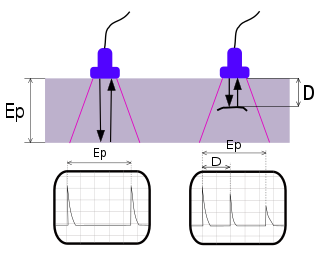
Ultrasonic testing (UT) is a family of non-destructive testing techniques based on the propagation of ultrasonic waves in the object or material tested. In most common UT applications, very short ultrasonic pulse-waves with center frequencies ranging from 0.1-15 MHz, and occasionally up to 50 MHz, are transmitted into materials to detect internal flaws or to characterize materials. A common example is ultrasonic thickness measurement, which tests the thickness of the test object, for example, to monitor pipework corrosion.
A refractometer is a laboratory or field device for the measurement of an index of refraction (refractometry). The index of refraction is calculated from Snell's law while for mixtures, the index of refraction can be calculated from the composition of the material using several mixing rules such as the Gladstone–Dale relation and Lorentz–Lorenz equation.
A test method is a method for a test in science or engineering, such as a physical test, chemical test, or statistical test. It is a definitive procedure that produces a test result. In order to ensure accurate and relevant test results, a test method should be "explicit, unambiguous, and experimentally feasible.", as well as effective and reproducible.
ISO 25178: Geometric Product Specifications (GPS) – Surface texture: areal is an International Organisation for Standardisation collection of international standards relating to the analysis of 3D areal surface texture.
Graduations are soul of a ruler A ' is a mark used to points on a visual scale.

A laser beam profiler captures, displays, and records the spatial intensity profile of a laser beam at a particular plane transverse to the beam propagation path. Since there are many types of lasers — ultraviolet, visible, infrared, continuous wave, pulsed, high-power, low-power — there is an assortment of instrumentation for measuring laser beam profiles. No single laser beam profiler can handle every power level, pulse duration, repetition rate, wavelength, and beam size.
Waviness is the measurement of the more widely spaced component of surface texture. It is a broader view of roughness because it is more strictly defined as "the irregularities whose spacing is greater than the roughness sampling length". It can occur from machine or work deflections, chatter, residual stress, vibrations, or heat treatment. Waviness should also be distinguished from flatness, both by its shorter spacing and its characteristic of being typically periodic in nature.

A baghouse,also known as a baghouse filter, bag filter, or fabric filter is an air pollution control device and dust collector that removes particulates or gas released from commercial processes out of the air. Power plants, steel mills, pharmaceutical producers, food manufacturers, chemical producers and other industrial companies often use baghouses to control emission of air pollutants. Baghouses came into widespread use in the late 1970s after the invention of high-temperature fabrics capable of withstanding temperatures over 350 °F (177 °C).

An Audio Analyzer is a test and measurement instrument used to objectively quantify the audio performance of electronic and electro-acoustical devices. Audio quality metrics cover a wide variety of parameters, including level, gain, noise, harmonic and intermodulation distortion, frequency response, relative phase of signals, interchannel crosstalk, and more. In addition, many manufacturers have requirements for behavior and connectivity of audio devices that require specific tests and confirmations.


















