
Unified Extensible Firmware Interface is a specification that defines the architecture of the platform firmware used for booting the computer hardware and its interface for interaction with the operating system. Examples of firmware that implement the specification are AMI Aptio, Phoenix SecureCore, TianoCore EDK II, InsydeH2O. UEFI replaces the BIOS which was present in the boot ROM of all personal computers that are IBM PC compatible, although it can provide backwards compatibility with the BIOS using CSM booting. Intel developed the original Extensible Firmware Interface (EFI) specification. Some of the EFI's practices and data formats mirror those of Microsoft Windows. In 2005, UEFI deprecated EFI 1.10.
Alpine Linux is a Linux distribution designed to be small, simple, and secure. It uses musl, BusyBox, and OpenRC instead of the more commonly used glibc, GNU Core Utilities, and systemd. This makes Alpine one of few Linux distributions not to be based on the GNU Core Utilities.
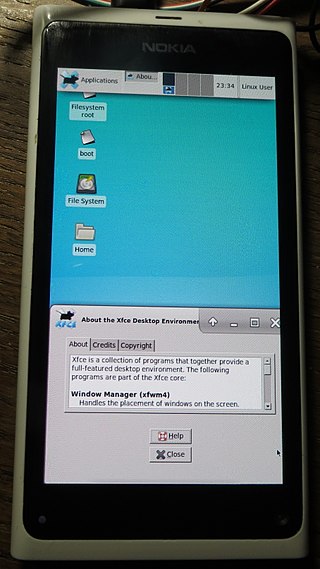
The hacking of consumer electronics is a common practice that users perform to customize and modify their devices beyond what is typically possible. This activity has a long history, dating from the days of early computer, programming, and electronics hobbyists.

Sailfish OS is a paid Linux-based operating system based on free software, and open source projects such as Mer as well as including a closed source UI. The project is being developed by the Finnish company Jolla.

Allwinner Technology Co., Ltd is a fabless semiconductor company, they design mixed-signal systems on a chip (SoC). The company is headquartered in Zhuhai, Guangdong, China. It has a sales and technical support office in Shenzhen, Guangdong, and logistics operations in Hong Kong.
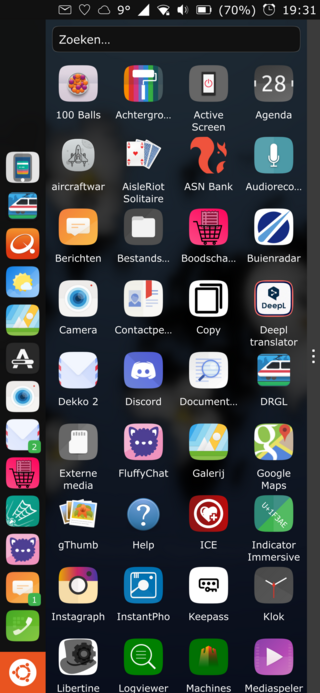
Ubuntu Touch is a mobile version of the Ubuntu operating system, being developed by the UBports community. Its user interface is written in Qt, and is designed primarily for touchscreen mobile devices such as smartphones and tablet computers, but the original goal of convergence was intended to bring Ubuntu Touch to laptops, desktops, IOT devices and TVs for a complete unified user experience.

Manjaro is a free and open-source Linux distribution based on the Arch Linux operating system that has a focus on user-friendliness and accessibility. It uses a rolling release update model and Pacman as its package manager. It is developed mainly in Austria, France and Germany.
Linux for mobile devices, sometimes referred to as mobile Linux, is the usage of Linux-based operating systems on portable devices, whose primary or only Human interface device (HID) is a touchscreen. It mainly comprises smartphones and tablet computers, but also some mobile phones, personal digital assistants (PDAs) portable media players that come with a touchscreen separately.

Librem is a line of computers manufactured by Purism, SPC featuring free (libre) software. The laptop line is designed to protect privacy and freedom by providing no non-free (proprietary) software in the operating system or kernel, avoiding the Intel Active Management Technology, and gradually freeing and securing firmware. Librem laptops feature hardware kill switches for the microphone, webcam, Bluetooth and Wi-Fi.
Pine Store Limited, known by its trade name Pine64, is a Hong Kong-based organization that designs, manufactures, and sells single-board computers, notebook computers, as well as smartwatch/smartphones. Its name was inspired by the mathematical constants pi and e with a reference to 64-bit computing power.

Purism, SPC is an American computer technology corporation based in San Francisco, California and registered in the state of Washington.

The Pinebook is a low-cost notebook developed by Hong Kong-based computer manufacturer Pine64. The Pinebook was announced in November 2016 and production started in April 2017. It is based on the platform of Pine64's existing Pine A64 single board computer, costing US$89 or US$99 for the 11.6" and 14" model respectively. Its appearance resembles the MacBook Air. The Pinebook is sold "at-cost" by Pine64 as a community service.

postmarketOS is an operating system primarily for smartphones, based on the Alpine Linux distribution.
Halium is a collaborative project to unify the Hardware Abstraction Layer for projects which run Linux on mobile devices with pre-installed Android. The project aims to standardize the middleware software used by various projects to talk with android daemons and make use of hardware on installed devices. It is distributed as free and open-source software under a mix of software licenses.

The PinePhone is a smartphone developed by Hong Kong-based computer manufacturer Pine64, intended to allow the user to have full control over the device. Measures to ensure this are: running mainline Linux-based mobile operating systems, assembling the phone with screws, and simplifying the disassembly for repairs and upgrades. LTE, GPS, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth and both cameras can be physically switched off. The PinePhone ships with the Manjaro Linux operating system using the Plasma Mobile graphic interface, although other distributions can be installed by users.

The PineTab is a low-cost tablet developed by Hong Kong-based computer manufacturer Pine64. The PineTab was announced in May 2020, with shipping beginning in September 2020. It is based on the platform of the existing Pine A64 single board computer, with the platform being used in related devices, such as the Pinebook and PinePhone.
The scope for this page is that used for list of open-source mobile phones.

Plasma Mobile is a Plasma variant for smartphones. It is currently available for the Pinephone, and supported devices for postmarketOS such as the OnePlus 6.
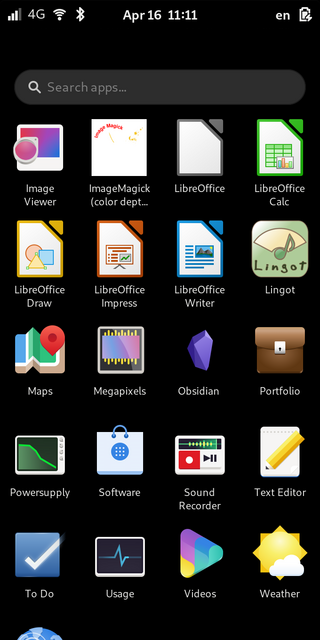
Mobian is a project to port the Debian GNU/Linux distribution running the mainline Linux kernel to smartphones and tablets. The project was announced in 2020. It is available for the PinePhone, PineTab, Librem 5, OnePlus 6/6T and Pocophone F1.














