
The Apple III is a business-oriented personal computer produced by Apple Computer and released in 1980. Running the Apple SOS operating system, it was intended as the successor to the Apple II series, but was largely considered a failure in the market. It was designed to provide key features business users wanted in a personal computer: a true typewriter-style upper/lowercase keyboard and an 80-column display.

A motherboard is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in general-purpose computers and other expandable systems. It holds and allows communication between many of the crucial electronic components of a system, such as the central processing unit (CPU) and memory, and provides connectors for other peripherals. Unlike a backplane, a motherboard usually contains significant sub-systems, such as the central processor, the chipset's input/output and memory controllers, interface connectors, and other components integrated for general use.

Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard that specifies the physical interfaces and protocols for connecting, data transferring and powering of hosts, such as personal computers, peripherals, e.g. keyboards and mobile devices, and intermediate hubs. USB was designed to standardize the connection of peripherals to computers, replacing various interfaces such as serial ports, parallel ports, game ports, and ADB ports. It has become commonplace on a wide range of devices, such as keyboards, mice, cameras, printers, scanners, flash drives, smartphones, game consoles, and power banks.

The Commodore 128, also known as the C128, C-128, C= 128, is the last 8-bit home computer that was commercially released by Commodore Business Machines (CBM). Introduced in January 1985 at the CES in Las Vegas, it appeared three years after its predecessor, the Commodore 64, the bestselling computer of the 1980s.

The Macintosh Plus computer is the third model in the Macintosh line, introduced on January 16, 1986, two years after the original Macintosh and a little more than a year after the Macintosh 512K, with a price tag of US$2,599. As an evolutionary improvement over the 512K, it shipped with 1 MB of RAM standard, expandable to 4 MB, and an external SCSI peripheral bus, among smaller improvements. Originally, the computer's case was the same beige color as the original Macintosh, Pantone 453; however, in 1987, the case color was changed to the long-lived, warm gray "Platinum" color. It is the earliest Macintosh model able to run System Software 5, System 6, and System 7, up to System 7.5.5, but not System 7.5.2.

A laptop computer or notebook computer, also known as a laptop or notebook for short, is a small, portable personal computer (PC). Laptops typically have a clamshell form factor with a flat panel screen on the inside of the upper lid and an alphanumeric keyboard and pointing device on the inside of the lower lid, although 2-in-1 PCs with a detachable keyboard are often marketed as laptops or as having a "laptop mode". Most of the computer's internal hardware is fitted inside the lower lid enclosure under the keyboard, although many laptops have a built-in webcam at the top of the screen and some modern ones even feature a touch-screen display. In most cases, unlike tablet computers which run on mobile operating systems, laptops tend to run on desktop operating systems which have been traditionally associated with desktop computers.

The Apple IIc, the fourth model in the Apple II series of personal computers, is Apple Computer's first endeavor to produce a portable computer. The result was a 7.5 lb (3.4 kg) notebook-sized version of the Apple II that could be transported from place to place — a portable alternative and complement to the Apple IIe. The c in the name stood for compact, referring to the fact it was essentially a complete Apple II computer setup squeezed into a small notebook-sized housing. While sporting a built-in floppy drive and new rear peripheral expansion ports integrated onto the main logic board, it lacks the internal expansion slots and direct motherboard access of earlier Apple II models, making it a closed system like the Macintosh. However, that was the intended direction for this model — a more appliance-like machine, ready to use out of the box, requiring no technical know-how or experience to hook up and therefore attractive to first-time users.
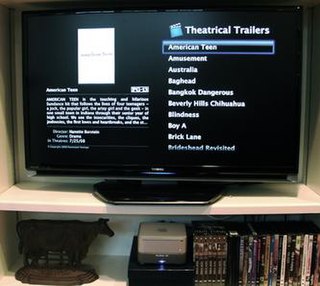
A home theater PC (HTPC) or media center computer is a convergent device that combines some or all the capabilities of a personal computer with a software application that focuses on video, photo, audio playback, and sometimes video recording functionality. Since the mid-2000s, other types of consumer electronics, including game consoles and dedicated media devices, have crossed over to manage video and music content. The term "media center" also refers to specialized application software designed to run on standard personal computers.

A computer case, also known as a computer chassis, is the enclosure that contains most of the hardware of a personal computer. The components housed inside the case are referred as the internal hardware, while hardware outside the case are known as peripherals.

