
Pocahontas is a town in Tazewell County, Virginia, United States. It was named for Chief Powhatan's daughter, Pocahontas, who lived in the 17th-century Jamestown Settlement. The town was founded as a company mining town by the Southwest Virginia Improvement Company in 1881. It was the first company mining town in Virginia. The post office opened on June 30, 1882.

Anthracite, also known as hard coal and black coal, is a hard, compact variety of coal that has a submetallic lustre. It has the highest carbon content, the fewest impurities, and the highest energy density of all types of coal and is the highest ranking of coals.

Coal mining is the process of extracting coal from the ground or from a mine. Coal is valued for its energy content and since the 1880s has been widely used to generate electricity. Steel and cement industries use coal as a fuel for extraction of iron from iron ore and for cement production. In the United Kingdom and South Africa, a coal mine and its structures are a colliery, a coal mine is called a "pit", and above-ground mining structures are referred to as a "pit head". In Australia, "colliery" generally refers to an underground coal mine.
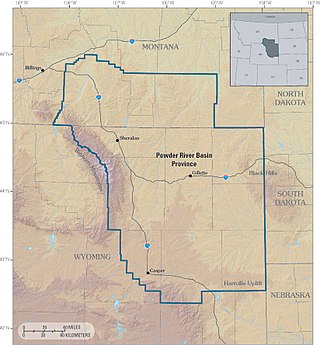
The Powder River Basin is a geologic structural basin in southeast Montana and northeast Wyoming, about 120 miles (190 km) east to west and 200 miles (320 km) north to south, known for its extensive coal reserves. The former hunting grounds of the Oglala Lakota, the area is very sparsely populated and is known for its rolling grasslands and semiarid climate.

Mountaintop removal mining (MTR), also known as mountaintop mining (MTM), is a form of surface mining at the summit or summit ridge of a mountain. Coal seams are extracted from a mountain by removing the land, or overburden, above the seams. This process is considered to be safer compared to underground mining because the coal seams are accessed from above instead of underground. In the United States, this method of coal mining is conducted in the Appalachian Mountains in the eastern United States. Explosives are used to remove up to 400 vertical feet of mountain to expose underlying coal seams. Excess rock and soil is dumped into nearby valleys, in what are called "holler fills" or "valley fills".

For most of the 20th century, the United States Bureau of Mines (USBM) was the primary United States government agency conducting scientific research and disseminating information on the extraction, processing, use, and conservation of mineral resources. The Bureau was abolished in 1996.

The U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System responsible for collecting, analyzing, and disseminating energy information to promote sound policymaking, efficient markets, and public understanding of energy and its interaction with the economy and the environment. EIA programs cover data on coal, petroleum, natural gas, electric, renewable and nuclear energy. EIA is part of the U.S. Department of Energy.

Massey Energy Company was a coal extractor in the United States with substantial operations in West Virginia, Kentucky and Virginia. By revenue, it was the fourth largest producer of coal in the United States and the largest coal producer in Central Appalachia. By coal production weight, it was the sixth largest producer of coal in the United States.

The Capitol Power Plant is a fossil-fuel burning power plant which provides steam and chilled water for the United States Capitol, the Supreme Court, the Library of Congress and 19 other buildings in the Capitol Complex. Located at 25 E St SE in southeast Washington, D.C., the CPP was the only coal-burning power plant in the District of Columbia, and it now mostly uses natural gas. The plant has been serving the Capitol since 1910, and is under the administration of the Architect of the Capitol.
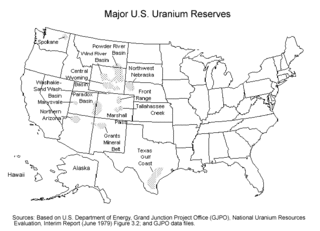
Uranium mining in the United States produced 224,331 pounds (101.8 tonnes) of U3O8 in 2023, 15% of the 2018 production of 1,447,945 pounds (656.8 tonnes) of U3O8. The 2023 production represents 0.4% of the uranium fuel requirements of the US's nuclear power reactors for the year. Production came from five in-situ leaching plants, four in Wyoming (Nichols Ranch ISR Project, Lance Project, Lost Creek Project, and Smith Ranch-Highland Operation) and one in Nebraska (Crowe Butte Operation); and from the White Mesa conventional mill in Utah.
Coal mining regions are significant resource extraction industries in many parts of the world. They provide a large amount of the fossil fuel energy in the world economy.

