
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range greater than 5,500 kilometres (3,400 mi), primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery. Conventional, chemical, and biological weapons can also be delivered with varying effectiveness, but have never been deployed on ICBMs. Most modern designs support multiple independently targetable reentry vehicle (MIRVs), allowing a single missile to carry several warheads, each of which can strike a different target. The United States, Russia, China, France, India, the United Kingdom, Israel, and North Korea are the only countries known to have operational ICBMs. Pakistan is the only nuclear-armed state that does not possess ICBMs.

National missile defense (NMD) refers to the nationwide antimissile program the United States has had under development since the 1990s. After the renaming in 2002, the term now refers to the entire program, not just the ground-based interceptors and associated facilities.
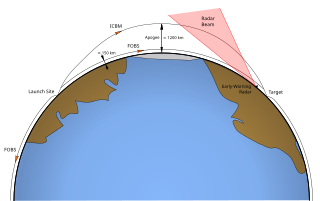
A Fractional Orbital Bombardment System (FOBS) is a warhead delivery system that uses a low Earth orbit towards its target destination. Just before reaching the target, it deorbits through a retrograde engine burn.

The maneuverable reentry vehicle is a type of warhead for ballistic missiles that is capable of maneuvering and changing its trajectory.
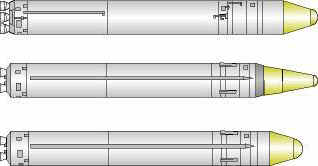
The UR-100N, also known as RS-18A, is an intercontinental ballistic missile in service with Soviet and Russian Strategic Missile Troops. The missile was given the NATO reporting name SS-19 Stiletto and carries the industry designation 15A30.

Hypersonic flight is flight through the atmosphere below altitudes of about 90 km (56 mi) at speeds greater than Mach 5, a speed where dissociation of air begins to become significant and high heat loads exist. Speeds over Mach 25 have been achieved below the thermosphere as of 2020.
The Surya missile is a speculated intercontinental ballistic missile being developed by Defence research and development organization of India. Its operational range is beyond 16,000 Km, covering the entire earth.
Conventional Prompt Strike (CPS), formerly called Prompt Global Strike (PGS), is a United States military effort to develop a system that can deliver a precision-guided conventional weapon strike anywhere in the world within one hour, in a similar manner to a nuclear ICBM. Such a weapon would allow the United States to respond far more swiftly to rapidly emerging threats than is possible with conventional forces. A CPS system could also be useful during a nuclear conflict, potentially replacing the use of nuclear weapons against up to 30% of targets. The CPS program encompasses numerous established and emerging technologies, including conventional surface-launched missiles and air- and submarine-launched hypersonic missiles.

An anti-ship ballistic missile (ASBM) is a military ballistic missile system designed to hit a warship at sea.

The HSTDV is an unmanned scramjet demonstration aircraft for hypersonic flight. It is being developed as a carrier vehicle for hypersonic and long-range cruise missiles, and will have multiple civilian applications including the launching of small satellites at low cost. The HSTDV program is being run by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).

The Alpha Draco missile, also known as Weapons System 199D (WS-199D), was an experimental ballistic missile developed by McDonnell Aircraft in the late 1950s to investigate the aerodynamic physics of the boost-glide reentry trajectory. Three test flights were conducted in 1959, of which two were successful.
India has studied, produced and used various strategic and tactical missile systems since its independence. Decades long projects have realised development of all types of missile systems including ballistic, cruise, anti-ship, air-defence, air-to-air and anti-missile systems. India is one of seven countries in the world with intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) and one of four countries with anti-ballistic missile systems. Since 2016, India has been a member of Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR).
The DF-ZF is a hypersonic glide vehicle (HGV) developed by the People's Republic of China. It is launched by the DF-17 medium-range ballistic missile. The combined weapon system was likely operational by October 2019.
A hypersonic glide vehicle (HGV) is a type of warhead for ballistic missiles that can maneuver and glide at hypersonic speed. It is used in conjunction with ballistic missiles to significantly change their trajectories after launch. Conventional ballistic missiles follow a predictable ballistic trajectory and are vulnerable to interception by the latest anti-ballistic missile (ABM) systems. The in-flight maneuverability of HGVs makes them unpredictable, allowing them to effectively evade air defenses. As of 2022, hypersonic glide vehicles are the subject of an arms race.

Non-ballistic atmospheric entry is a class of atmospheric entry trajectories that follow a non-ballistic trajectory by employing aerodynamic lift in the high upper atmosphere. It includes trajectories such as skip and glide.

The Avangard is a Russian hypersonic glide vehicle (HGV). It can be carried as a multiple independently targetable reentry vehicle (MIRV) payload of heavy intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs), such as the UR-100UTTKh, R-36M2 and RS-28 Sarmat. It can deliver both nuclear and conventional payloads. The Avangard is reportedly capable of travelling at re-entry speeds.

The Dongfeng-17, is a Chinese solid-fuelled road-mobile medium-range ballistic missile designed to carry the DF-ZF hypersonic glide vehicle.

A hypersonic weapon is a weapon capable of travelling at hypersonic speed, defined as above Mach 5, or above 5 times the speed of sound.
The Hypersonic Ballistic Tracking Space Sensor (HBTSS) is a satellite-based sensor system being developed by the Missile Defense Agency (MDA) along with the Glide Phase Interceptor (GPI) to address hypersonic threats. The product of the 2019 Missile Defense Review's (MDR) for further enhancement of the US national missile defense system, the HBTSS will provide quality intercept data to the GPI. Equipped with "Birth-to-death" capability, the HBTSS can track potential threats from their launch until interception. The HBTSS will ultimately be integrated into the broader set of satellite constellations being developed by the Space Development Agency (SDA).

The Long Range – Anti Ship Missile (LRAShM) is a member of the family of hypersonic missiles being developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) for the Indian Armed Forces.