An AC adapter or AC/DC adapter is a type of external power supply, often enclosed in a case similar to an AC plug. Other common names include wall wart, power brick, wall charger, and power adapter. Adapters for battery-powered equipment may be described as chargers or rechargers. AC adapters are used with electrical devices that require power but do not contain internal components to derive the required voltage and power from mains power. The internal circuitry of an external power supply is very similar to the design that would be used for a built-in or internal supply.

A home network or home area network (HAN) is a type of computer network that facilitates communication among devices within the close vicinity of a home. Devices capable of participating in this network, for example, smart devices such as network printers and handheld mobile computers, often gain enhanced emergent capabilities through their ability to interact. These additional capabilities can be used to increase the quality of life inside the home in a variety of ways, such as automation of repetitive tasks, increased personal productivity, enhanced home security, and easier access to entertainment.
The Apple Network Server (ANS) was a line of PowerPC-based server computers designed, manufactured and sold by Apple Computer, Inc. from February 1996 to April 1997. It was codenamed "Shiner" and originally consisted of two models, the Network Server 500/132 and the Network Server 700/150, which got a companion model, the Network Server 700/200 with a faster CPU in November 1996.

The Macintosh Quadra 605 is a personal computer designed, manufactured, and sold by Apple Computer from October 1993 to July 1996. The model names reflect a decision made at Apple in 1993 to follow an emerging industry trend of naming product families for their target customers – Quadra for business, LC for education, and Performa for home. Accordingly, the Performa 475 and 476 was sold in department stores and electronics stores such as Circuit City, whereas the Quadra was purchased through an authorized Apple reseller.

The PowerBook 5300 is the first generation of PowerBook laptops manufactured by Apple Computer to use the PowerPC processor. Released in August 1995, these PowerBooks were notable for being the first to feature hot-swappable expansion modules for a variety of different units such as Zip drives; PC card slots as standard; and an infrared communication port. In common with most preceding Macintosh portables, SCSI, Serial, and ADB ports were included as standard. An internal expansion slot was also available for installing a variety of modules including Ethernet and video cards to drive a second monitor in mirroring or dual-screen modes.
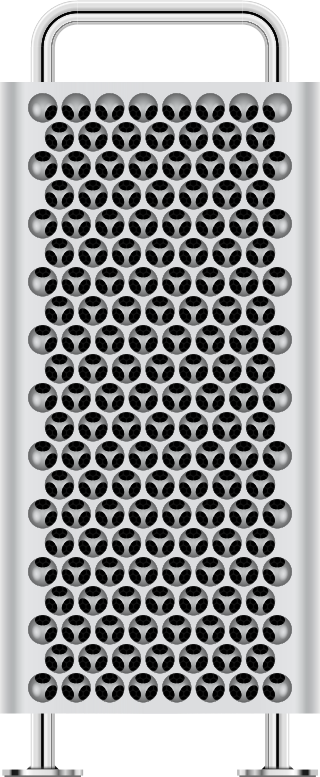
Mac Pro is a series of workstations and servers for professionals that have been designed, developed and marketed by Apple Inc. since 2006. The Mac Pro, by some performance benchmarks, is the most powerful computer that Apple offers. It is one of four desktop computers in the current Mac lineup, sitting above the Mac Mini, iMac and Mac Studio.

A power supply unit (PSU) converts mains AC to low-voltage regulated DC power for the internal components of a computer. Modern personal computers universally use switched-mode power supplies. Some power supplies have a manual switch for selecting input voltage, while others automatically adapt to the mains voltage.

A plug computer is an external device, often configured for use in the home or office as a compact computer. The name is derived from the small configuration of such devices; they are often enclosed in an AC power plug or AC adapter.

The SheevaPlug is a "plug computer" designed to allow standard computing features in as small a space as possible. It was a small embedded Linux ARM computer without a display which can be considered an early predecessor to the subsequent Raspberry Pi.

DreamPlug is a compact and low power plug computer running Debian Linux, based on Marvell's Kirkwood 88F6281 ARM9E SoC. It is intended to be a device that could act as a web server, a printing server or any other network service. It uses micro-SD internal storage and an external Secure Digital slot, but also offers USB ports and a Serial ATA port to connect external disks.
The initial versions of the USB standard specified connectors that were easy to use and that would have acceptable life spans; revisions of the standard added smaller connectors useful for compact portable devices. Higher-speed development of the USB standard gave rise to another family of connectors to permit additional data paths. All versions of USB specify cable properties; version 3.x cables include additional data paths. The USB standard included power supply to peripheral devices; modern versions of the standard extend the power delivery limits for battery charging and devices requiring up to 100 watts. USB has been selected as the standard charging format for many mobile phones, reducing the proliferation of proprietary chargers.



















