
A personal digital assistant (PDA), also known as a handheld PC, is a variety mobile device which functions as a personal information manager. PDAs have been mostly displaced by the widespread adoption of highly capable smartphones, in particular those based on iOS and Android.
Java Platform, Micro Edition or Java ME is a computing platform for development and deployment of portable code for embedded and mobile devices. Java ME was formerly known as Java 2 Platform, Micro Edition or J2ME. As of December 22, 2006, the Java ME source code is licensed under the GNU General Public License, and is released under the project name phoneME.
Psion was a designer and manufacturer of mobile handheld computers for commercial and industrial uses. The company was headquartered in London, England with major operations in Mississauga, Ontario, Canada, and other company offices in Europe, the United States, Asia, Latin America, and the Middle East. It was a public company listed on the London Stock Exchange and was once a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index.
Symbian Ltd. was a software development and licensing consortium company, known for the Symbian operating system (OS), for smartphones and some related devices. Its headquarters were in Southwark, London, England, with other offices opened in Cambridge, Sweden, Silicon Valley, Japan, India, China, South Korea, and Australia.

Palm was a line of personal digital assistants (PDAs) and mobile phones developed by California-based Palm, Inc., originally called Palm Computing, Inc. Palm devices are often remembered as "the first wildly popular handheld computers," responsible for ushering in the smartphone era.

A smartphone is a portable computer device that combines mobile telephone and computing functions into one unit. They are distinguished from feature phones by their stronger hardware capabilities and extensive mobile operating systems, which facilitate wider software, internet, and multimedia functionality, alongside core phone functions such as voice calls and text messaging. Smartphones typically contain a number of metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) integrated circuit (IC) chips, include various sensors that can be leveraged by pre-included and third-party software, and support wireless communications protocols.

The Sharp Zaurus is the name of a series of personal digital assistants (PDAs) made by Sharp Corporation. The Zaurus was the most popular PDA during the 1990s in Japan and was based on a proprietary operating system. The first Sharp PDA to use the Linux operating system was the SL-5000D, running the Qtopia-based Embedix Plus. The Linux Documentation Project considers the Zaurus series to be "true Linux PDAs" because their manufacturers install Linux-based operating systems on them by default. The name derives from the common suffix applied to the names of dinosaurs.

UIQ was a software platform based upon Symbian OS, created by UIQ Technology AB. It is a graphical user interface layer that provides additional components to the core operating system, to enable the development of feature-rich mobile phones that are open to expanded capabilities through third-party applications.

The Sony Ericsson P900 is a Symbian OS v7.0 based smartphone from Sony Ericsson.
Qt Extended is an application platform for embedded Linux-based mobile computing devices such as personal digital assistants, video projectors and mobile phones. It was initially developed by Qt Software, a subsidiary of Nokia. When they cancelled the project the free software portion of it was forked by the community and given the name Qt Extended Improved. The QtMoko Debian-based distribution is the natural successor to these projects as continued by the efforts of the Openmoko community.

MontaVista Software is a company that develops embedded Linux system software, development tools, and related software. Its products are made for other corporations developing embedded systems such as automotive electronics, communications equipment, mobile phones, and other electronic devices and infrastructure.
OpenMAX, often shortened as "OMX", is a non-proprietary and royalty-free cross-platform set of C-language programming interfaces. It provides abstractions for routines that are especially useful for processing of audio, video, and still images. It is intended for low power and embedded system devices that need to efficiently process large amounts of multimedia data in predictable ways, such as video codecs, graphics libraries, and other functions for video, image, audio, voice and speech.
The Motorola ROKR, the first version of which was informally known as the iTunes phone, was a series of mobile phones from Motorola, part of a 4LTR line developed before the spin out of Motorola Mobility. ROKR models were released starting in September 2005 and ending in 2009. They were notable for incorporating support of media player features.

The Motorola A780 is the second cellular PDA running the Linux operating system.

The Open Handset Alliance (OHA) is a consortium of 84 firms to develop open standards for mobile devices. Member firms include HTC, Sony, Dell, Intel, Motorola, Qualcomm, Texas Instruments, Google, Samsung Electronics, LG Electronics, T-Mobile, Sprint Corporation, Nvidia, and Wind River Systems.
A mobile operating system is an operating system for mobile phones, tablets, smartwatches, 2-in-1 PCs, smart speakers, or other mobile devices. While computers such as typical laptops are 'mobile', the operating systems used on them are generally not considered mobile ones, as they were originally designed for desktop computers that historically did not have or need specific mobile features. This line distinguishing mobile and other forms has become blurred in recent years, this is due to the fact that newer devices have become smaller and more mobile unlike hardware of the past. Key notabilities blurring this line are the introduction of tablet computers and light-weight laptops.

A Personal Navigation Assistant (PNA) also known as Personal Navigation Device or Portable Navigation Device (PND) is a portable electronic product which combines a positioning capability and navigation functions.
Open Kernel Labs is a privately owned company that develops microkernel-based hypervisors and operating systems for embedded systems. The company was founded in 2006 by Steve Subar and Gernot Heiser as a spinout from NICTA. It was headquartered in Chicago, while research and development was located in Sydney, Australia. The company was acquired by General Dynamics in September 2012.

Symbian is a discontinued mobile operating system (OS) and computing platform designed for smartphones. Symbian was originally developed as a proprietary software OS for PDAs in 1998 by the Symbian Ltd. consortium. Symbian OS is a descendant of Psion's EPOC, and was released exclusively on ARM processors, although an unreleased x86 port existed. Symbian was used by many major mobile phone brands, like Samsung, Motorola, Sony Ericsson, and above all by Nokia. It was also prevalent in Japan by brands including Fujitsu, Sharp and Mitsubishi. As a pioneer that established the smartphone industry, it was the most popular smartphone OS on a worldwide average until the end of 2010, at a time when smartphones were in limited use, when it was overtaken by iOS and Android. It was notably less popular in North America.
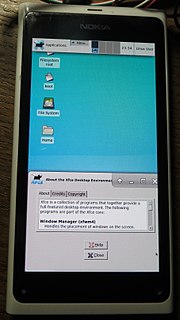
The hacking of consumer electronics is an increasingly common practice which users perform in order to customize and modify their devices beyond what is typically possible. This activity has a long history, dating from the days of early computer, programming, and electronics hobbyists.