Coal generated about 19.5% of the electricity at utility-scale facilities in the United States in 2022, down from 38.6% in 2014 and 51% in 2001. In 2021, coal supplied 9.5 quadrillion British thermal units (2,800 TWh) of primary energy to electric power plants, which made up 90% of coal's contribution to U.S. energy supply. Utilities buy more than 90% of the coal consumed in the United States. There were over 200 coal powered units across the United States in 2024. Coal plants have been closing since the 2010s due to cheaper and cleaner natural gas and renewables. Due to measures such as scrubbers air pollution from the plants kills far fewer people nowadays, but deaths in 2020 from PM25 have been estimated at 1600. Environmentalists say that political action is needed to close them faster, to also reduce greenhouse gas emissions by the United States and better limit climate change.
Arch Resources, previously known as Arch Coal, is an American coal mining and processing company. The company mines, processes, and markets bituminous and sub-bituminous coal with low sulfur content in the United States. Arch Resources is the second-largest supplier of coal in the United States, behind Peabody Energy. As of 2011 the company supplied 15% of the domestic market. Demand comes mainly from generators of electricity.
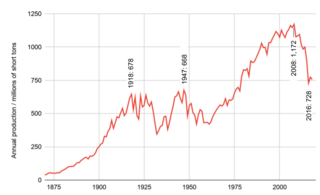
Coal mining is an industry in transition in the United States. Production in 2019 was down 40% from the peak production of 1,171.8 million short tons in 2008. Employment of 43,000 coal miners is down from a peak of 883,000 in 1923. Generation of electricity is the largest user of coal, being used to produce 50% of electric power in 2005 and 27% in 2018. The U.S. is a net exporter of coal. U.S. coal exports, for which Europe is the largest customer, peaked in 2012. In 2015, the U.S. exported 7.0 percent of mined coal.

The history of coal mining in the United States starts with the first commercial use in 1701, within the Manakin-Sabot area of Richmond, Virginia. Coal was the dominant power source in the late 1800s and early 1900s, and although in rapid decline it remains a significant source of energy in 2024.
The Cordero Rojo Mine is a coal mining complex located in the state of Wyoming in the United States, in the coal-rich Powder River Basin. The mine is of open pit construction and employs several dragline excavators. Two coal-processing facilities are located on-site, and crushed coal is shipped by rail to electric utility customers in the south and west of the United States. The mine employs between 430 and 540 people.
Foundation Coal Holdings, Inc. was a large American coal mining company. Until its July 31, 2009 merger with Alpha Natural Resources to form the third largest American coal company, the company was publicly traded on the New York Stock Exchange under the symbol FCL. With corporate offices in Linthicum Heights, Maryland, the former Foundation Coal operates coal mines in Pennsylvania, West Virginia and Wyoming, and was, prior to its merger with Alpha Natural Resources, the fourth-largest American coal producer by tonnage.
The United States has the second largest electricity sector in the world, with 4,178 Terawatt-hours of generation in 2023. In 2023 the industry earned $491b in revenue at an average price of $0.127/kWh.

Coal mining in Wyoming has long been a significant part of the state's economy. Wyoming has been the largest producer of coal in the United States since 1986, and in 2018, coal mines employed approximately 1% of the state's population. In 2013, there were 17 active coal mines in Wyoming, which produced 388 million short tons, 39 percent of all the coal mined in the US, and more than three times the production of second-place West Virginia. Market forces, including the low price of natural gas from the fracking boom—coal's main competition—contributed to the steep drop in coal production in the 2000s as electricity generation switched from coal to gas.













